5 Other Functions
5-22
NJ/NX-series Database Connection CPU Units User’s Manual (W527)
5-5 Timeout Monitoring Functions
This section describes timeout monitoring for the DB Connection Service.
5-5-1 Timeout Monitoring Functions
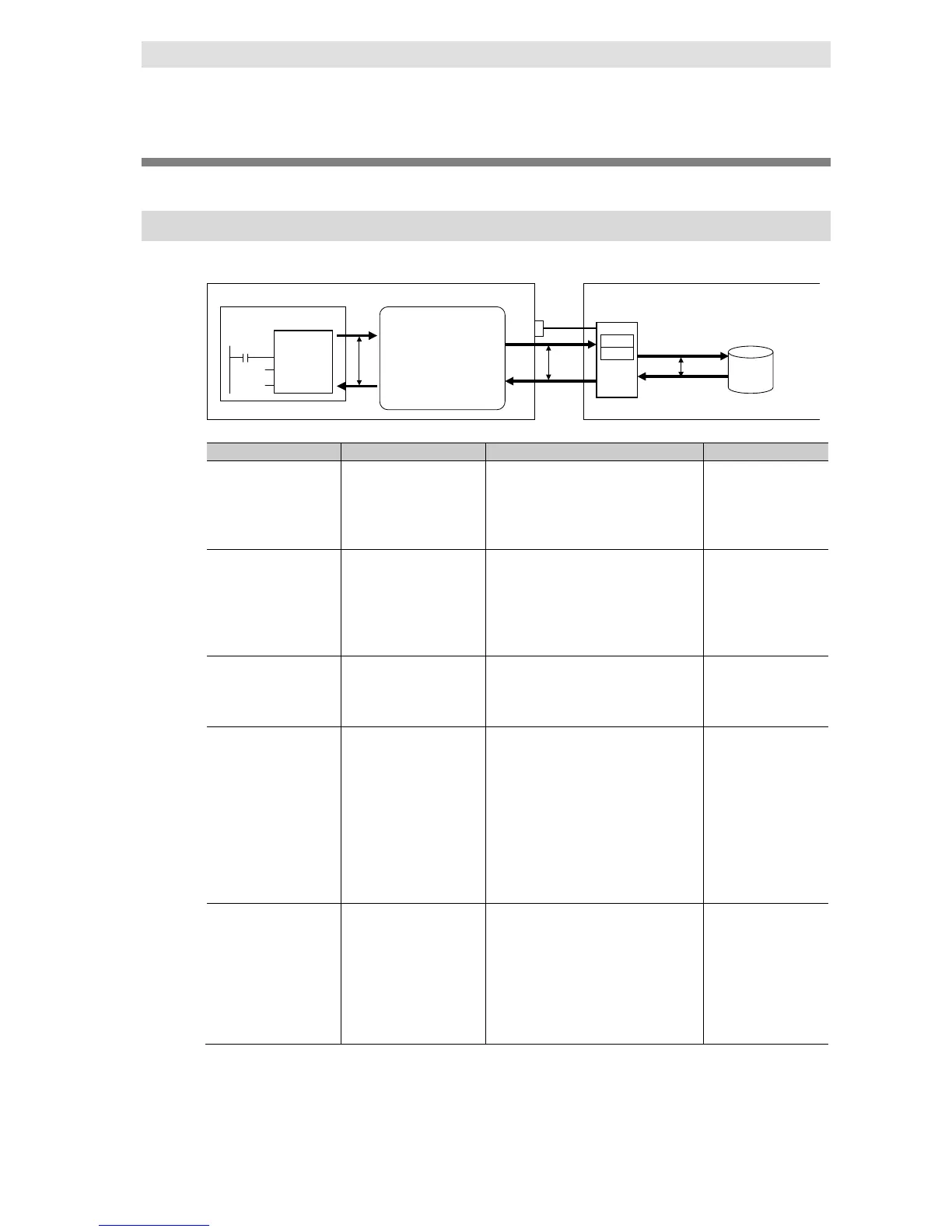
The following figure shows the types of timeouts that can be monitored.
DB Connection
Instruction
Login timeout 1 to 60 seconds
Default: 10 seconds
Time until the DB Connection Service
detects a login failure due to a
communications failure between DB
Connection Service and DB or server’s
Refer to 2-2-2 DB
Connection Settings.
Query execution
timeout ((a) in the
above figure)
1 to 600 seconds
Default: 30 seconds
Time until the DB Connection Service
detects an error when the DB takes
time for query execution.
You can cancel the SQL operation
when the DB takes longer than
expected for query execution.
Refer to 2-2-2 DB
Connection Settings.
Communications
timeout ((b) in the
above figure)
Time specified for Query
execution timeout plus
10 seconds*
Time until the DB Connection Service
detects an error due to a
communications failure between DB
Connection Service and DB
---
Instruction execution
timeout ((c) in the
above figure)
Not monitored, or
0.05 to180 seconds
Default: Not monitored
Time until the DB Connection Service
detects an error when a DB_Insert,
DB_Update, DB_Select or DB_Delete
instruction takes time due to a
communications failure between DB
Connection Service and DB or server’s
problem or heavy load.
You can use this when you do not want
to extend the takt time (i.e., lower the
Refer to Appendix
DB Connection
Instructions.
Keep Alive monitoring
time
1 to 65535 seconds
Default: 300 seconds
This function is used to check whether
the server is normally connected.
When you set this Keep Alive
monitoring time, a communications
failure can be detected even while the
DB Connection Service is waiting for a
response from the server because the
Refer to the
NJ/NX-series CPU
Unit Built-in
EtherNet/IP Port
User’s Manual (Cat.
No. W506).
* The time to detect a communications timeout differs by the DB type and DB status.

 Loading...
Loading...