Operator’s Manual – OPTI CCA-TS2 Na-1
ANALYTES SODIUM
Sodium (Na
+
)
Clinical Signicance
1
Sodium is the major cation of extracellular uid. Its primary functions in the body are to chemically
maintain osmotic pressure and acid-base balance and to transmit nerve impulses. Sodium functions at
the cell membrane level by creating an electrical potential between different cell membranes causing the
transmission of nerve impulses and neuromuscular excitability to be maintained. Sodium is involved in
some enzyme catalyzed reactions as a cofactor. The body has a strong tendency to maintain a total base
content, and only slight changes are found even under pathologic conditions.
Low sodium values, hyponatremia, usually reect a relative excess of body water rather than a low total
body sodium. Reduced sodium levels may be associated with: low sodium intake; sodium losses due
to vomiting or diarrhea with adequate water and inadequate salt replacement, diuretics abuse, or salt-
losing nephropathy; osmotic diuresis, metabolic acidosis; adrenocortical insufciency; congenital adrenal
hyperplasia; dilution type due to edema, cardiac failure, hepatic failure; and hypothyroidism.
Elevated sodium values, hypernatremia, are associated with conditions with water loss in excess of salt
loss through profuse sweating, prolonged hyperpnea, severe vomiting or diarrhea, diabetes insipidus
or diabetic acidosis; increased renal sodium conservation in hyperaldosteronism, Cushing’s syndrome;
inadequate water intake because of coma or hypothalamic diseases; dehydration; or excessive saline
therapy.
The sodium value obtained may be used in the diagnosis or monitoring of all disturbances of the water
balance, infusion therapies, vomiting, diarrhea, burns, heart and kidney insufciencies, central or renal
diabetes insipidus, endocrine disturbances and primary or secondary cortex insufciency of the adrenal
gland or other diseases involving electrolyte imbalance.
Measurement Principle
The Na
+
ion optodes are closely related to the more familiar Ion Selective Electrodes (ISEs).
The optodes use ion selective recognition elements (ionophores) similar to those used in ISEs, however
the ionophores are linked to uorescent dyes instead of electrodes. These types of dyes have been
used since the 1970’s to visualize and quantify cellular ion levels in uorescence microscopy and cell
counters
2
. As the ion concentration increases, these ionophores bind larger amounts of ions and cause the
uorescence intensity to increase or decrease, depending on the particular ion. Like the pH optode, the
ion optodes do not need a reference electrode, however, several of them do exhibit a small pH sensitivity
which is automatically compensated in the OPTI CCA-TS2 using the measured pH.
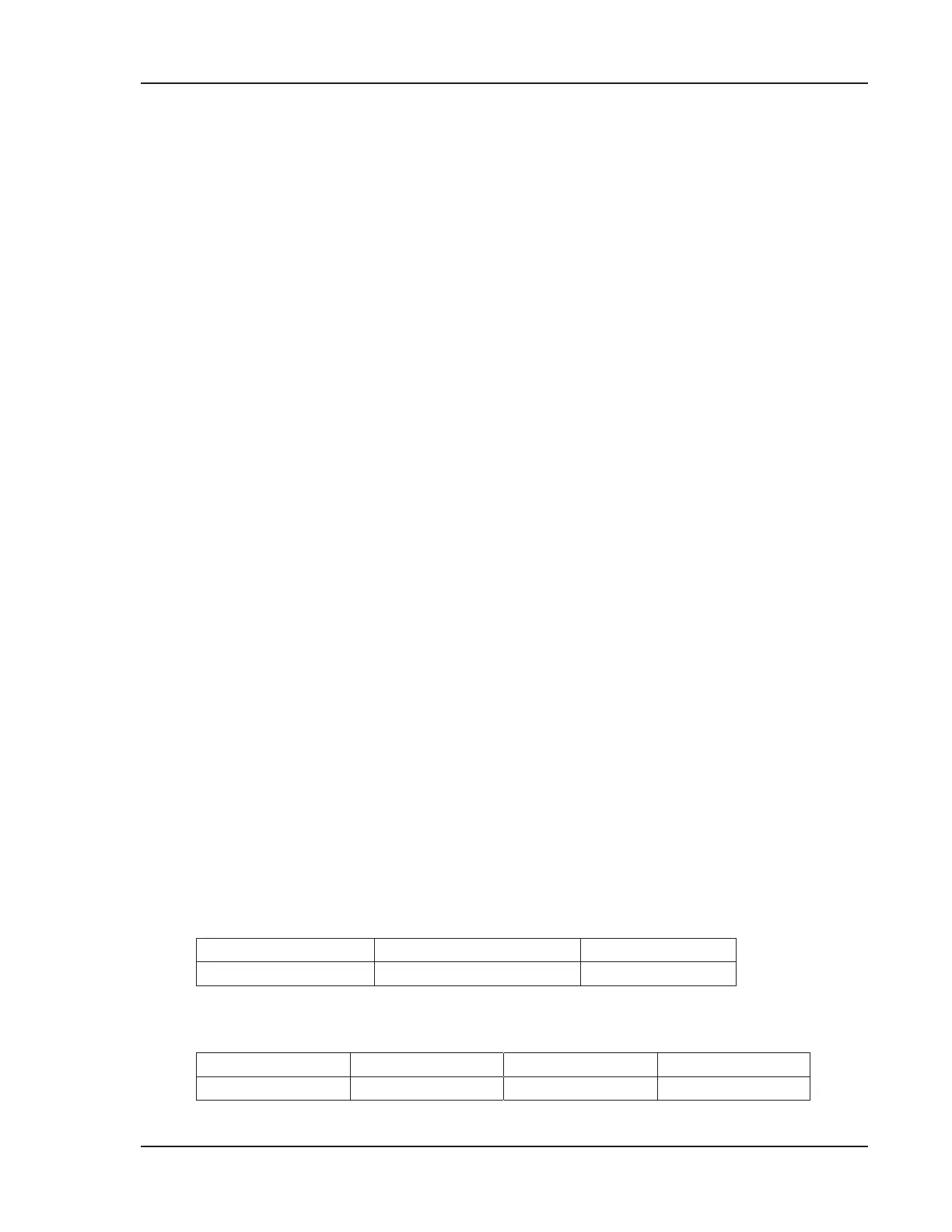
Measurement Range
Range Resolution (Low/High) Units
10 to 180 1/0.1 mmol/L
Standard Reference Cassette (SRC) Limit Values
LOW NORMAL HIGH Units
125.0 ± 2.0 145.0 ± 2.0 165.0 ± 2.0 mmol/L

 Loading...
Loading...