OSPF Routing Components
Before implementing OSPF, you must know what the routing components are and what purpose they serve.
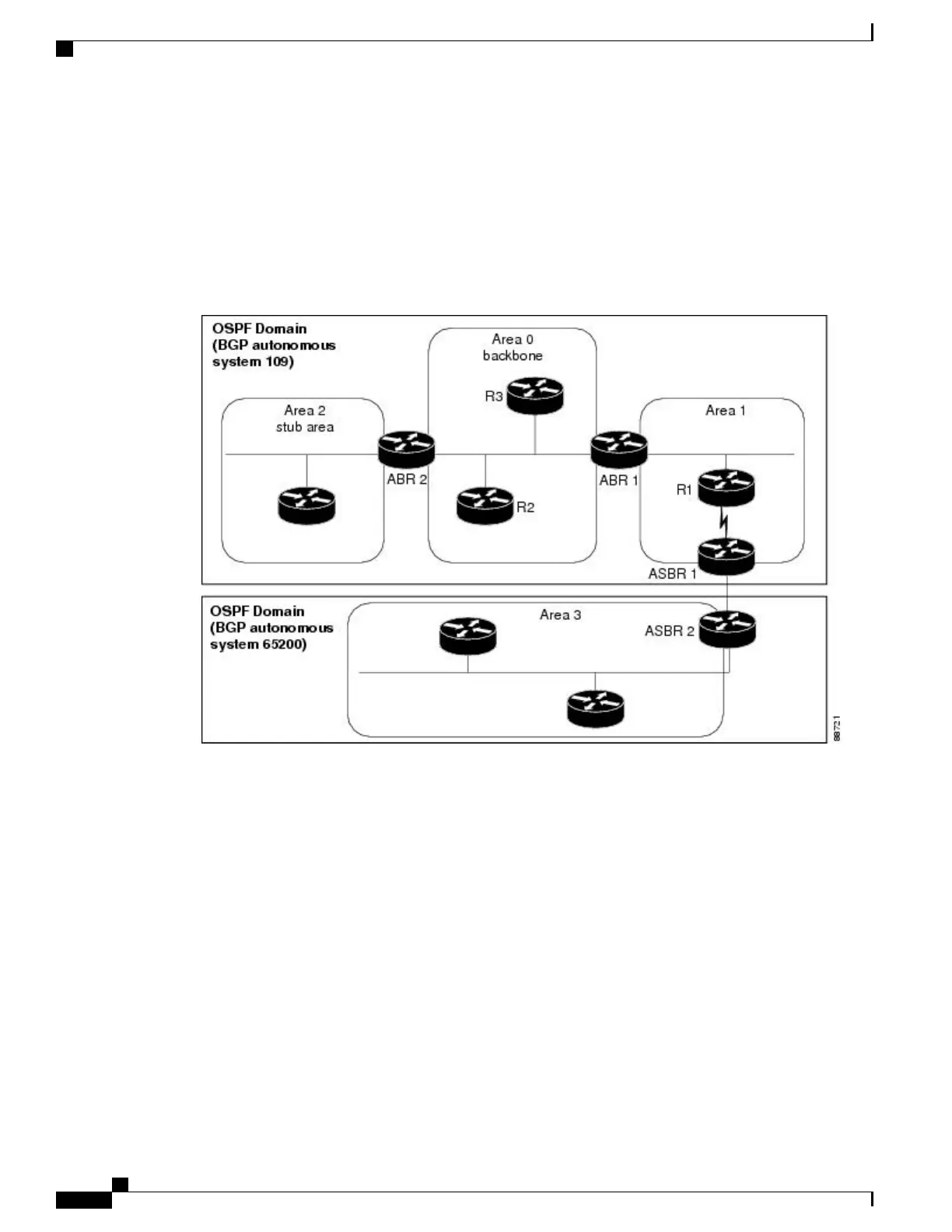
They consist of the autonomous system, area types, interior routers, ABRs, and ASBRs.
This figure illustrates the routing components in an OSPF network topology.
Figure 16: OSPF Routing Components
Autonomous Systems
The autonomous system is a collection of networks, under the same administrative control, that share routing
information with each other. An autonomous system is also referred to as a routing domain. Figure 16: OSPF
Routing Components, on page 336 shows two autonomous systems: 109 and 65200. An autonomous system
can consist of one or more OSPF areas.
Areas
Areas allow the subdivision of an autonomous system into smaller, more manageable networks or sets of
adjacent networks. As shown in Figure 16: OSPF Routing Components, on page 336, autonomous system
109 consists of three areas: Area 0, Area 1, and Area 2.
OSPF hides the topology of an area from the rest of the autonomous system. The network topology for an
area is visible only to routers inside that area. When OSPF routing is within an area, it is called intra-area
routing. This routing limits the amount of link-state information flood into the network, reducing routing
Cisco ASR 9000 Series Aggregation Services Router Routing Configuration Guide, Release 5.1.x
336 OL-30423-03
Implementing OSPF
OSPF Routing Components

 Loading...
Loading...











