xStack
®
DGS-3426G Layer 2 Gigabit Ethernet Managed Switch
152
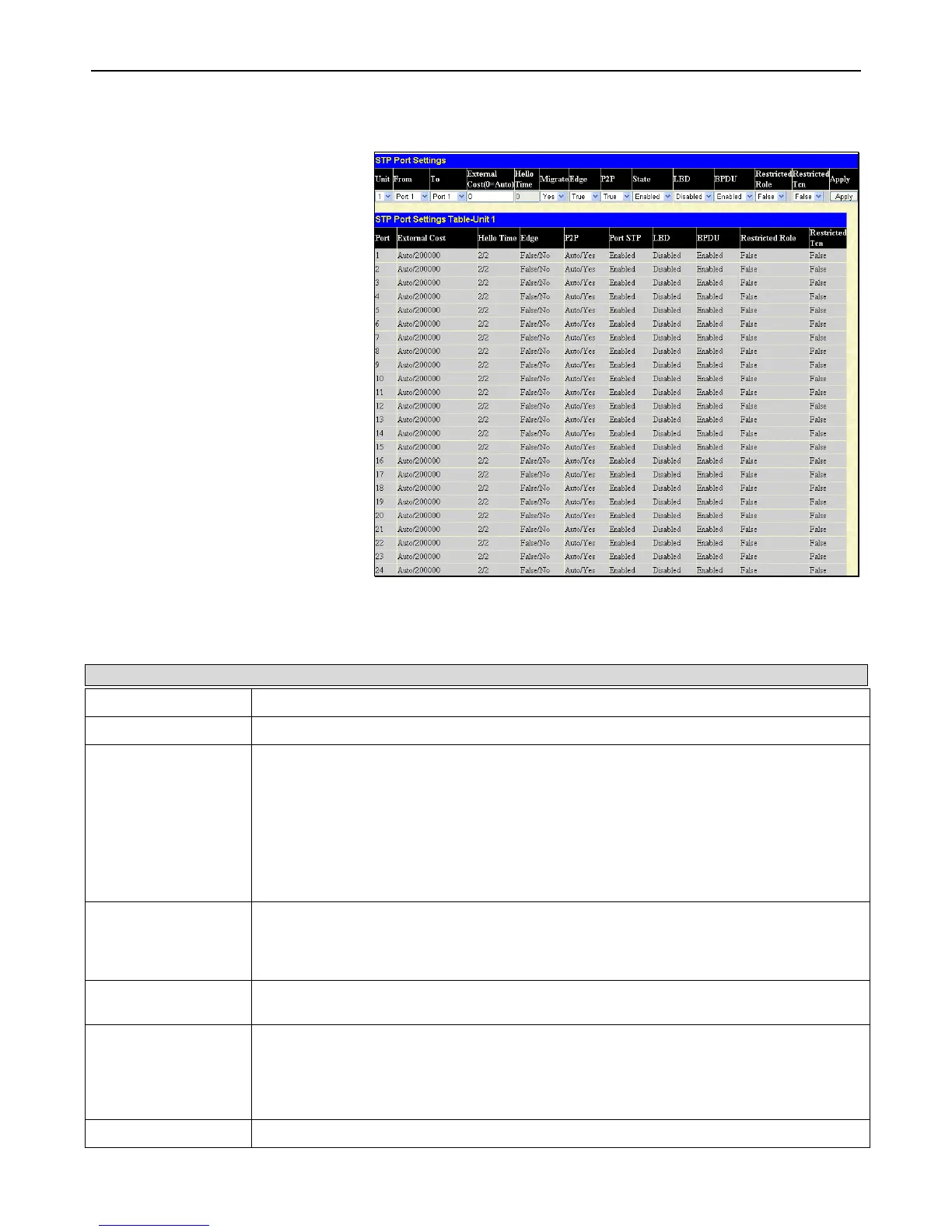
STP Port Settings
STP can be set up on a port per port basis. In
addition to setting Spanning Tree parameters
for use on the switch level, the Switch allows
for the configuration of groups of ports, each
port-group of which will have its own
spanning tree, and will require some of its
own configuration settings. An STP Group
will use the switch-level parameters entered
above, with the addition of Port Priority and
Port Cost. An STP Group spanning tree
works in the same way as the switch-level
spanning tree, but the root bridge concept is
replaced with a root port concept. A root port
is a port of the group that is elected based on
port priority and port cost, to be the
connection to the network for the group.
Redundant links will be blocked, just as
redundant links are blocked on the switch
level. The STP on the switch level blocks
redundant links between switches (and
similar network devices). The port level STP
will block redundant links within an STP
Group.
To view this window, click L2 Features >
Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings as
shown on the right:
Figure 3 - 53 STP Port Settings window
It is advisable to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports.
The following STP Port Settings fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Unit
Select the switch in the switch stack to be modified.
From/To
A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
External Cost
This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified
port list. Port cost can be set automatically or as a metric value. The default value is 0 (auto).
0 (auto) – Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding
packets to the specified port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency. Default port cost: 100Mbps
port = 200000. Gigabit port = 20000.
value 1-200000000 – Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine the external
cost. The lower the number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward
packets.
Hello Time
The time interval between transmissions of configuration messages by the designated port,
to other devices on the bridged LAN. The user may choose a time between 1 and 10
seconds. The default is 2 seconds. If the inputted Hello Time is greater than 2, the Hello
Time is 2. This field is only operable when the Switch is enabled for MSTP.
Migration
When operating in RSTP mode, selecting yes forces the port that has been selected to
transmit RSTP BPDUs.
Edge
Choosing the True parameter designates the port as an edge port. Edge ports cannot create
loops, however an edge port can lose edge port status if a topology change creates a
potential for a loop. An edge port normally should not receive BPDU packets. If a BPDU
packet is received, it automatically loses edge port status. Choosing the False parameter
indicates that the port does not have edge port status.
P2P
Choosing the True parameter indicates a point-to-point (P2P) shared link. P2P ports are
 Loading...
Loading...











