ASDA Series Application Note Introduction of PR Operation
March, 2015 1-35
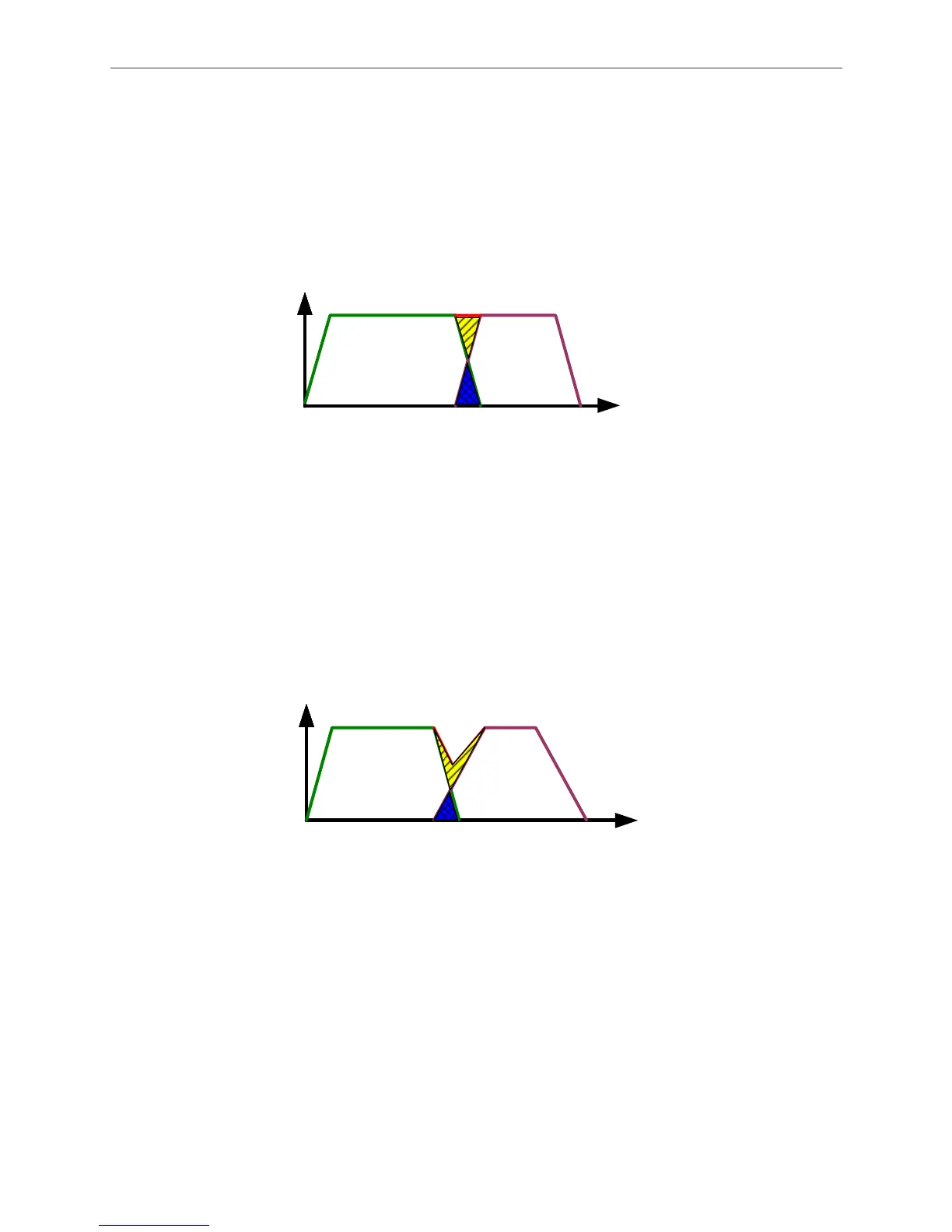
See Figure 1.46 for example, the meshed part is the overlapped area. When speed of the two
position commands is identical and the absolute value of deceleration curve slope of previous
command equals acceleration curve slope of the next command, the measure of meshed area
can compensate the area with slanting lines, allowing motor to keep the same speed when
switching from the first command to the second one and keep the total operation procedure the
same.
Time
Position Command 1
(Type 3) (Type 2)(Type 3)
Position Command 2
(Type 2)
Speed
(Type 3) (Type 2)
Figure 1.46 Overlap Command with Consistent Slopes
In Figure 1.47, the absolute value of deceleration curve slope does not equal to that of the
acceleration curve slope. Since the overall procedure cannot be changed, which means the sum
of two position command’s measurement of the speed curve should be identical. When the
meshed area can only compensate part of the area with slanting lines, it will cause speed
changing when connecting to position commands and the two commands cannot connect
smoothly during the process.
(Type 3)
Position Command 2
(Type 2)
Speed
(Type 3)
(Type 2)
Time
(Type 3)
(Type 2)
Position Command 1
Figure 1.47 Overlap Command with Inconsistent Slope
1.3.4 Interrupt of Command
Interrupt command, a command that is being executed and being replaced or combined with the
other command before it is completed. The final result of command varies with the command
types. The function of interrupt is to replace the previous command with the latter command.
Interrupting method can be categorized into two types: internal and external. Description is as
follows.

 Loading...
Loading...











