Networking Peer-to-peer networks
Digi XBee3® 802.15.4 RF Module User Guide
62
Peer-to-peer networks
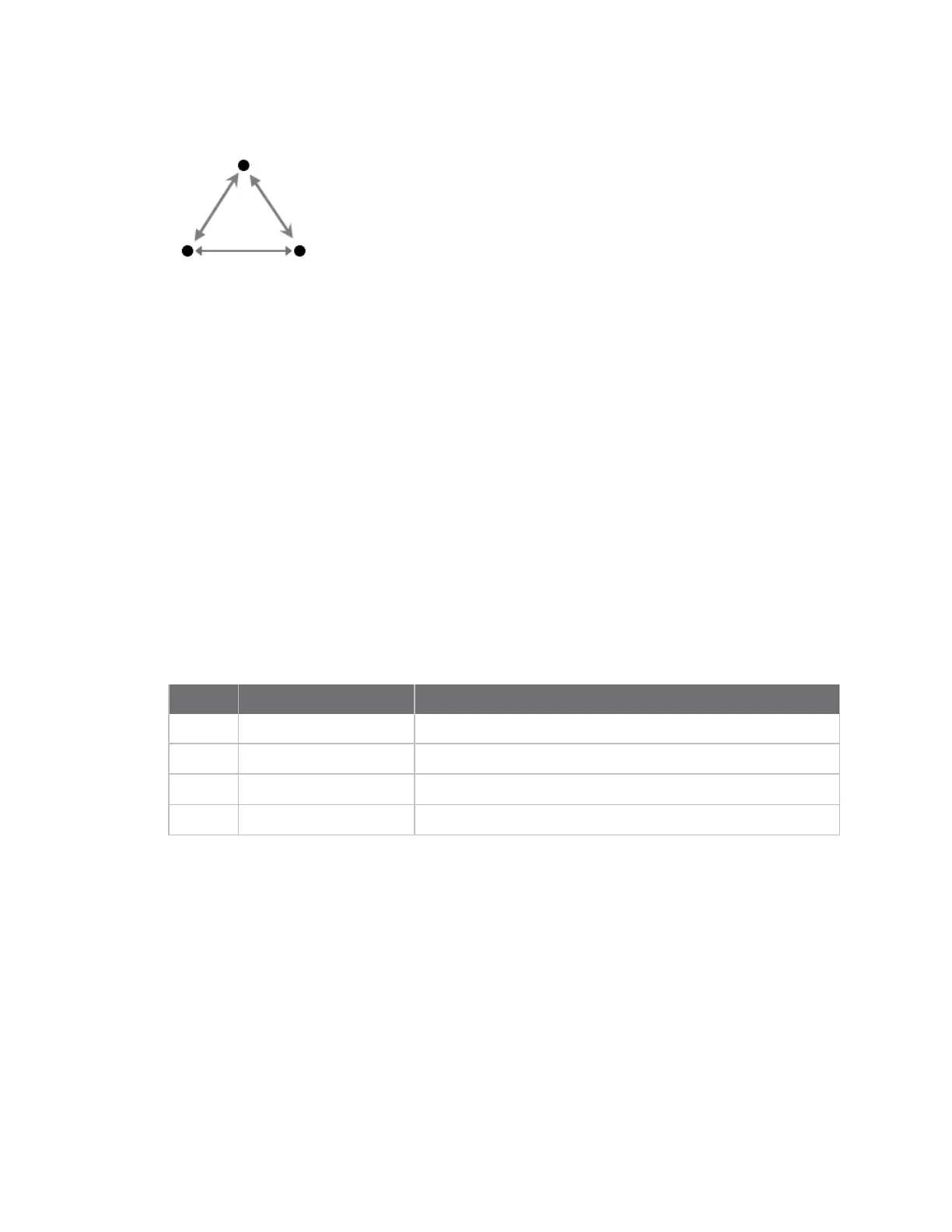
By default, XBee3 802.15.4 RF Modules are configured to operate within a peer-to-peer network
topology and therefore are not dependent upon master/slave relationships. Our peer-to-peer
architecture features fast synchronization times and fast cold start times. This default configuration
accommodates a wide range of RF data applications.
To form a peer-to-peer network, set each device to the same channel and PAN ID and configure either
a unique short address (MY) for each device or set MY to 0xFFFF to use the unique long addresses.
Master/slave networks
In a Master Slave network, there is a coordinator and one or more end devices. When end devices
associate to the coordinator, they become members of that Personal Area Network (PAN). As such,
they share the same channel and PAN ID. PAN IDs must be unique to prevent miscommunication
between PANs. Depending on the A1 and A2 parameters, association may assist in automatically
assigning the PAN ID and the channel. These parameters are specified below based on the network
role (end device or coordinator).
End device association
End device association occurs if CE is 0 and A1 has bit 2 set. See the following table and A1 (End Device
Association).
Bit Hex value Meaning
0 0x01 Allow PAN ID reassignment
1 0x02 Allow channel reassignment
2 0x04 Auto association
3 0x08 Poll coordinator on pin wake
By default, A1 is 0, which disables association and causes a device to operate in peer-to-peer mode.
When bit 2 is set, the module becomes an end device and associates to a coordinator. This is done by
sending out an active scan to detect beacons from nearby networks. The active scan iterates through
each channel defined by SCand transmits a Beacon Request command to the broadcast address and
the broadcast PAN ID. It then listens on that channel for beacons from any coordinator operating on
that channel. Once that time expires, the active scan selects the next channel, repeating until all the
channels defined by SC have been scanned.
If A1 is 0x04 (bit 0 clear, bit 1 clear, and bit 2 set), then the active scan will reject all beacons that do
not match both the configured PAN ID and the configured channel. This is the best way to join a
particular coordinator.
If A1 is 0x05 (bit 0 set, bit 1 clear, and bit 2 set), then the active scan will accept a beacon from any
PAN ID, providing the channel matches. This is useful if the channel is known, but not the PAN ID.

 Loading...
Loading...