Networking Encryption
Digi XBee3® 802.15.4 RF Module User Guide
67
discards the data after SP*2.5 time. It is also important to keep the pin woke device awake for ST
time after receiving indirect messages, otherwise the coordinator could attempt to transmit directly
while the end device is asleep, and the transmission will fail. For this reason we recommend only using
indirect messaging with cyclic sleep.
Encryption
The XBee3 802.15.4 RF Module supports AES 128-bit encryption. 128-bit encryption refers to the
length of the encryption key entered with the KY command (128 bits = 16 bytes). The 802.15.4
protocol specifies eight security modes, enumerated as shown in the following table.
Level Name Encrypted?
Length of message integrity
check
Packet length
overhead
0 N/A No 0 (no check) 0
1 MIC-32 No 4 9
2 MIC-64 No 8 13
3 MIC-128 No 16 21
4 ENC Yes 0 (no check) 5
5 ENC-MIC-32 Yes 4 9
6 ENC-MIC-64 Yes 8 13
7 ENC-MIC-128 Yes 16 21
The XBee3 802.15.4 RF Module only supports security levels 0 and 4. It does not support message
integrity checks. EE 0 selects security level 0 and EE 1 selects security level 4. When using encryption,
all devices in the network must use the same 16-byte encryption key for valid data to get through.
Mismatched keys will corrupt the data output on the receiving device. Mismatched EE parameters will
prevent the receiving device from outputting received data.
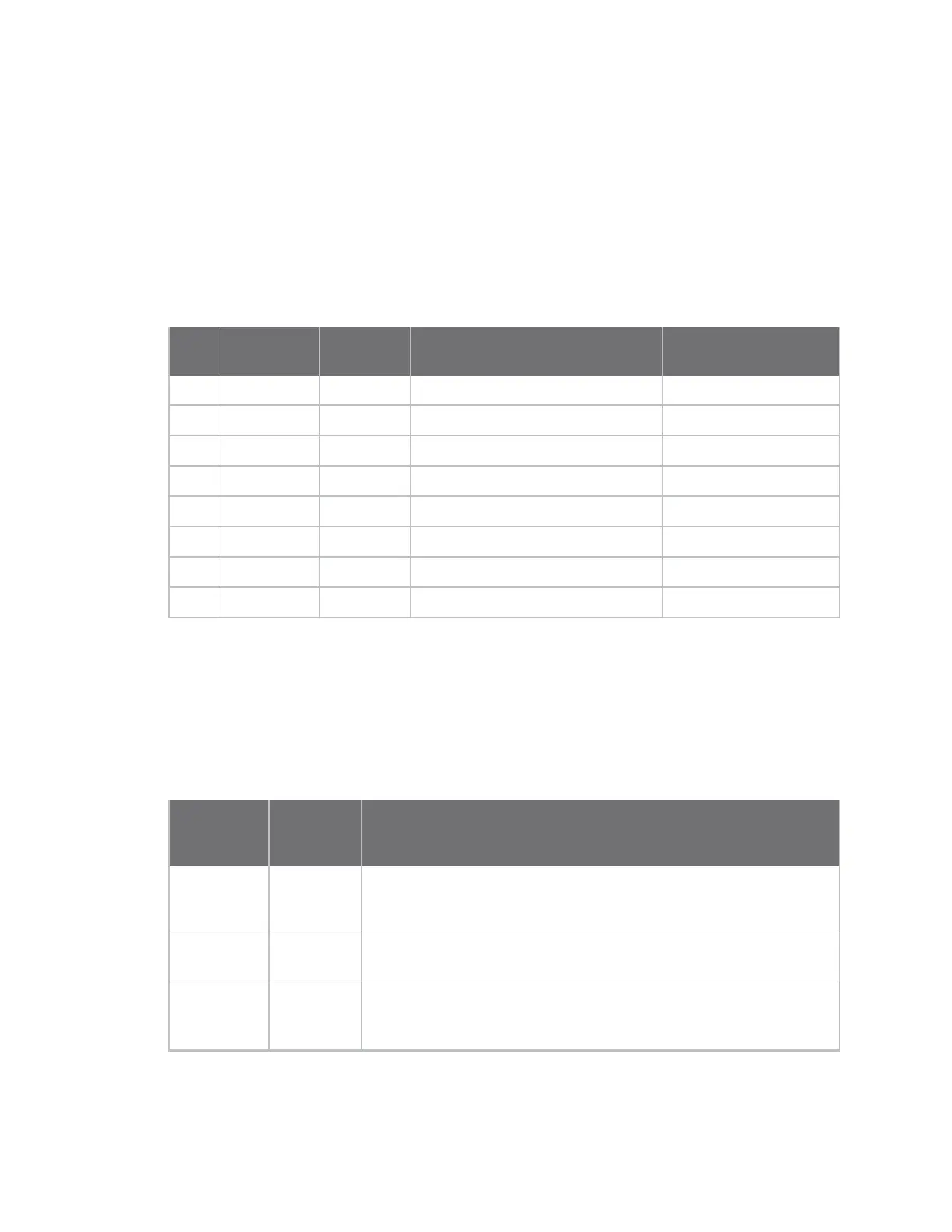
Working from a maximum packet size of 116 bytes, encryption affects the maximum payload as shown
in the following table.
Factor
Effect on
maximum
payload Comment
Compatibility
mode
Force to 95 If C8 bit 0 is set, all packets are limited to 95 bytes, regardless of other
factors listed below. This is how the Legacy 802.15.4 module (S1
hardware) functions.
Packet
overhead
Reduce by 5 This penalty for enabling encryption is unavoidable due to the 802.15.4
protocol.
Source
address
Reduce by 6 This penalty is unavoidable because the 802.15.4 requires encrypted
packets to be sent with a long source address, even if a short address
would otherwise be used.
 Loading...
Loading...