190
Differentiated Instructions Section 5-4
5-4 Differentiated Instructions
Most instructions are provided in both differentiated and non-differentiated
forms. Differentiated instructions are distinguished by an @ in front of the
instruction mnemonic.
A non-differentiated instruction is executed each time it is scanned as long as
its execution condition is ON. A differentiated instruction is executed only once
after its execution condition goes from OFF to ON. If the execution condition
has not changed or has changed from ON to OFF since the last time the
instruction was scanned, the instruction will not be executed. The following
two examples show how this works with MOV(21) and @MOV(21), which are
used to move the data in the address designated by the first operand to the
address designated by the second operand.
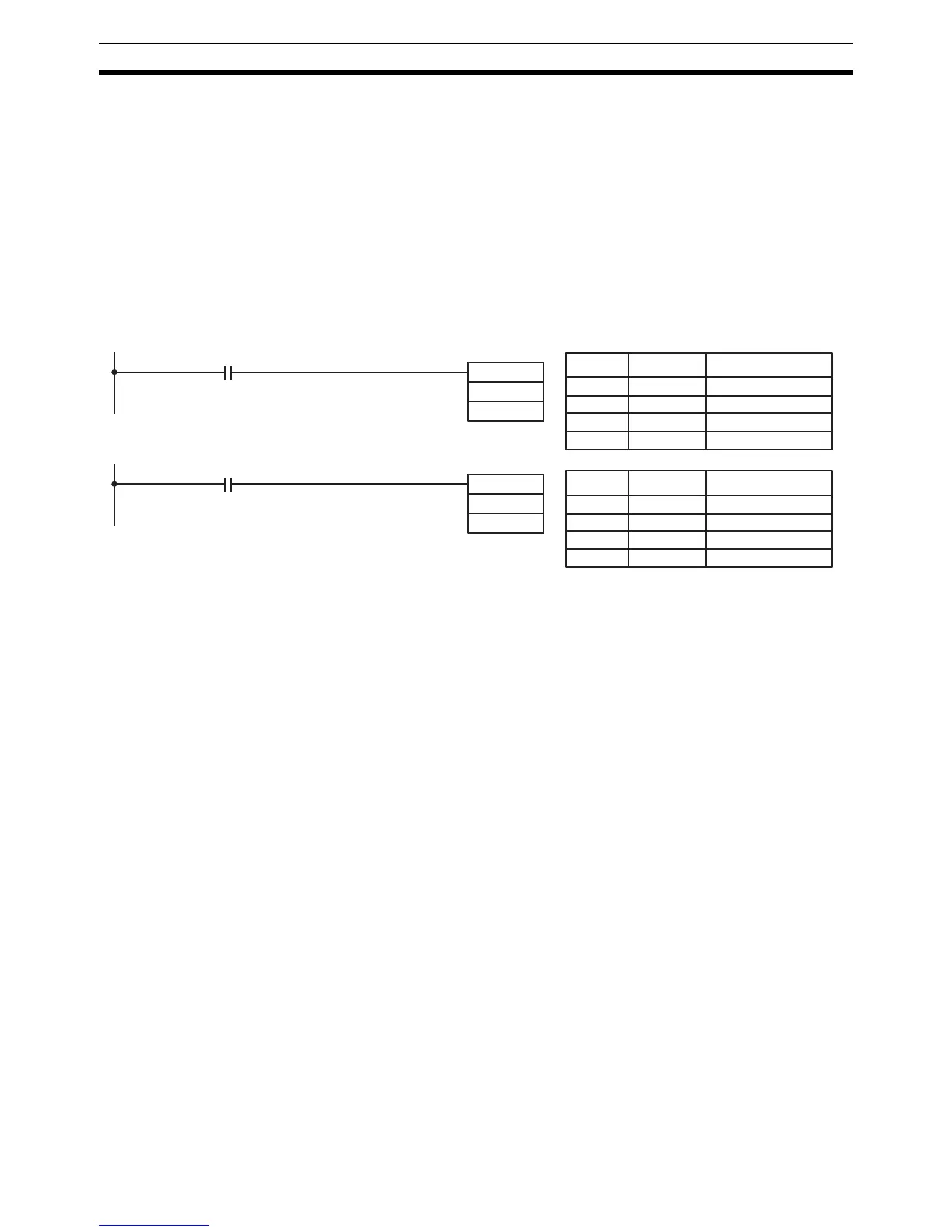
In diagram A, the non-differentiated MOV(21) will move the content of HR 10
to DM 0000 whenever it is scanned with 00000. If the cycle time is 80 ms and
00000 remains ON for 2.0 seconds, this move operation will be performed 25
times and only the last value moved to DM 0000 will be preserved there.
In diagram B, the differentiated @MOV(21) will move the content of HR 10 to
DM 0000 only once after 00000 goes ON. Even if 00000 remains ON for 2.0
seconds with the same 80 ms cycle time, the move operation will be executed
only once during the first cycle in which 00000 has changed from OFF to ON.
Because the content of HR 10 could very well change during the 2 seconds
while 00000 is ON, the final content of DM 0000 after the 2 seconds could be
different depending on whether MOV(21) or @MOV(21) was used.
All operands, ladder diagram symbols, and other specifications for instruc-
tions are the same regardless of whether the differentiated or non-differenti-
ated form of an instruction is used. When inputting, the same function codes
are also used, but NOT is input after the function code to designate the differ-
entiated form of an instruction. Most, but not all, instructions have differenti-
ated forms.
Refer to 5-11 INTERLOCK and INTERLOCK CLEAR – IL(02) and ILC(03) for
the effects of interlocks on differentiated instructions.
The CQM1 also provides differentiation instructions: DIFU(13) and DIFD(14).
DIFU(13) operates the same as a differentiated instruction, but is used to turn
ON a bit for one cycle. DIFD(14) also turns ON a bit for one cycle, but does it
when the execution condition has changed from ON to OFF. Refer to 5-8-4
DIFFERENTIATE UP and DOWN – DIFU(13) and DIFD(14) for details.
00000
MOV(21)
HR 10
DM 0000
Diagram A
00000
@MOV(21)
HR 10
DM 0000
Diagram B
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 MOV(21)
HR 10
DM 0000
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 @MOV(21)
DM 0000
HR 10
 Loading...
Loading...