296
Binary Calculation Instructions Section 5-21
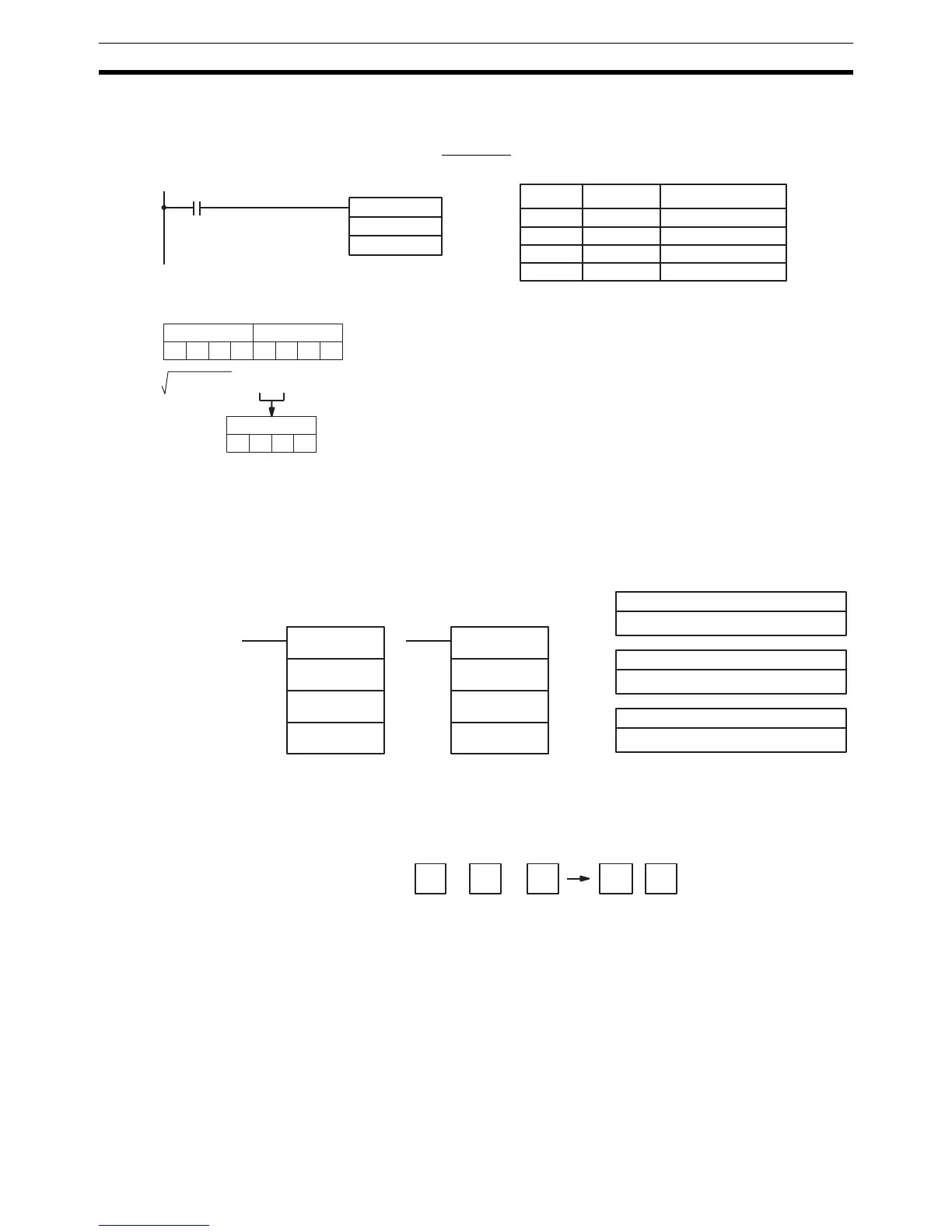
Example The following example shows how to take the square root of an eight digit
number. The result is a four-digit number, with the remainder rounded off. and
then round the result.
In this example,
√63250561 = 7953.0221..., which is rounded off to 7953.
5-21 Binary Calculation Instructions
5-21-1 BINARY ADD – ADB(50)
Limitations DM 6144 to DM 6655 cannot be used for R.
Description When the execution condition is OFF, ADB(50) is not executed. When the exe-
cution condition is ON, ADB(50) adds the contents of Au, Ad, and CY, and
places the result in R. CY will be set if the result is greater than FFFF.
ADB(50) can also be used to add signed binary data. With the CQM1-
CPU4@-EV1, CPM1A, and SRM1, the underflow and overflow flags (SR
25404 and SR 25405) indicate whether the result has exceeded the lower or
upper limits of the 16-bit signed binary data range.
Flags ER: Indirectly addressed DM word is non-existent. (Content of *DM word
is not BCD, or the DM area boundary has been exceeded.)
CY: ON when the result is greater than FFFF.
EQ: ON when the result is 0.
OF: ON when the result exceeds +32,767 (7FFF).
(CQM1-CPU4@-E/-EV1 only)
00000
@ROOT(72)
DM 0000
001
DM 0001 DM 0000
63250561
63,250,561 = 7953.0221
001
7953
Address Instruction Operands
00000 LD 00000
00001 @ROOT(72)
DM 0000
001
(The remainder is rounded off.)
Au: Augend word (binary)
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
Ad: Addend word (binary)
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, TC, LR, #
Ladder Symbols
Operand Data Areas
R: Result word
IR, SR, AR, DM, HR, LR
ADB(50)
Au
Ad
R
@ADB(50)
Au
Ad
R
Au + Ad + CY CY R
 Loading...
Loading...