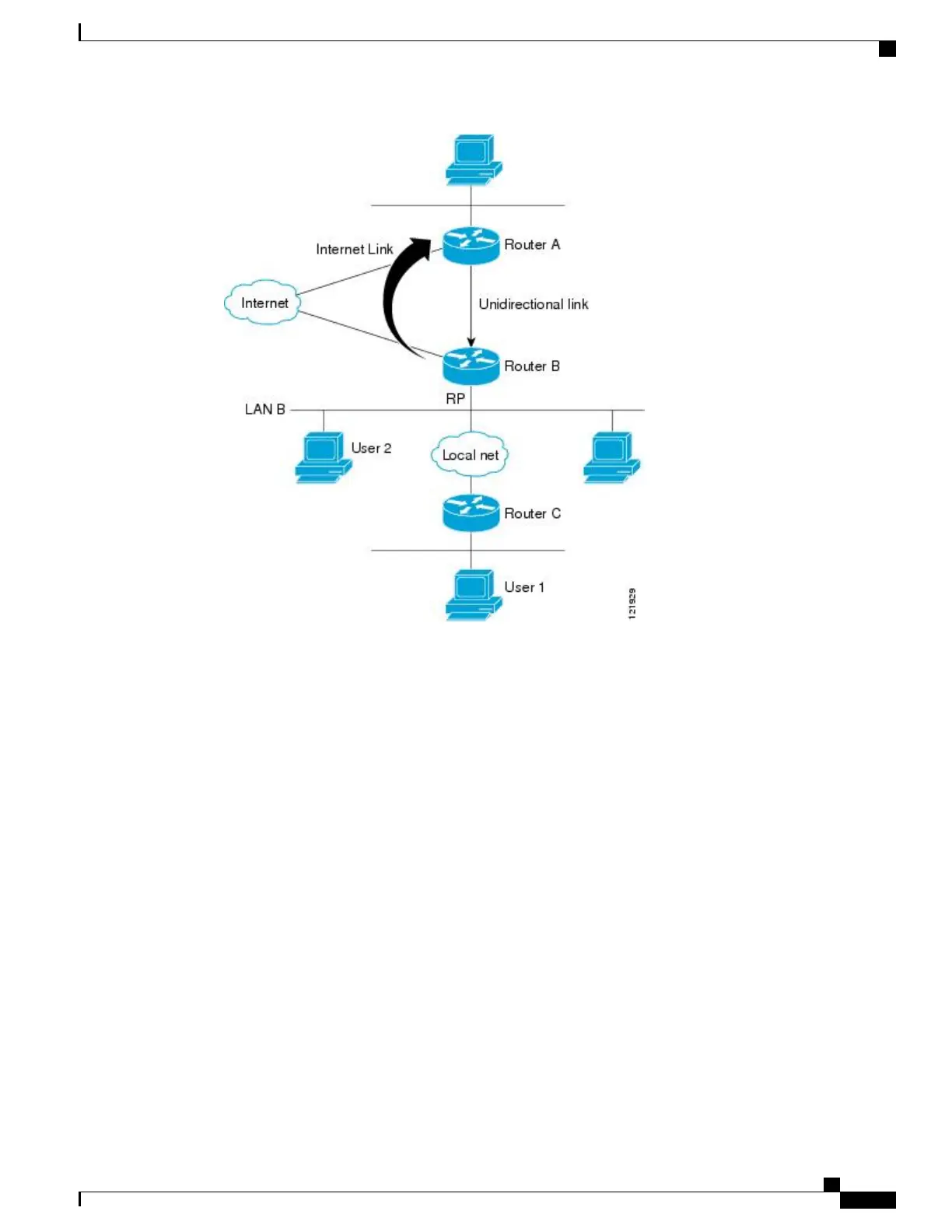
Scenario 1--Traditional UDLR Scenario (UDL Device with Directly Connected Receivers)
For scenario 1, no IGMP proxy mechanism is needed. In this scenario, the following sequence of events
occurs:
1
User 2 sends an IGMP membership report requesting interest in group G.
2
Router B receives the IGMP membership report, adds a forwarding entry for group G on LAN B, and
proxies the IGMP report to Router A, which is the UDLR upstream device.
3
The IGMP report is then proxied across the Internet link.
4
Router A receives the IGMP proxy and maintains a forwarding entry on the unidirectional link.
Scenario 2--IGMP Proxy Scenario (UDL Device without Directly Connected Receivers)
For scenario 2, the IGMP proxy mechanism is needed to enable hosts that are not directly connected to a
downstream device to join a multicast group sourced from an upstream network. In this scenario, the following
sequence of events occurs:
1
User 1 sends an IGMP membership report requesting interest in group G.
2
Router C sends a PIM Join message hop-by-hop to the RP (Router B).
3
Router B receives the PIM Join message and adds a forwarding entry for group G on LAN B.
4
Router B periodically checks its mroute table and proxies the IGMP membership report to its upstream
UDL device across the Internet link.
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-29890-01 91
Configuring IGMP Proxy
IGMP Proxy
 Loading...
Loading...











