1 or version 2 hosts wanting to join the multicast group respond by sending a join message to the device. The
device CPU creates a multicast forwarding-table entry for the group if it is not already present. The CPU also
adds the interface where the join message was received to the forwarding-table entry. The host associated
with that interface receives multicast traffic for that multicast group.
Figure 1: Initial IGMP Join Message
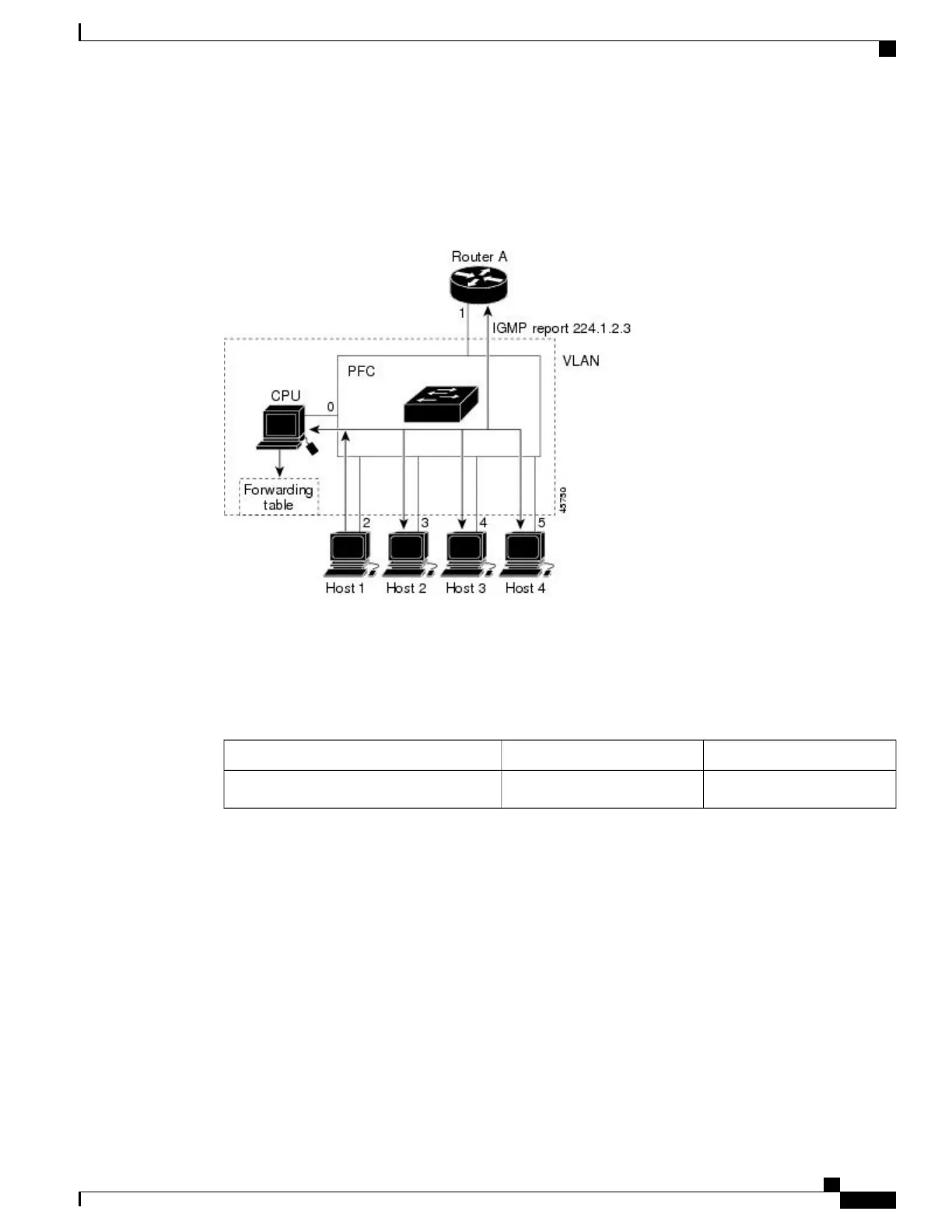
Router A sends a general query to the device, which forwards the query to ports 2 through 5, which are all
members of the same VLAN. Host 1 wants to join multicast group 224.1.2.3 and multicasts an IGMP
membership report (IGMP join message) to the group. The device CPU uses the information in the IGMP
report to set up a forwarding-table entry that includes the port numbers connected to Host 1 and to the router.
Table 5: IGMP Snooping Forwarding Table
PortsType of PacketDestination Address
1, 2IGMP224.1.2.3
The device hardware can distinguish IGMP information packets from other packets for the multicast group.
The information in the table tells the switching engine to send frames addressed to the 224.1.2.3 multicast IP
address that are not IGMP packets to the router and to the host that has joined the group.
If another host (for example, Host 4) sends an unsolicited IGMP join message for the same group, the CPU
receives that message and adds the port number of Host 4 to the forwarding table. Because the forwarding
IP Multicast Routing Configuration Guide, Cisco IOS XE Release 3SE (Catalyst 3650 Switches)
OL-29890-01 29
Configuring IGMP
IGMP Snooping
 Loading...
Loading...











