302 Matrix SPARSH VP110 User Guide
SRTP
Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (SRTP) encrypts the RTP streams during VoIP phone calls to avoid
interception and eavesdropping. The parties participating in the call must enable SRTP feature simultaneously.
When this feature is enabled on both phones, the type of encryption to utilize for the session is negotiated between
the IP phones. This negotiation process is compliant with RFC 4568.
When a user places a call on the enabled SRTP phone, the IP phone sends an INVITE message with the RTP
encryption algorithm to the destination phone.
Example of the RTP encryption algorithm carried in the SDP of the INVITE message:
The callee receives the INVITE message with the RTP encryption algorithm, and then answers the call by
responding with a 200 OK message which carries the negotiated RTP encryption algorithm.
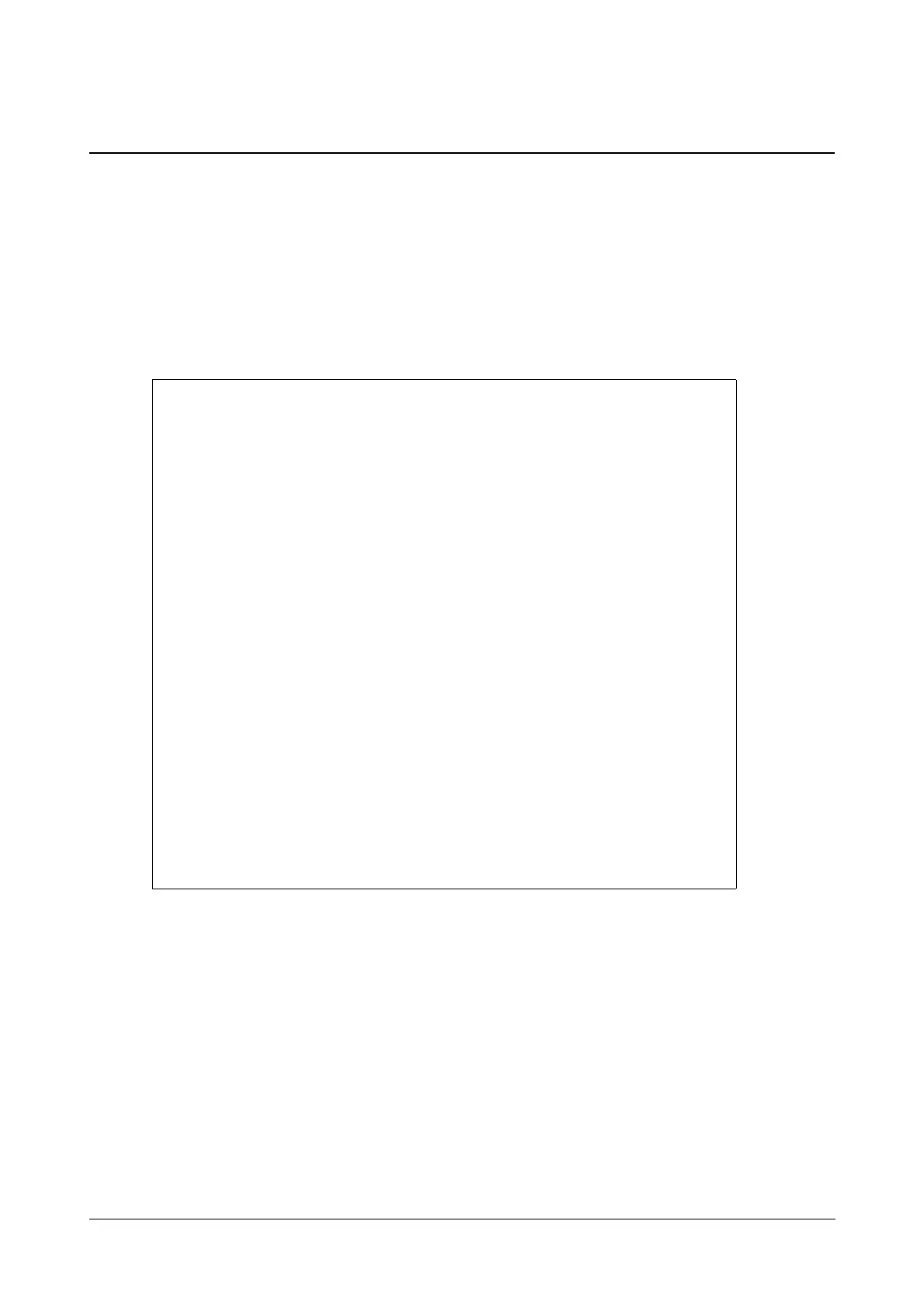
Example of the RTP encryption algorithm carried in the SDP of the 200 OK message:
m=audio11780RTP /SAVP08189101
a=crypto:1AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_80
inline:NzFlNTUwZDk2OGVlOTc3YzNkYTkwZWVkMTM1YWFj
a=crypto:2AES_CM_128_HMAC_SHA1_32
inline:NzkyM2FjNzQ2ZDgxYjg0MzQwMGVmMGUxMzdmNWFm
a=crypto:3F8_128_HMAC_SHA1_80inline:NDliMWIzZGE1ZTAwZjA5ZGFhNjQ5YmEANTMzYzA0
a=rtpmap:0PCMU/8000
a=rtpmap:8PCMA/8000
a=rtpmap:18G729/8000
a=fmtp:18annexb=no
a=rtpmap:9G722/8000
a=fmtp:1010‐15
a=rtpmap:101telephone‐event/8000
a=ptime:20
a=sendrecv
 Loading...
Loading...