81
Connecting to the Host’s RS-232C Port Section 5-1
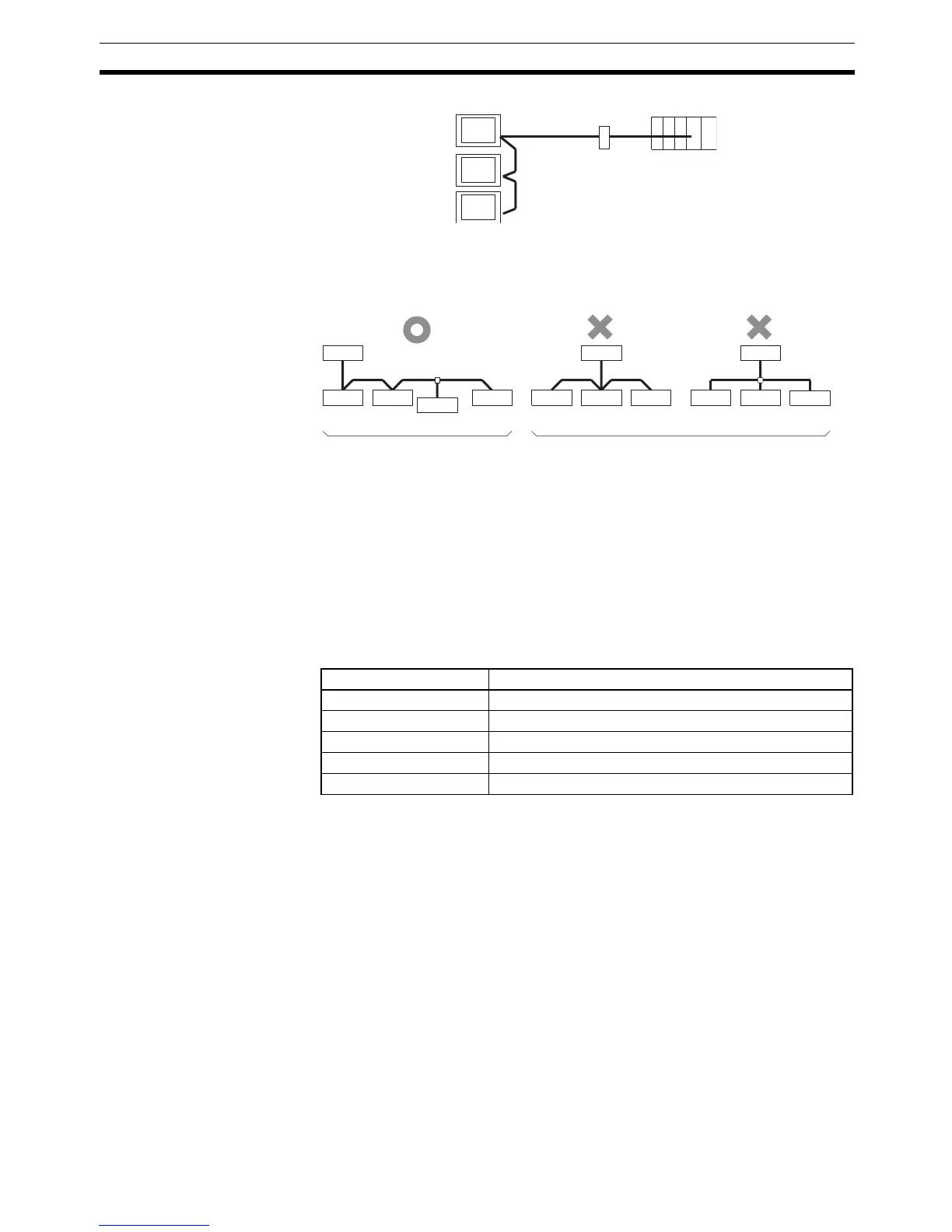
Note One end of the wire must always be connected to the host (PLC), and there
must be no branching. Branching will cause problems such as transmission
delays and communications failures.
Reference: CS/CJ-series CPU Units cannot be connected with the 1:1 connection NT link
method. Use the 1:N connection NT Link method (standard or high-speed) in-
stead to make the 1:1 connection. For details, refer to Using the NT link (1:N)
method (page 64) or Using the High-speed NT link (1:N) method (page 69).
5-1-1 The Type of Host and Settings
The using condition is the same as the connecting PT side RS-232C and the
host side RS-232C.
For the available type and settings of the host, refer to the pages listed below.
Settings at the RS-232C/
RS-422A Adapter (NT-
AL001)
When making a connection between RS-232C and RS-422A/485 ports using
an RS-232C/RS-422A Adapter, set the DIP switches on the NT-AL001 as fol-
lows.
PT Host
RS-232C/RS422A
convertor unit
RS-232C
cable
(max. 2 m)
RS-485 cable
(max. total length
500 m)
NT31
NT31C
PLC
PLC
NT31
PLC
NT31C NT31CNT31 NT31 NT31 NT31 NT31
(At termination)
Relay terminal block Relay terminal bloc
les of Bad Connections
(Not at
termination)
(Not at
termination)
(Not at
termination)
(At
termination)
Method Reference
Host link Host Link Method (page 46)
NT link (1:1) NT Link (1:1) method (page 61)
NT link (1:N) Using the NT Link (1:N) Method (page 64)
High-speed NT link (1:N) Using the High-speed NT Link (1:N) Method (page 69)
Memory link Memory Link Method (page 72)

 Loading...
Loading...