9
Printing using the IEEE 802.11b Interface
This section describes how to print after installing the optional 802.11b Interface Kit.
There are two methods of using this machine as a network printer with IEEE
802.11b.
Note
❒ IEEE 802.11b (wireless LAN) is unavailable in some countries, or its use may
be limited.
❖
❖❖
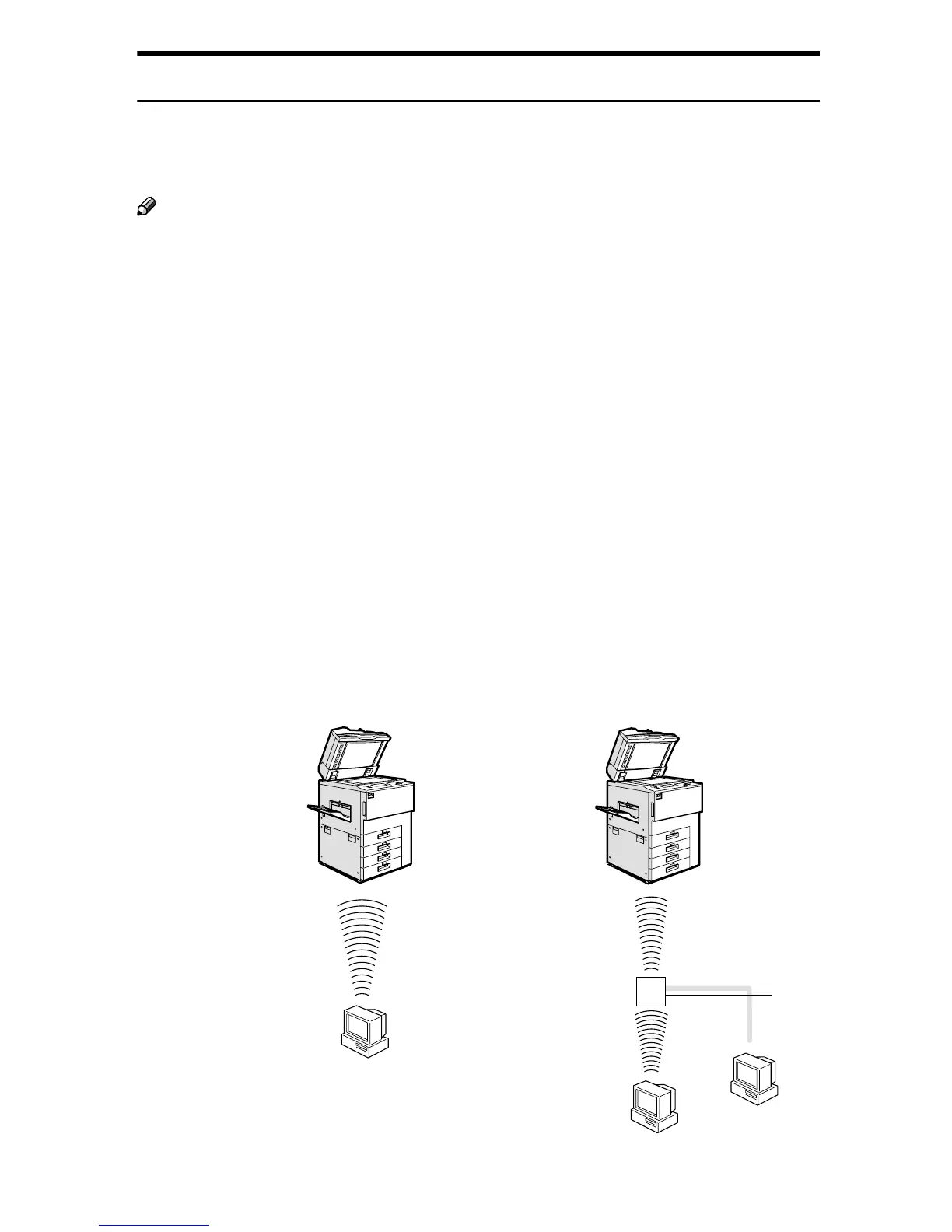
❖ ad hoc mode (802.11 ad hoc mode/ad hoc mode)
This is the mode for transmitting between each wireless LAN client. You must
make the channels the same for each wireless LAN client to transmit using this
basic transmitting method which does not require an access point. When using
“802.11b ad hoc mode”, the SSID must be set. The ad hoc mode settings can be
made from telnet or a web browser. See
p.102 “Using in Ad hoc Mode”.
❖
❖❖
❖ infrastructure mode
This is the mode for transmitting via an access point. The SSID
*1
must be the
same as the access point. When setting WEP
*2
, you must set the same values
as an access point. By connecting the access point to Ethernet, you can transmit
the current network environment. See
p.102 “Using in Infrastructure Mode”
.
*1
This is called a Service Set ID and is used in the connection between the wireless
LAN client and the access point. Only a wireless LAN client and an access point
that have the same SSID can transmit to each other. (The character strings to be set
are in the range ASCII 0x20-0x7e and the SSID is case-sensitive to 32 bytes.)
*2
This is used to protect coded wireless data transmission. When both the wireless
LAN client and the transmission access point are coded using a 64-bit key, you
must set the same WEP key as the printer. (You can set only 10 hexadecimal char-
acters when using 64-bit or 26 hexadecimal characters when using 128-bit.)
❖ad hoc mode
access point
❖infrastructure mode

 Loading...
Loading...











