Corrected capacitance can be enabled for simultaneous C-V measurements by setting the
LeakageCorrection parameter to 1 (see line 12 of the SIMCVsweep82 user module (on page 6-42)).
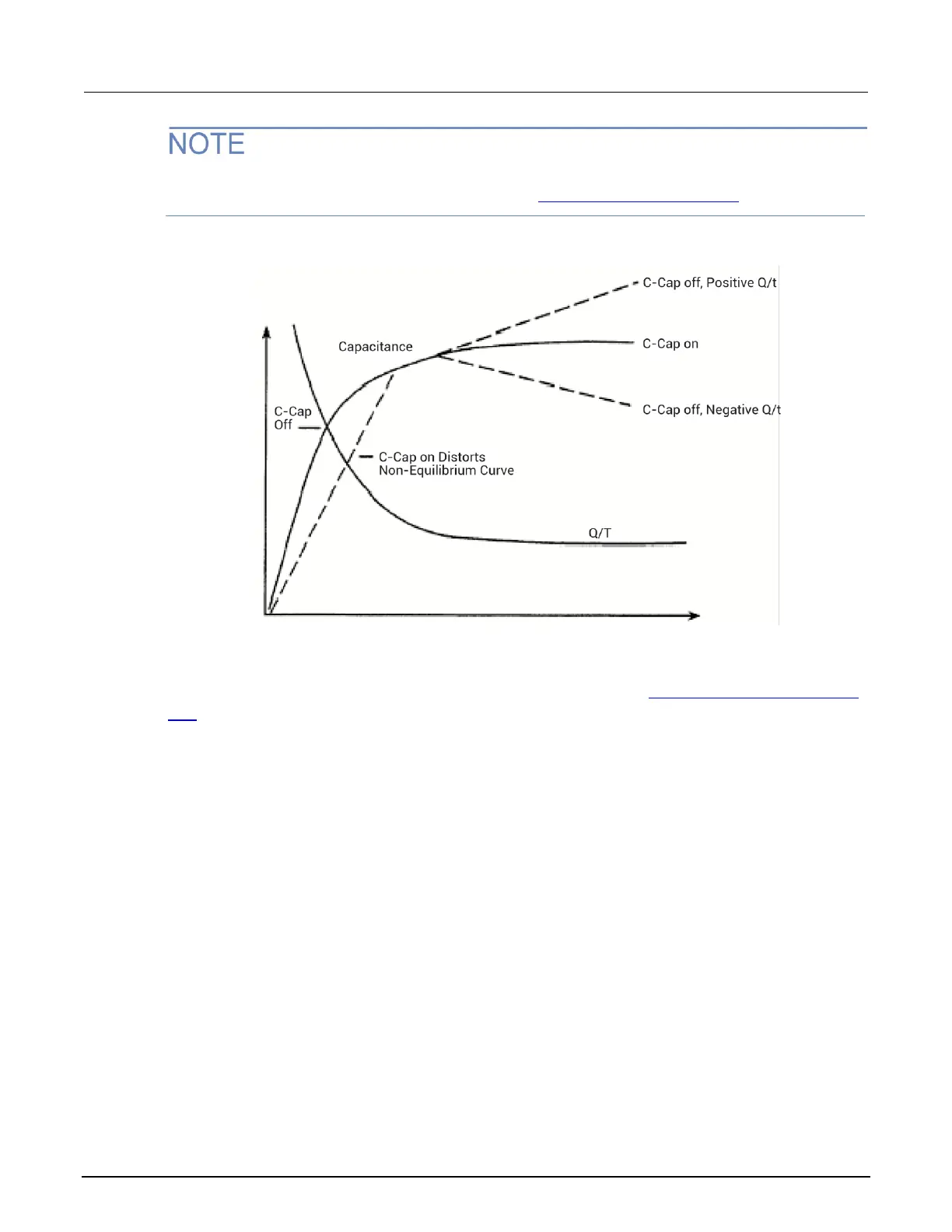
Figure 103: Capacitance and leakage current curves of leaky device
Testing slow devices
A decaying noise curve, such as the dotted line shown in the figure in Determining the optimal delay
time (on page 6-25), will result if the maximum delay time is too short for the device being tested. This
phenomenon, which is most prevalent with slow devices, occurs because the signal range is too small.
To eliminate such erroneous curves, choose a longer maximum delay time. A good starting point for
unknown devices is a 30-second maximum delay time.
Correcting residual errors
Controlling errors at the source is the best way to optimize C-V measurements, but doing so is not
always possible. Remaining residual errors include offset, gain, noise, and voltage-dependent errors.
Methods of correcting these error sources are discussed in the following paragraphs.
Offsets
Offset capacitance and conductance caused by the test apparatus can be eliminated by performing a
suppression with the probes in the up position. These offsets will then be nulled out when the
measurement is made. Whenever the system configuration is changed, the suppression procedure
should be repeated. For maximum accuracy, it is recommended that you perform a probes-up
suppression or at least verify before every measurement.

 Loading...
Loading...











