11.3.1 Interface Column
This example describes the configuration of static IP routing rules.
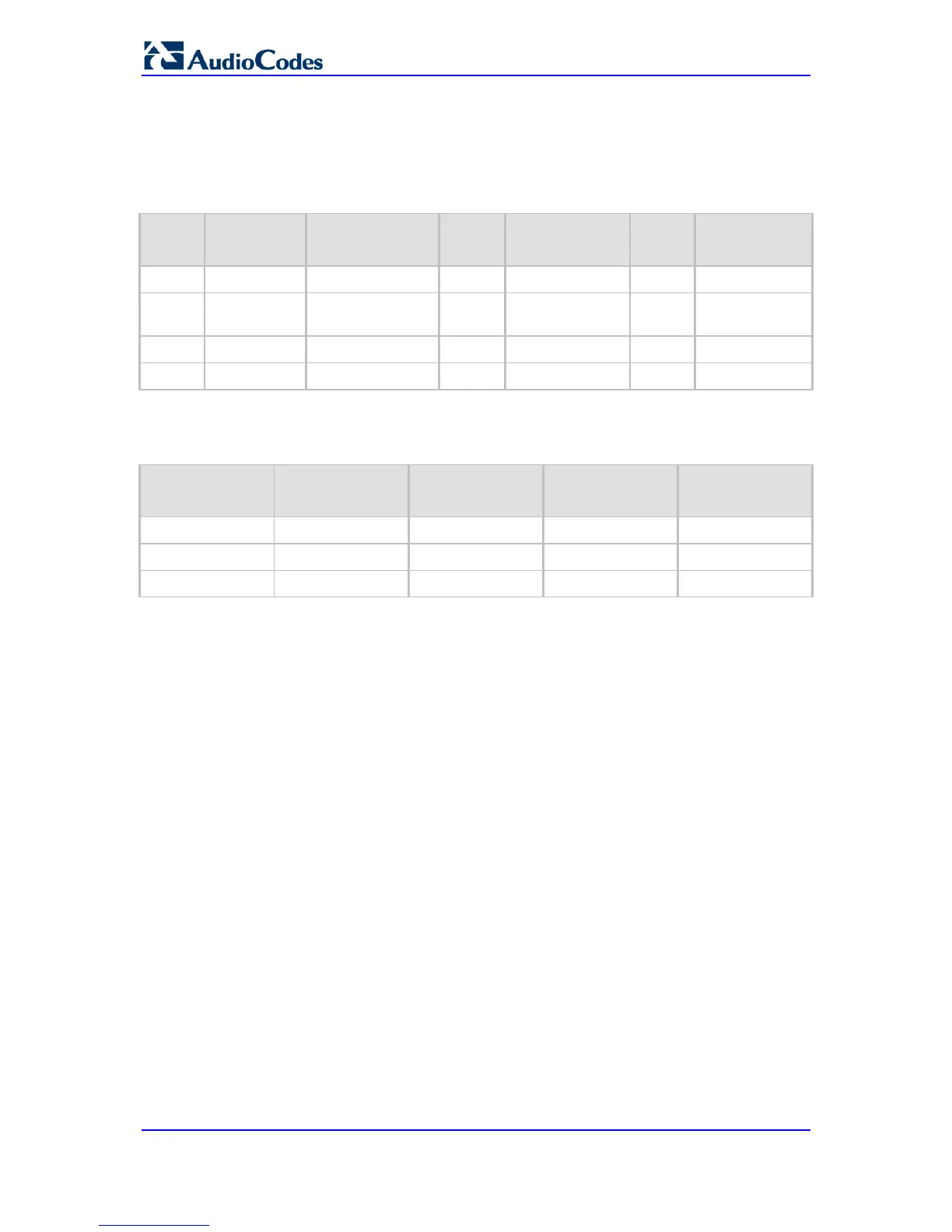
1. Configure network interfaces in the Multiple Interface table, as shown below:
Table 11-11: Configured Network Interfaces in Multiple Interface Table
Index
Application
Type
IP Address
Prefix
Length
Gateway
VLAN
ID
Interface Name
0 OAMP 192.168.0.2 16 192.168.0.1 501 Mng
1
Media &
Control
10.32.174.50 24 10.32.174.1 2012 MediaCntrl
2 Media 10.33.174.50 24 10.33.174.1 2013 Media1
3 Control 10.34.174.50 24 10.34.174.1 2014 Cntrl1
2. Configure static IP Routing rules in the IP Routing table, as shown below:
Table 11-12: Configured Static IP Routing Rules in IP Routing Table
Destination IP
Address
Prefix Length
Gateway IP
Address
Metric Interface Name
10.31.174.0 24 192.168.11.1 1 Mng
174.96.151.15 24 10.32.174.12 1 MediaCntrl
10.35.174.0 24 10.34.174.240 1 Cntrl1
Note that the IP address configured in the 'Gateway IP Address' field (i.e., next hop)
must reside on the same subnet as the IP address of the associated network interface
that is specified in the 'Interface Name' field.
11.3.2 Routing Table Configuration Summary and Guidelines
The Routing table configurations must adhere to the following rules:
The 'Gateway IP Address' field must be on the same subnet as the IP address of the
associated interface specified in the 'Interface Name' field.
For the configuration settings to take effect, you must reset the device with a "burn" to
flash memory.
11.3.3 Troubleshooting the Routing Table
When adding a new static routing rule, the added rule passes a validation test. If errors are
found, the routing rule is rejected and is not added to the IP Routing table. Failed routing
validations may result in limited connectivity (or no connectivity) to the destinations
specified in the incorrect routing rule. For any error found in the Routing table or failure to
configure a routing rule, the device sends a notification message to the Syslog server
reporting the problem.

 Loading...
Loading...











