6-16 PQM Power Quality Meter GE Power Management
6.6 POWER ANALYSIS 6 SOFTWARE
6
6.6.3 TRACE MEMORY
The trace memory feature allows the PQM to be setup to trigger on various conditions. The trace memory can
record maximum of 36 cycles of data (16 samples per cycle) for all voltage and current inputs simultaneously.
A Total Trace Triggers Counter has been implemented in the PQM Memory Map at Register 0x0B83. This reg-
ister will keep a running total of all valid Trace Memory Triggers from the last time power was applied to the
PQM. The Total Trace Triggers counter will rollover to 0 at 65536. The trace memory feature is implemented
into PQMPC as shown below.
1. Select the
Setpoint > PQM Setup
menu item to setup the trace memory feature. This launches the PQM
Setup dialog box shown below. Click on the
Trace Memory
tab to display the trace memory parameters.
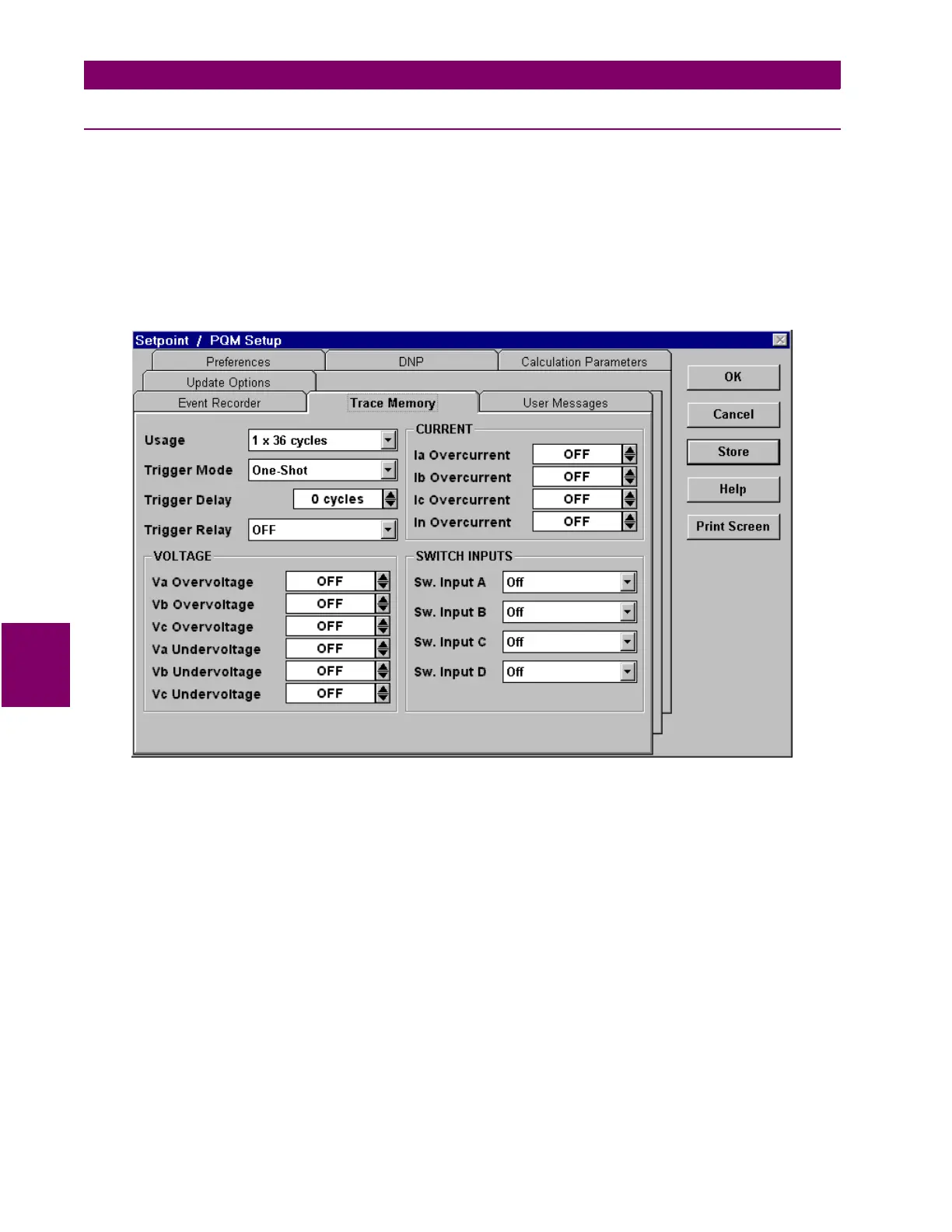
The
Memory Usage
is set as follows:
•
1 x 36 cycles
: upon trigger, the entire buffer is filled with 36 cycles of data
•
2 x 18 cycles
: 2 separate 18-cycle buffers are created and each is filled upon a trigger
•
3 x 12 cycles
: 3 separate 12 cycle buffers are created and each is filled upon a trigger
If the
Trigger Mode
is set to
One-Shot
, then the trace memory is triggered once per buffer; if it is set to
Retrig-
ger
, then it automatically retriggers and overwrites the previous data.
The
Trigger Delay
delays the trigger by the number of cycles specified.
The
VOLTAGE
,
CURRENT
, and
SWITCH INPUTS
selections are the parameters and levels that are used to trig-
ger the trace memory.
Clicking
Store
sends the current settings to the PQM.

 Loading...
Loading...