11.8 SVCREQ 7: Read or Change the Time-of-Day Clock
Use SVCREQ 7 to read or change the time of day clock in the PLC. The data can be
either BCD or ASCII. Either 2-digit-year or 4-digit-year format is available. The function
is successful unless some number other than 0 (read) or 1 (change) is entered for the
requested operation, or an invalid data format is specified, or data is provided in an
unexpected format.
11.8.1 Parameter Block Format for SVCREQ 7
For the date/time functions, the length of the parameter block depends on the data format.
The data block is either BCD or ASCII. BCD format requires 6 words; packed ASCII
requires 12 words (13 words for 4-digit year). For both data types:
• Hours are stored in 24-hour format.
• Day of the week is a numeric value from 1 (Sunday) to 7 (Saturday).
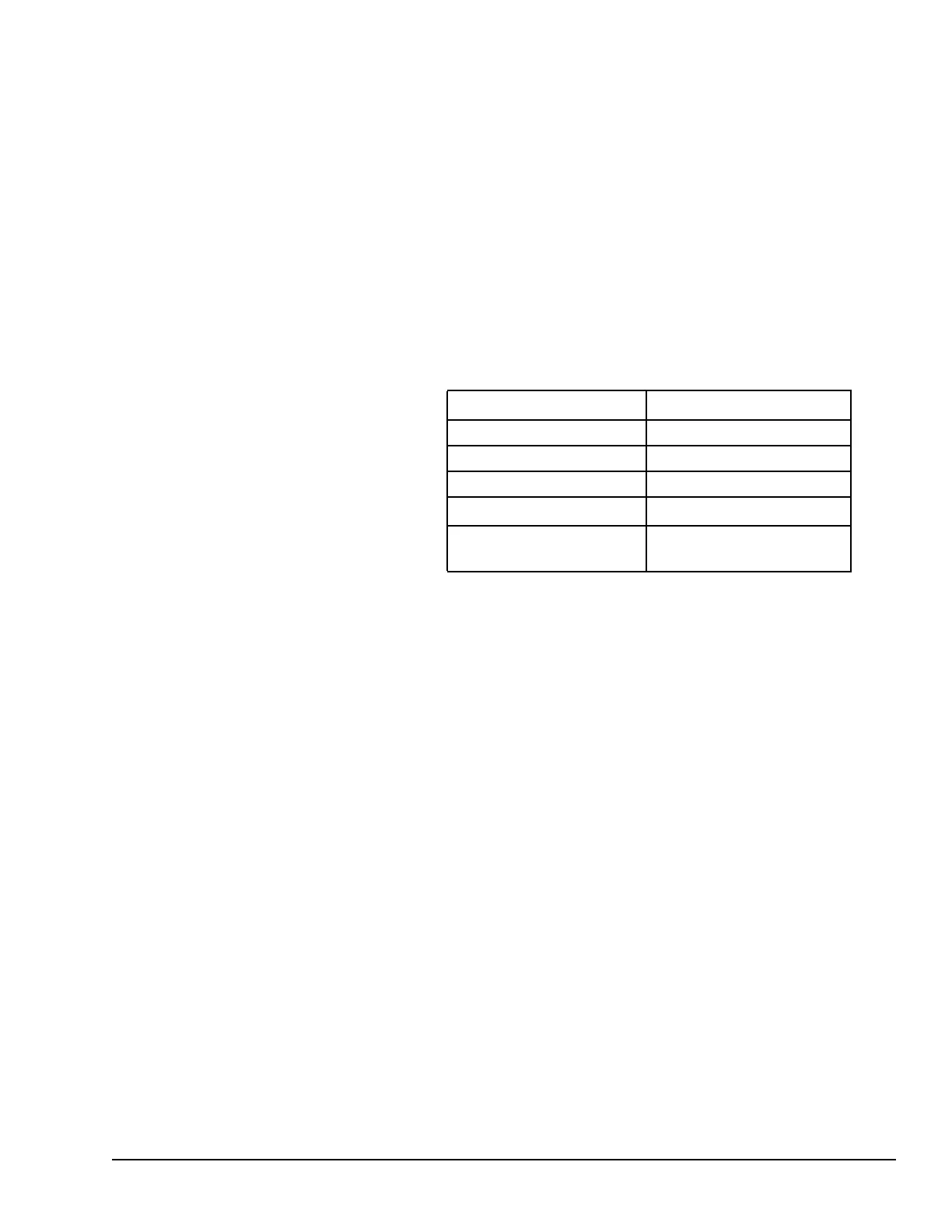
2-Digit Year Format 4-Digit Year Format
address
0 = read time and date 0 = read time and date
1 = set time and date 1 = set time and date
address + 1
1 = BCD format 81h = BCD format
3 = packed ASCII format 83h = packed ASCII format
address + 2 to
end
data data
Words 3 to the end of the parameter block contain output data returned by a read function,
or new data being supplied by a change function. In both cases, format of these data
words is the same. When reading the date and time, words (address + 2) to the end of the
parameter block are ignored on input.
The Service Request Function GFK-1503E User Manual 205
For public disclosure