13-1
13 Monitoring Carbon Dioxide
13.1 Introduction
CO
2
monitoring is a continuous, non-invasive technique for determining the concentration of
CO
2
in the patient’ airway by measuring the absorption of infrared (IR) light of specific
wavelengths. The CO
2
has its own absorption characteristic and the amount of light passing
the gas probe depends on the concentration of the measured CO
2.
When a specific band of IR
light is passed through respiratory gas samples, some of IR light will be absorbed by the CO
2
molecules. The amount of IR light transmitted after it has been passed through the respiratory
gas sample is measured with a photodetector. From the amount of IR light measured, the
concentration of CO
2
is calculated.
There are two methods for measuring CO
2
in the patient’s airway:
1. Mainstream measurement uses a CO
2
sensor attached to an airway adapter directly
inserted into the patient’s breathing system.
2. Sidestream/Microstream measurement samples expired patient gas at a constant sample
flow from the patient’s airway and analyzes it with a CO
2
sensor built into the CO
2
module.
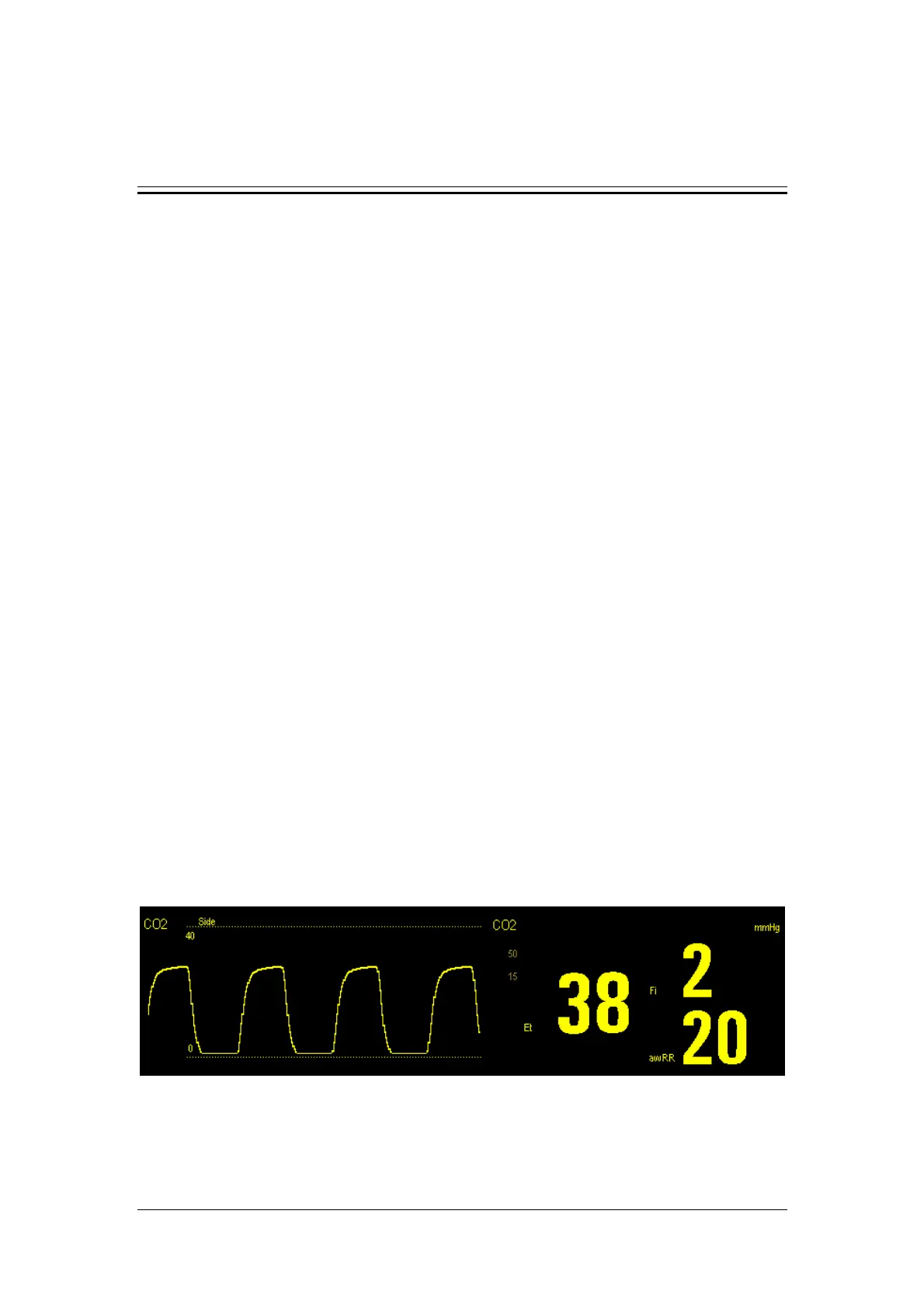
The measurement provides:
1. A CO
2
waveform
2. End tidal CO
2
value (EtCO
2
): the CO
2
value measured at the end of the expiration phase.
3. Fraction of inspired CO
2
(FiCO
2
): the CO
2
value measured during inspiration.
4. Airway respiration rate (awRR): the number of breaths per minute, calculated from the
CO
2
waveform.
 Loading...
Loading...