RL78/F13, F14 CHAPTER 15 SERIAL ARRAY UNIT
R01UH0368EJ0210 Rev.2.10 833
Dec 10, 2015
The channels supporting 3-wire serial I/O (CSI00, CSI01, CSI10, CSI11) are channels 0 and 1 of SAU0 and channels 0
and 1 of SAU1.
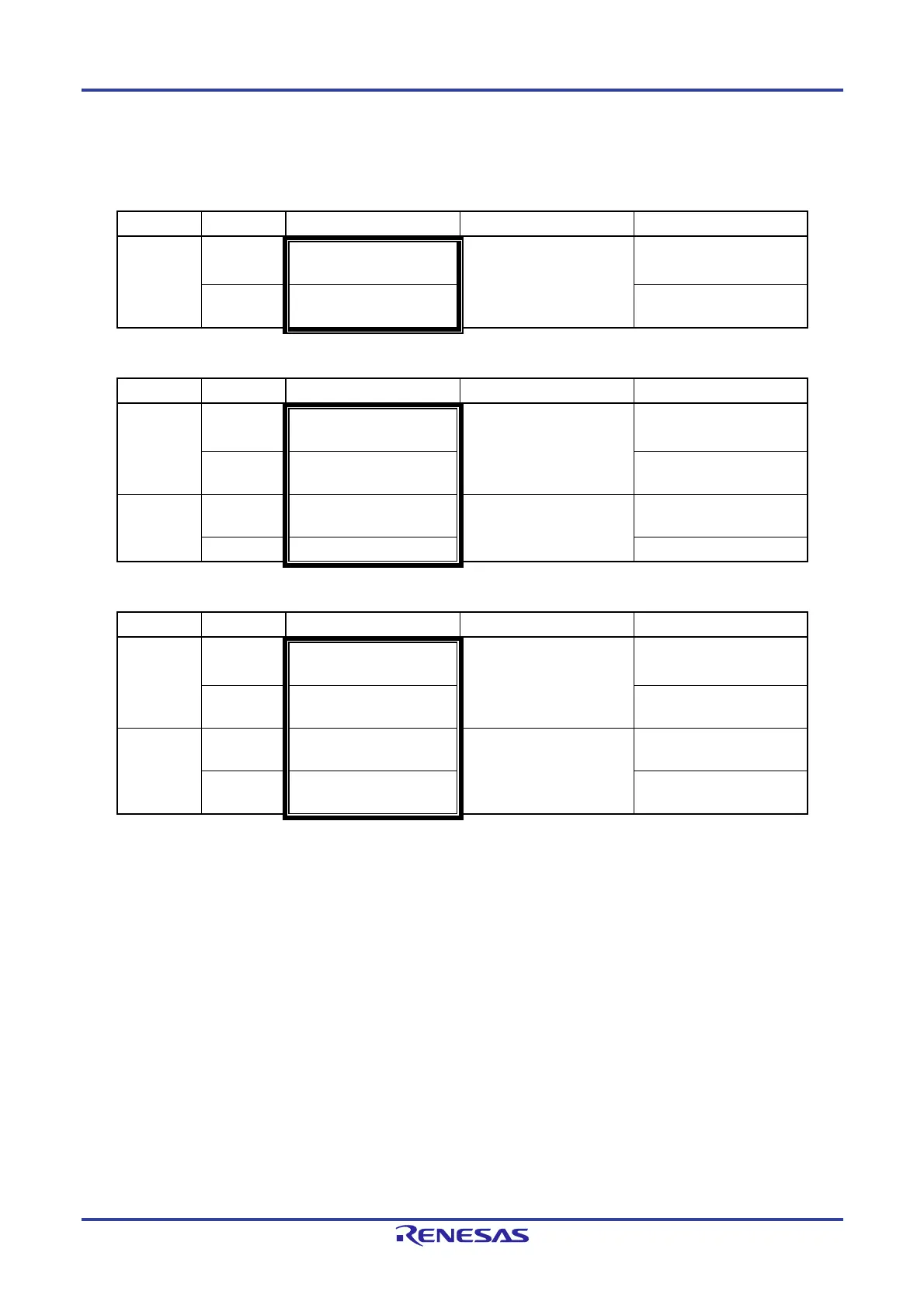
• Group A products
Unit Channel Used as CSI Used as UART
Used as Simplified I
2
C
0 0
CSI00 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
UART0 (supporting LIN-bus) IIC00
1
CSI01 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
IIC01
• Products of Groups C-1 and D-1
Unit Channel Used as CSI Used as UART
Used as Simplified I
2
C
0 0
CSI00 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
UART0 (supporting LIN-bus) IIC00
1
CSI01 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
IIC01
1 0
CSI10 (supporting SPI
function)
Note1, 2
UART1 IIC10
1 - -
• Products of Groups B, C-2, D-2, and E
Unit Channel Used as CSI Used as UART
Used as Simplified I
2
C
0 0
CSI00 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
UART0 (supporting LIN-bus) IIC00
1
CSI01 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
IIC01
1 0
CSI10 (supporting SPI
function)
Note1, 2
UART1 IIC10
1
CSI11 (supporting SPI
function)
Note2
IIC11
Notes 1. 48-pin, 32-pin and 30-pin products do not have SSI10
___________
pin.
2. Set CKPmn bit of SCRmn register to 1, when SSEmn = 1 (Enables SSImn
____________
pin input).
(m = 0, 1, n = 0, 1)
Remark Group A: RL78/F13 (LIN incorporated) products with 20, 30, 32, 48, or 64 pins and 16 Kbytes to 64 Kbytes
of code flash memory
Group B: RL78/F13 (LIN incorporated) products with 48 or 64 pins and 96 Kbytes to 128 Kbytes of code
flash memory or with 80 pins and 64 Kbytes to 128 Kbytes of code flash memory
Group C-1: RL78/F13 (CAN and LIN incorporated) products with 30 or 32 pins
Group C-2: RL78/F13 (CAN and LIN incorporated) products with 48, 64, or 80 pins
Group D-1: RL78/F14 products with 30 or 32 pins
Group D-2: RL78/F14 products with 48, 64, or 80 pins and 48 Kbytes to 96 Kbytes of code flash memory
Group E: RL78/F14 products with 48, 64, or 80 pins and 128 Kbytes to 256 Kbytes of code flash memory
or with 100 pins and 64 Kbytes to 256 Kbytes of code flash memory
3-wire serial I/O (CSI00, CSI01, CSI10, CSI11) performs the following six types of communication operations.
• Master transmission (See 15.5.1 Master transmission.)
• Master reception (See 15.5.2 Master reception.)
• Master transmission/reception (See 15.5.3 Master transmission/reception.)
• Slave transmission (See 15.5.4 Slave transmission.)
• Slave reception (See 15.5.5 Slave reception.)
• Slave transmission/reception (See 15.5.6 Slave transmission/reception.)
<R>

 Loading...
Loading...











