63
Using the Scaling Function
Conguring the scaling of the U8554/LR8534 Strain Unit
Strain gage-type converter
You can use values on the Strain gage-type converter’s inspection record to convert the converter’s
output into physical quantities.
Two methods are available: using a calibration factor*
1
and using rated capacity and rated output.
When an inspection record provides a calibration factor
Setting example
To display waveform data measured using a strain gauge converter having a calibration factor of
0.001442 G /1 × 10
−6
strain*
2
as gures in gravities (G) (*2: 10
−6
strain = μ
ε
)
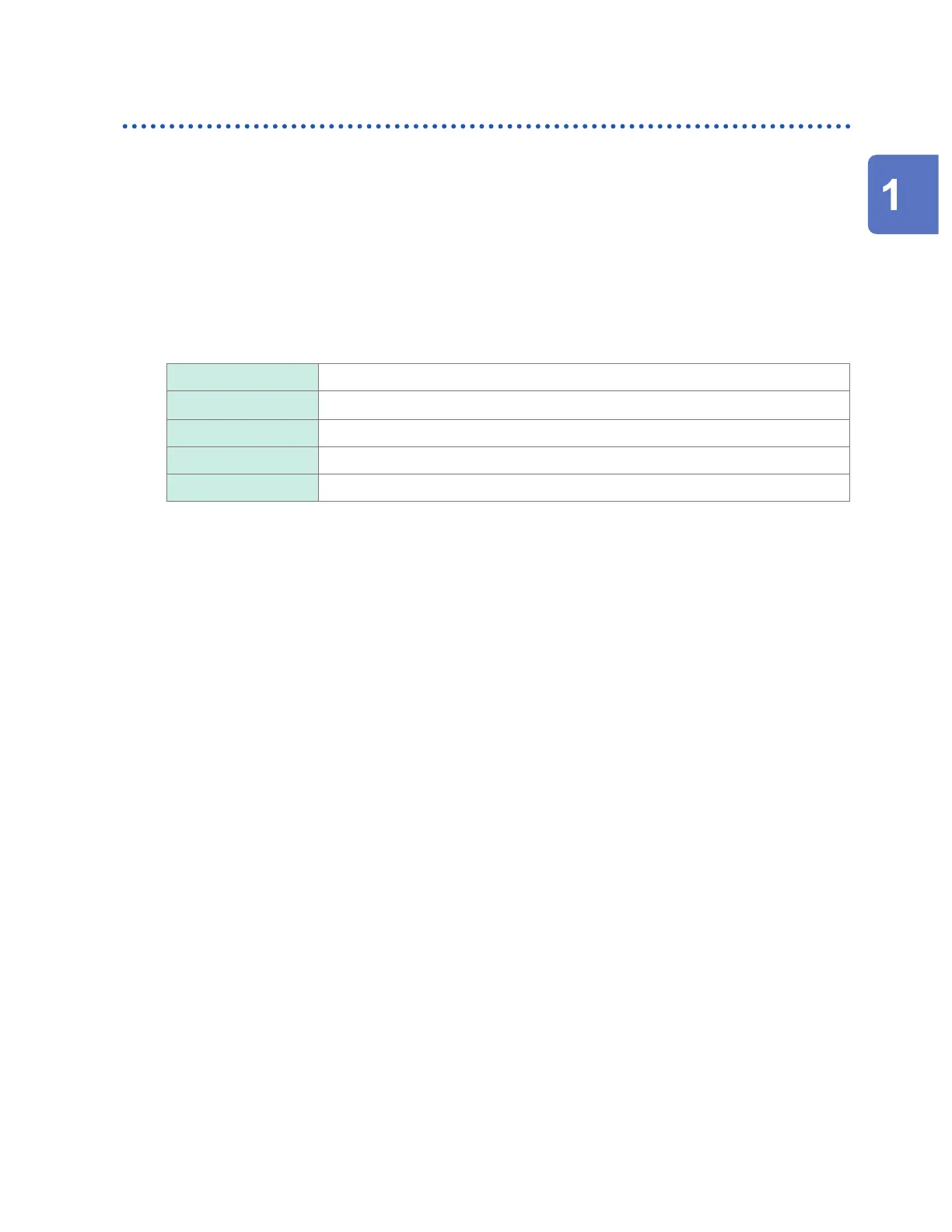
Scaling Decimal
Conversion method
Ratio
Unit G
Slope 0.001442 (Indicated as 1.442 m)
Oset 0
*1: Some inspection reports may provide a calibration factor in two representations: the one in per one
microvolt per volt (/1 μV/V) and the other in per 1 multiplied by 10 to the −6th power strain (/1×10
−6
strain).
In such a case, enter the quantity expressed in per 1 multiplied by 10 to the −6th power strain.
When an inspection record provides rated capacity and rated output
See “(When the scaling conversion method is set to [Rating])” (p. 60).
Strain gage
To convert values measured using strain gages into strain, determine the scaling conversion ratio
using the following corrections:
• Output correction based on strain gage conguration
• Correction based on Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio of an object under measurement
Also, make the following corrections as required:
• Wire-resistance correction
• Gage-ratio correction
See “11.2 Measuring Strain” (p. 374).
Settings and Operation
www.GlobalTestSupply.com
Find Quality Products Online at: sales@GlobalTestSupply.com

 Loading...
Loading...