Table 101 Monitoring Information (continued)
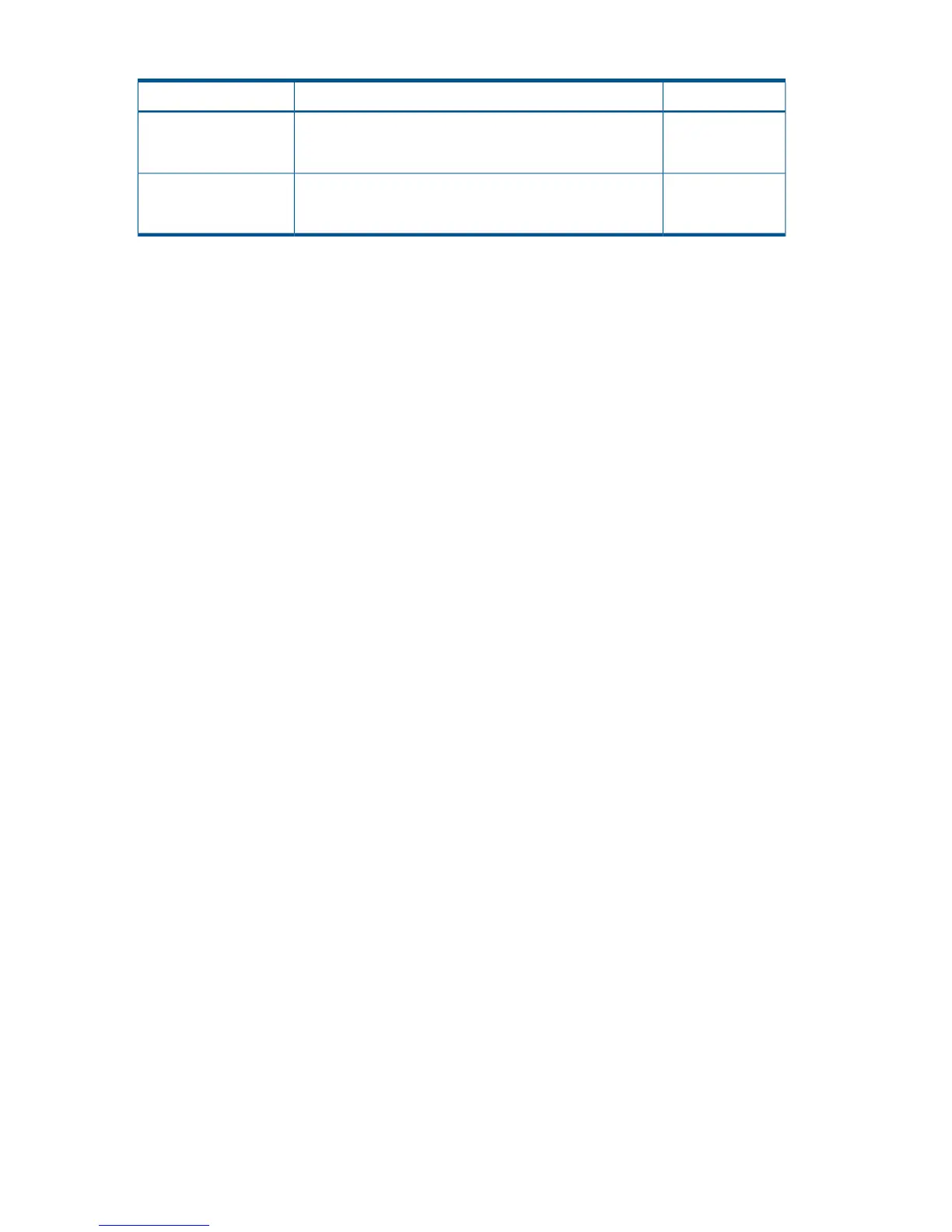
Target Copy TypePossible Reasons To Acquire This InformationMonitoring Information
Cnt Ac-J ZWhen inter-journal group operating information is NG for
a Cnt Ac-J Z, this might be due to a line failure or a failure
at another storage system.
Inter-journal group
operating information
Cnt Ac-J ZIf the usage rate is high for metadata or data secured on a
journal volume for a Cnt Ac-J Z, then a journal volume might
overflow.
Journal volume metadata
usage rate/data usage
rate
Trace Output Method
To help analyze the causes of failures, trace information can be used. Trace information, such as
user operations and macro calls to hardware, is saved in memory. In Business Continuity Manager,
all the trace information currently saved in memory is output to the ABEND dump when a CLI
command terminates abnormally.
Also, when an operator invokes GTF with the GTF parameter set to acquire USR trace information
(TRACE=USR), trace information is acquired as a GTF trace, with an event code from X'300' to
X'30F'.
Perform the following to output ABEND dumps:
• For scripts:
Specify a SYSABEND DD statement for JCL.
• For TSO/E:
After logging on to the TSO/E terminal, you need to enter the following commands before
executing any CLI commands:
◦ When an ABEND dump is output to the spool:
ALLOC DD(SYSABEND) SYSOUT(SYSOUT-class)
◦ When an ABEND dump is output to a dataset:
ALLOC DD(SYSABEND) DS(dataset-name)
When returning to the READY mode after a CLI command terminated abnormally, make sure that
you press the Enter key.
If a TSO/E command is entered without pressing the Enter key, an ABEND dump might not be
output.
Collecting Logs
Only trace information that needs to be presented to the user is output to a log.
Log Types
Table 102 (page 557) shows the different log types for Business Continuity Manager, and the
information collected and the output locations for each log type.
556 Troubleshooting
 Loading...
Loading...


















