Optimizing measurement accuracy
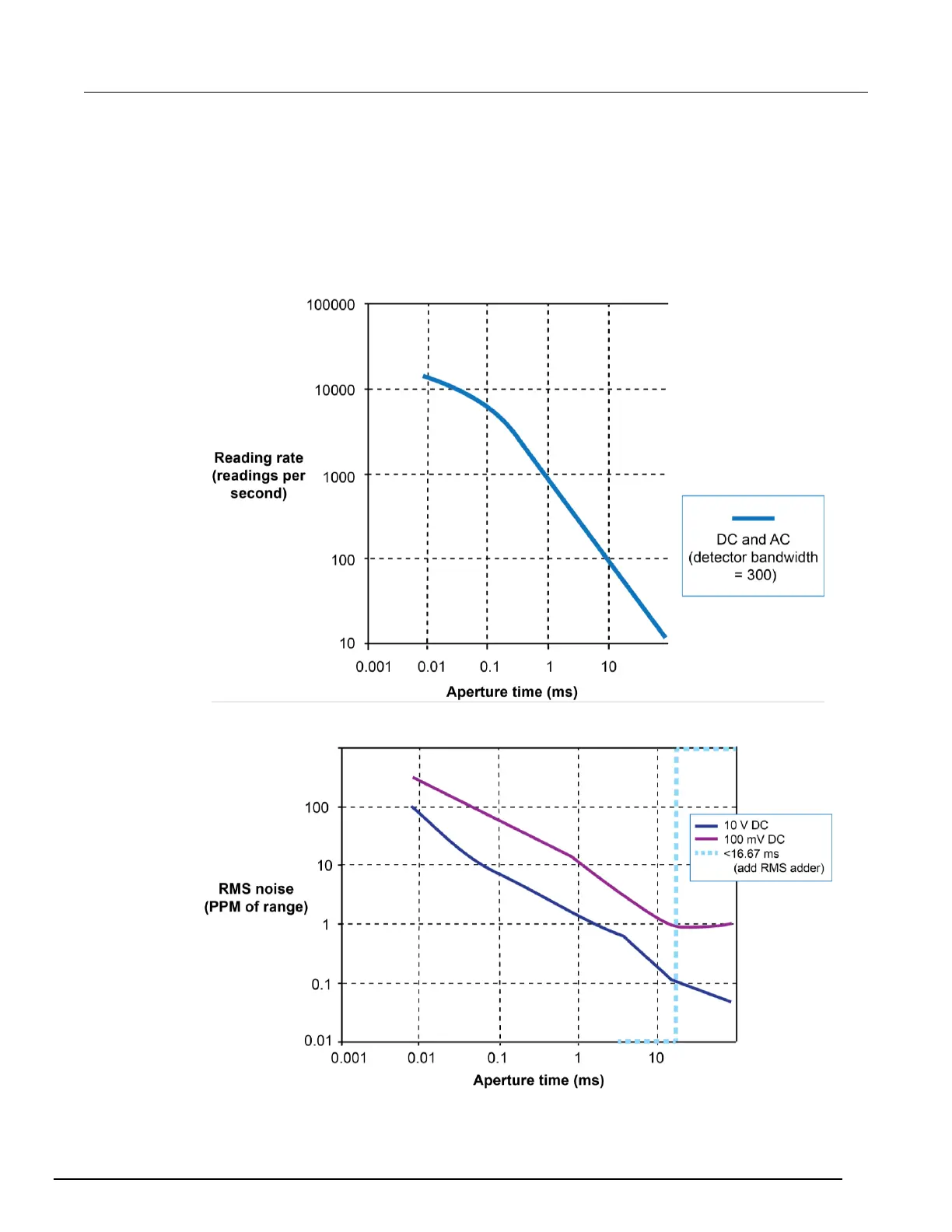
The following two charts represent root-mean-square (RMS) noise versus aperture time (or NPLC)
and reading rate versus aperture time (or NPLC). Refer to these charts when selecting best accuracy
at a given reading rate. Generally, increasing the aperture time reduces the RMS noise. For aperture
times more than 100 ms or 5 power line cycles, thermal offsets can increase the RMS noise.
Figure 67: Reading rate versus aperture time
Figure 68: RMS noise versus aperture time

 Loading...
Loading...