WaveSurfer DSO
WS-OM-E Rev B 95
Threshold levels for rise or fall time can also be selected using absolute or relative settings
(r@level, f@level). If absolute settings are chosen, the rise or fall time is measured as the time
interval separating the two crossing points on a rising or falling edge. But when relative settings
are chosen, the vertical interval spanned between the base and top lines is subdivided into a
percentile scale (base = 0 %, top = 100 %) to determine the vertical position of the crossing
points.
The time interval separating the points on the rising or falling edges is then estimated to yield the
rise or fall time. These results are averaged over the number of transition edges that occur within
the observation window.
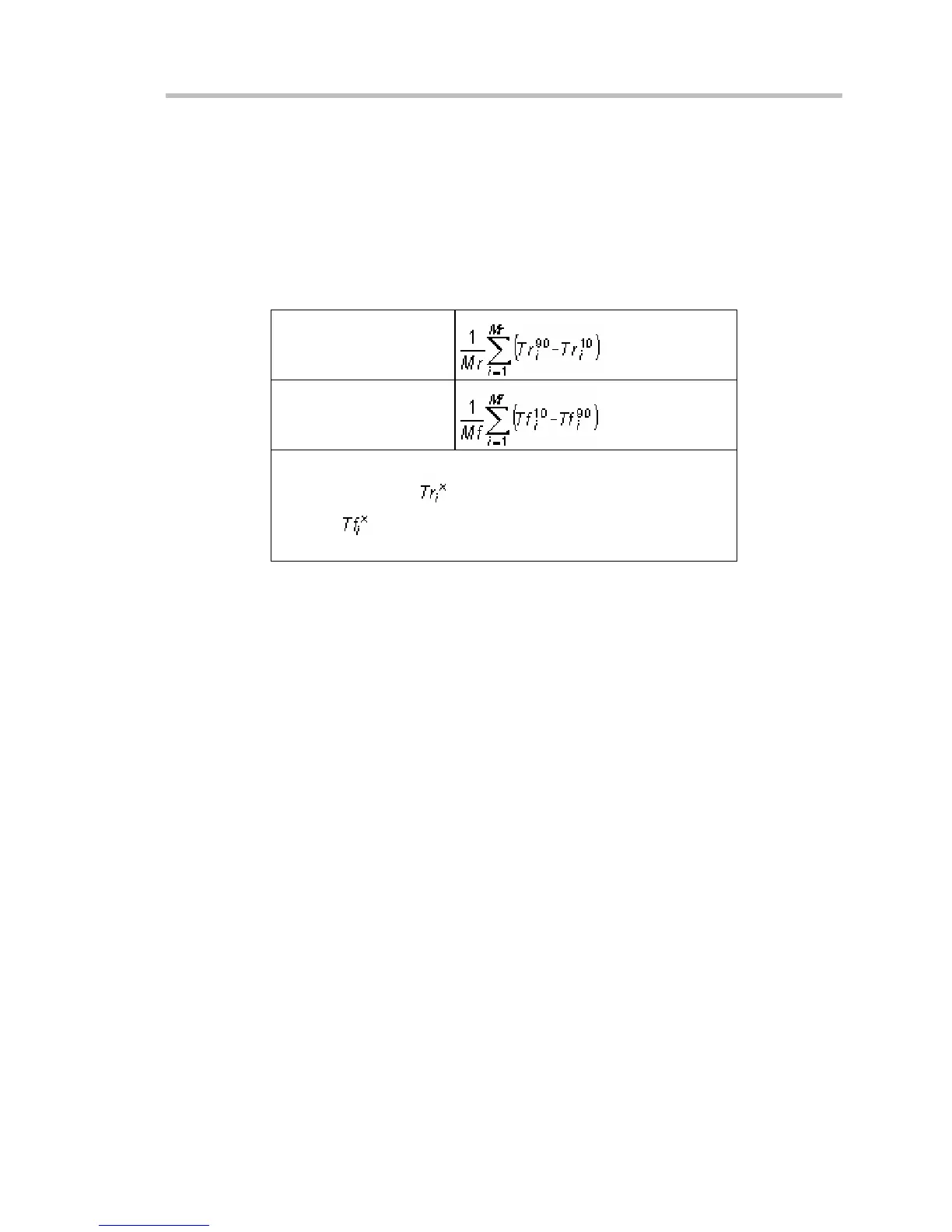
Rising Edge Duration
Falling Edge Duration
Where Mr is the number of leading edges found, Mf the number of
trailing edges found,
the time when rising edge i crosses the
x% level,
and the time when falling edge i crosses the x%
level.
Determining Time Parameters
Time parameter measurements such as width, period and delay are carried out with respect to
the mesial reference level (see Figure 2), located halfway (50%) between the top and base
reference lines.
Time-parameter estimation depends on the number of cycles included within the observation
window. If the number of cycles is not an integer, parameter measurements such as rms or mean
will be biased. However, only the last value is actually displayed, the mean being available when
statistics are enabled. To avoid these bias effects, the instrument uses cyclic parameters,
including crms and cmean, that restrict the calculation to an integer number of cycles.

 Loading...
Loading...