Power Control
M30240 Group
Rev.1.00 Sep 24, 2003 Page 280 of 360
2.12.3 Wait Mode Set-Up
Settings and operation for entering wait mode are described here.
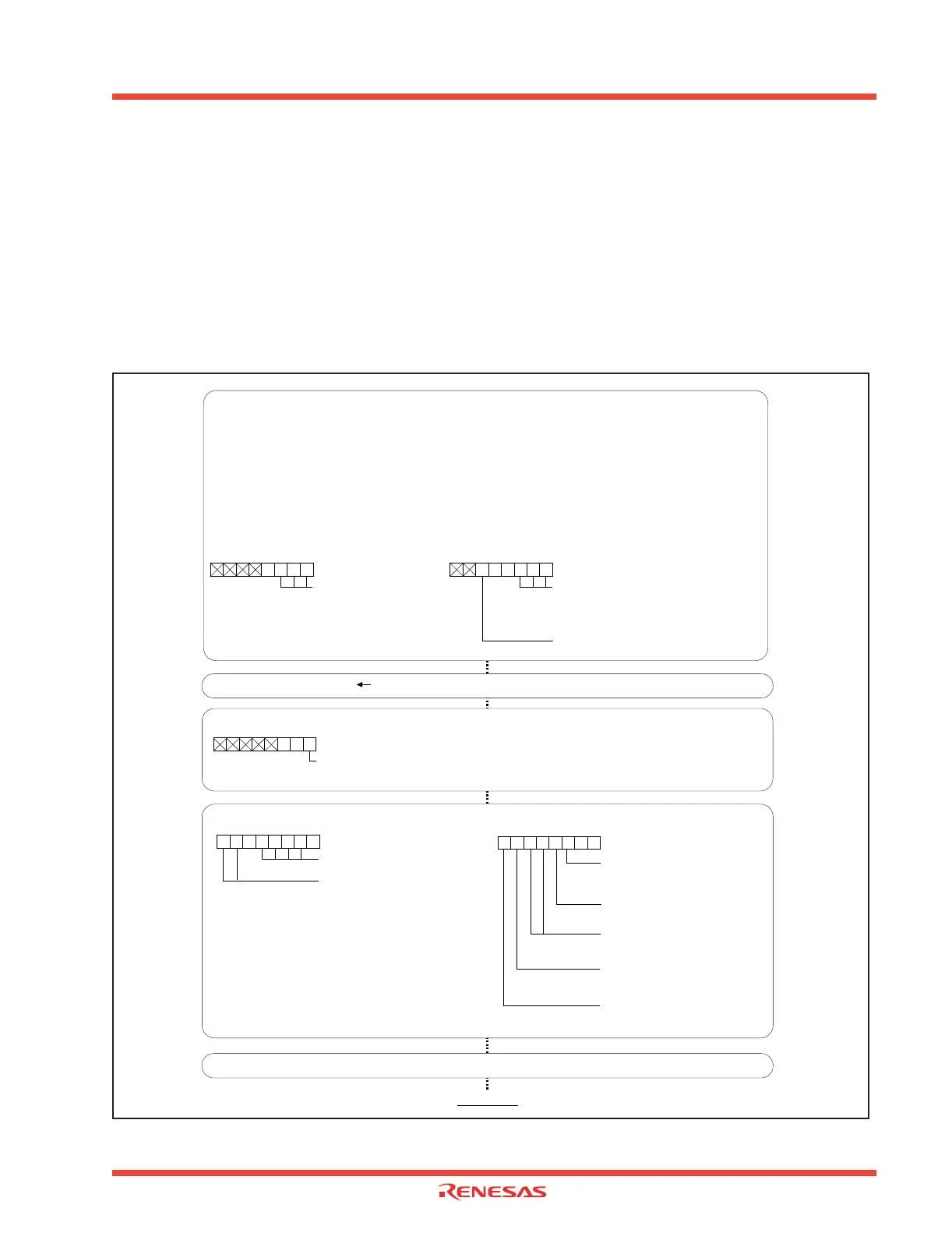
(1) Enable the interrupt used that is to be used for returning from wait mode.
(2) Set the interrupt enable flag (I flag) to “1”.
(3) Clear the protection register.
(4) Change the content of the system clock control register.
(5) Execute the WAIT instruction.
Figure 1.129 shows the set up for the Wait mode.
Figure 2.129: Set-up for Wait mode
Wait mode
(3) Canceling protect
b7 b0
Protect register [Address 000A
16
]
PRCR
1
Enables writing to system clock control registers 0 and 1
(addresses 0006
16
and 0007
16
)
1 : Write-enabled
(5) WAIT instruction
(4) Control of CPU clock
Note: When switching the system clock, it is necessary
to wait for the oscillation to stabilize.
b7 b0
WAIT peripheral function clock stop bit
0 : Do not stop f
1
, f
8
, f
32
in wait mode
1 : Stop f
1
, f
8
, f
32
in wait mode
Reserved bit. Must be set to "0"
Main clock division select bit 0
0 : CM16 and CM17 valid
1 : Division by 8 mode
Reserved bit. Must be set to "0'
System clock control register 0
[Address 0006
16
] CM0
b7 b0
System clock control register 1
[Address 0007
16
] CM10000
Reserved bit
Must be set to “0”
Main clock division select bit
0 0 : No division mode
0 1 : Division by 2 mode
1 0 : Division by 4 mode
1 1 : Division by 16 mode
b7 b6
Make sure that the interrupt priority
level of the interrupt which is used
to cancel the wait mode is higher
than the processor interrupt priority
(IPL) of the routine where the
WAIT instruction is executed.
Interrupt priority level select bit
b7 b0
Make sure that the interrupt priority level of the
interrupt which is used to cancel the wait mode is
higher than the processor interrupt priority (IPL) of
the routine where the WAIT instruction is executed.
Interrupt priority level select bit
b7 b0
0
Reserved bit
Must be set to “0”
(2) Interrupt enable flag (I flag) “1”
Interrupt control register
BCNIC [Address 004A
16
]
KUPIC [Address 004D
16
]
SiTIC(i=0 to 2) [Address 0051
16
, 0053
16
, 004F
16
]
SiRIC(i=0 to 2) [Address 0052
16
, 0054
16
, 0050
16
]
TAiIC(i=0 to 4) [Address 0055
16
to 0059
16
]
TBiIC(i=0 to 1) [Address 005A
16
to 005B
16
]
SUSPIC [Address 0044
16
]
RSMIC [Address 0046
16
]
RSTIC [Address 005C
16
]
USBFIC [Address 005F
16
]
(1) Setting interrupt to cancel stop mode
SOFIC [Address 0047
16
]
INTiIC (i=0 to 1)
[Address 005D
16
to 005E
16
]
0001
Reserved bit.
Must be set to "1"
 Loading...
Loading...











