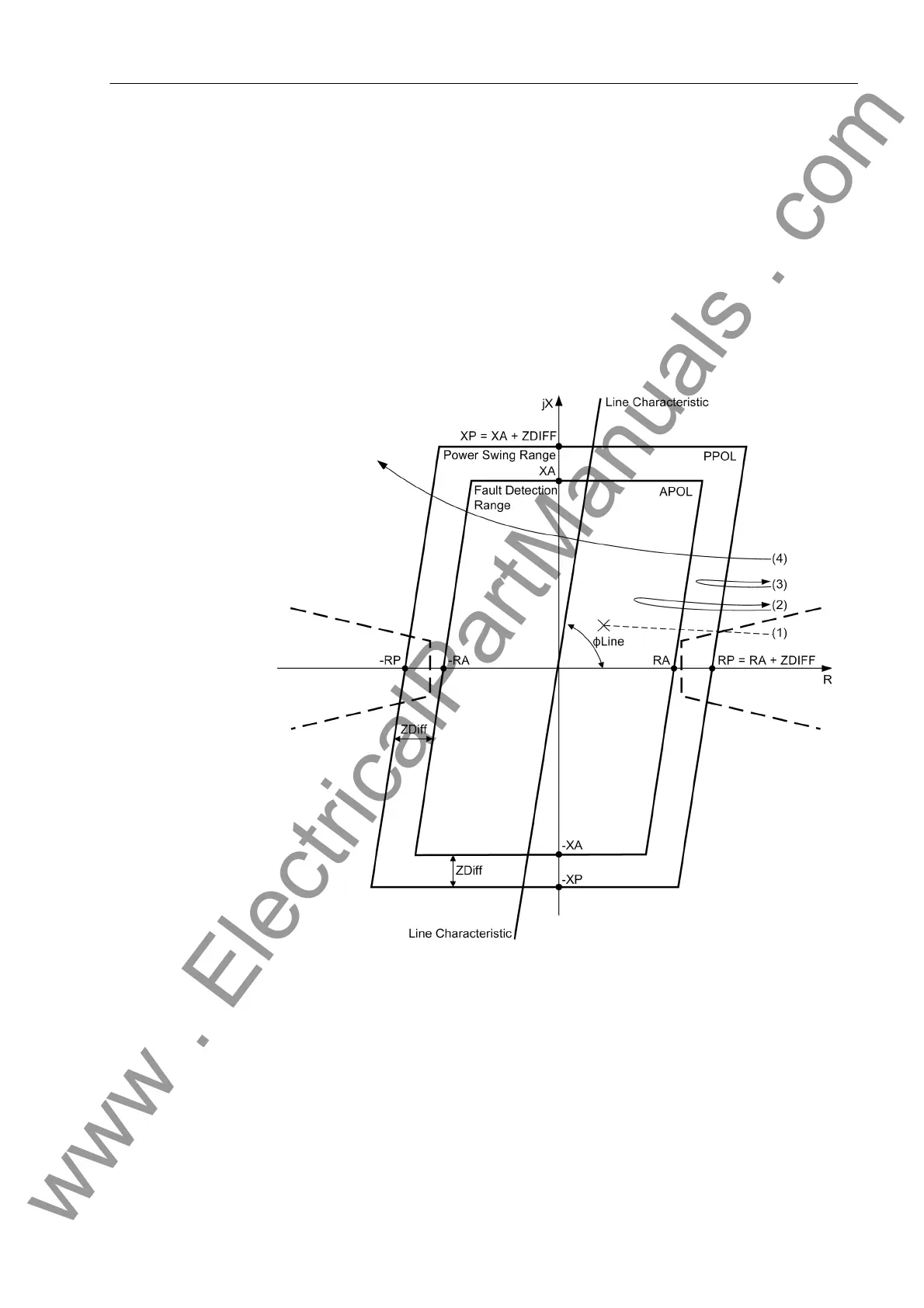
2.6 Power Swing Detection (optional)
169
7SD5 Manual
C53000-G1176-C169-1
tion are met. The fault detection range APOL is made up of the largest set values for
R and X (polygon characteristic) or of the largest set value for ZR (MHO characteristic)
of all the activated zones. The power swing zone has a minimum distance Z
Diff
of 5 Ω
(at I
N
= 1 A) or 1 Ω (at I
N
= 5 A) in all directions from the fault detection zone. In the
event of a short-circuit (1), the impedance vector abruptly changes from the load con-
dition into this fault detection range. However, in the event of a power swing, the ap-
parent impedance vector initially enters the power swing range PPOL and only later
enters the fault detection range APOL (2). It is also possible that a power swing vector
will enter the area of the power swing range and leave it again without coming into
contact with the fault detection range (3). If the vector enters the power swing polygon
and passes through it leaving on the opposite side, then the sections of the network
seen from the relay location have lost synchronism (4): the power transfer is unstable.
Figure 2-61 Pickup characteristic of the power swing detection for a polygon.
The same applies to the MHO characteristic (refer to Figure 2-62). The power swing
circle also has a distance Z
Diff
of 5 Ω (at I
N
= 1 A) or 1 Ω (at I
N
= 5 A) from the largest
zone circle. If one or more reverse zones are set, this impedance distance from all
zones is maintained.
The rate of change of the 3 impedance vectors is monitored in
1
/
4
cycle intervals.
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com
 Loading...
Loading...











