2 Functions
260
7SD5 Manual
C53000-G1176-C169-1
2.11 Direct Local Trip
Any signal from an external protection or monitoring device can be coupled into the
signal processing of the 7SD5 by means of a binary input. This signal may be delayed,
alarmed and routed to one or several output relays.
2.11.1 Functional Description
External Trip of the
Local Circuit
Breaker
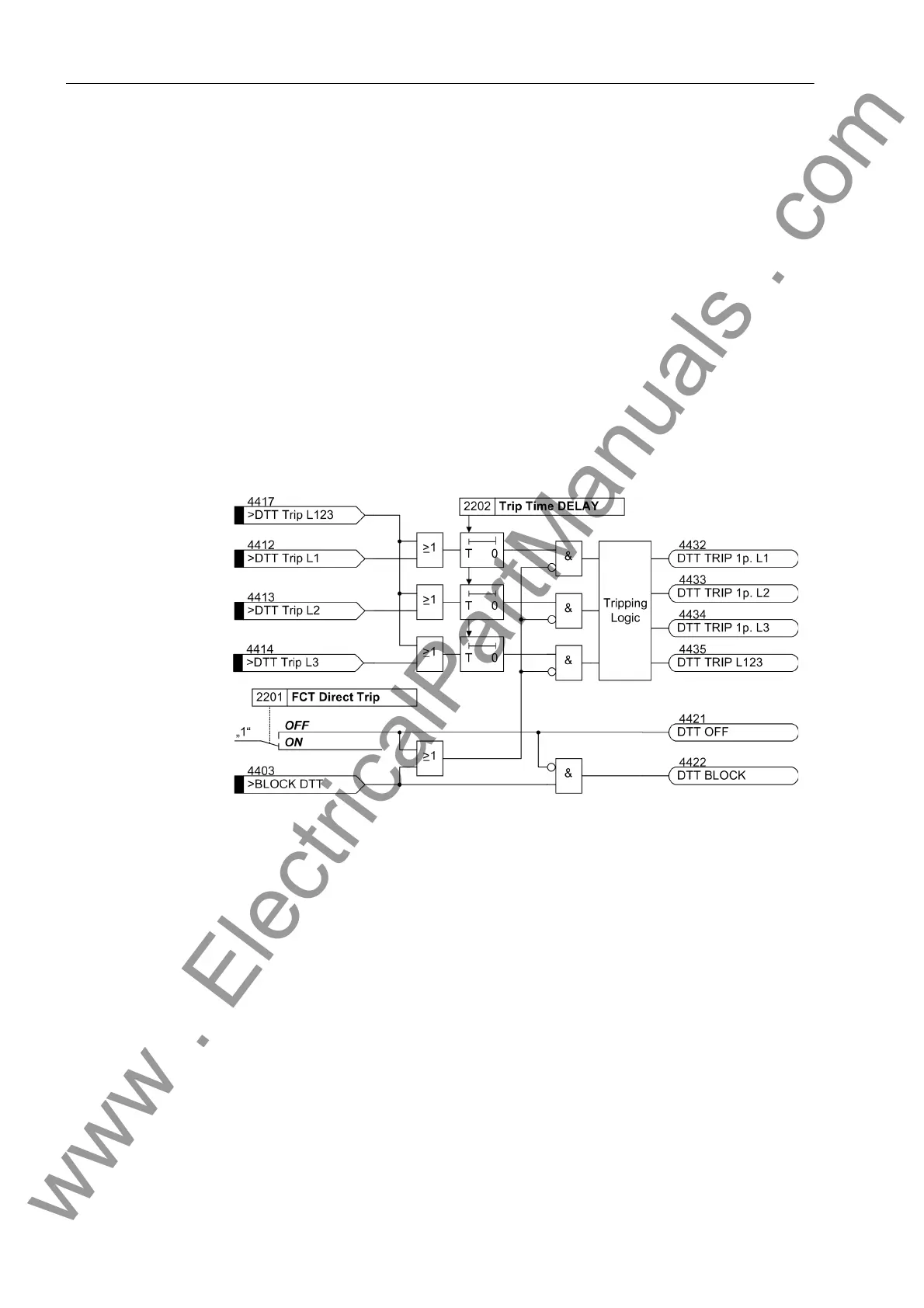
Figure 2-115 shows the logic diagram. If the device and circuit breaker are capable of
single-phase operation, it is also possible to trip single phase. The tripping logic of the
device in this case ensures that the conditions for single-phase tripping are satisfied
(e.g. single-phase tripping enabled, automatic reclosure ready).
The external tripping can be switched on and off with a setting parameter and may be
blocked via binary input.
Figure 2-115 Logic diagram of the local external tripping
Remote Trip of the
Circuit Breaker at
the Opposite Line
End
On conventional transmission paths, one transmission channel per desired transmis-
sion direction is required for remote tripping at the remote end. For example, fibre optic
connections or voice frequency modulated high frequency channels via pilot cables,
power line carrier or microwave radio links can be used for this purpose in the following
ways.
If the trip command of the distance protection is to be transmitted, it is best to use the
integrated teleprotection function for the transmission of the signal as this already in-
corporates the optional extension of the transmitted signal, as described in Section
2.7. Any of the commands can of course be used to trigger the transmitter to initiate
the send signal.
On the receiver side, the local external trip function is used. The receive signal is
routed to a binary input which is assigned to the logical binary input function „>DTT
Trip L123“. If single-pole tripping is desired, you can also use binary inputs „>DTT
Trip L1“, „>DTT Trip L2“ and „>DTT Trip L3“. Figure 2-115 therefore also
applies in this case.
www . ElectricalPartManuals . com
 Loading...
Loading...











