WORKSHOP MANUAL
EDITION
PAGE
119 /
124
Worn armature / brake poles • End of the clutch life • Replace the clutch
Contaminated friction surfaces • Oil seeping on the brake
• Check and repair leaks
• Replace the clutch
Low supply voltage (less than 12 VDC
to the clutch)
• Faulty battery • Replace the battery
• Faulty charging system • Repair or replace.
• Faulty wiring or connections of the
PTO switch
• Check, repair or replace
Inadequate power supply
• Clutch cables broken • Repair or replace.
• Faulty electrical system
• Measure the clutch coil resist-
ance and the voltage supply. If
both are correct, the electrical
system is defective. Repair or
replace.
Overloaded clutch
• Clogged cutting deck • Remove the excess grass
• Deformed shafts. etc. • Replace
Contaminated friction surfaces • Oil seeping on the brake
• Check and repair leaks
• Replace the clutch
The plate hits against the anti-rotational
bracket
• A little bit of noise is normal
• If the noise is excessive, repair
or replace the anti-rotational
device.
Loose clutch on the motor shaft
• Loose assembly (screw not prop-
erly tightened)
• Tighten the mounting screw
according to the specifications
(60-70Nm)
• Fastening screw is too long and
does not allow to axially lock the
clutch
• Use an original replacement
screw
• The mounting washers are too thin
and deformed after tightening the
screw
• Use original spare parts
Broken spring • Loose fitting • Replace the clutch
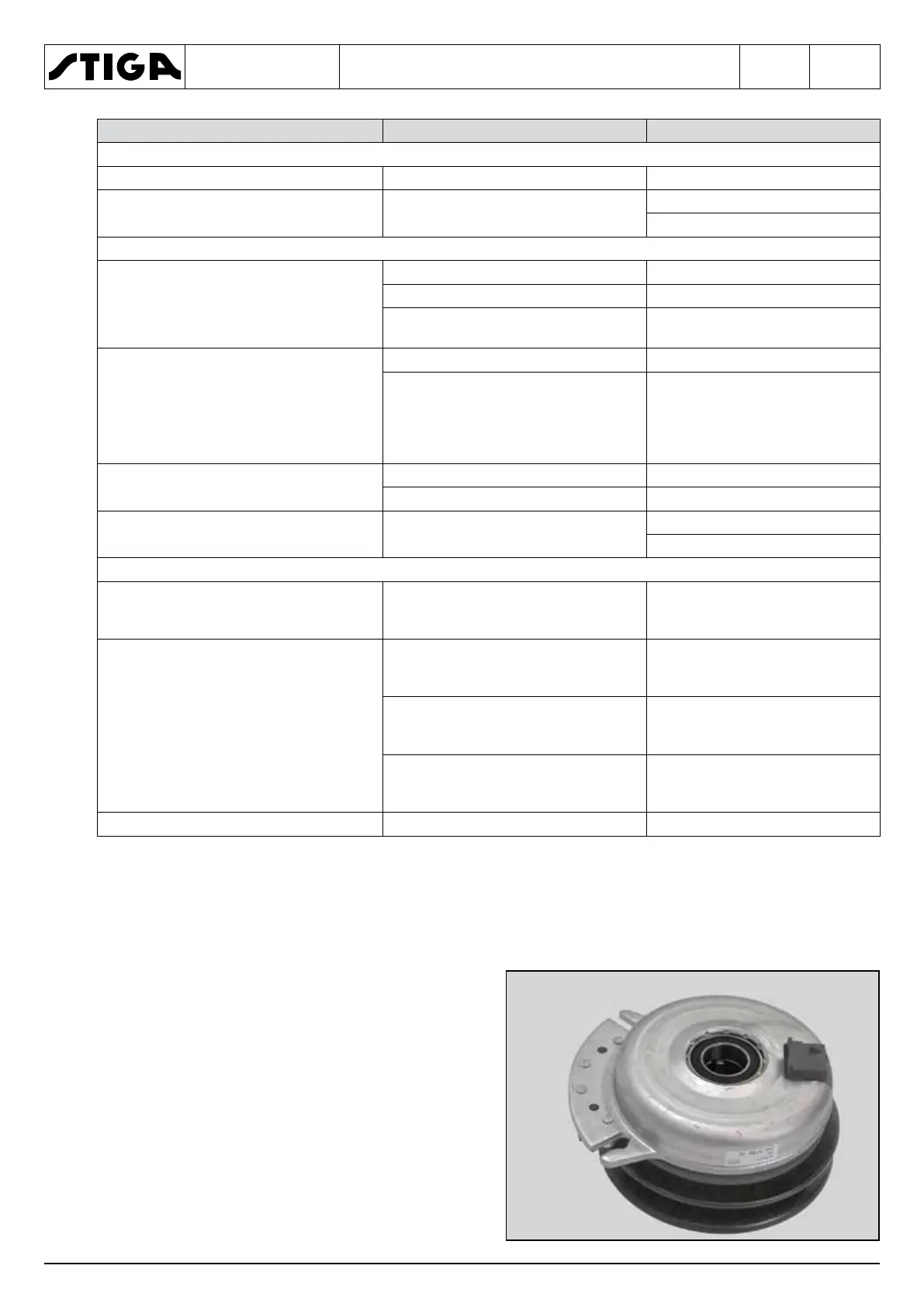
The electromagnetic clutch is used to connect or
disconnect, via a switch, the equipment used on
the machine. In addition, the clutch is designed
to activate a brake on the output shaft, when it is
disengaged.
• The field coil is mounted to a bearing support
and does not rotate.
• The rotor is attached to the power output shaft
and rotates around the field assembly.
• The assembly is connected to the output pulley.
• The armature unit is assembled close to the
brake unit rotor.

 Loading...
Loading...











