Administrator’s Guide for SIP-T2 Series/T19(P) E2/T4 Series/CP860 IP Phones
578
If a domain name is configured for a server, the IP address(es) associated with that
domain name will be resolved through DNS as specified by RFC 3263. The DNS query
involves NAPTR, SRV and A queries, which allows the IP phone to adapt to various
deployment environments. The IP phone performs NAPTR query for the NAPTR pointer
and transport protocol (UDP, TCP and TLS), the SRV query on the record returned from
the NAPTR for the target domain name and the port number, and the A query for the IP
addresses.
If an explicit port (except 0) is specified, A query will be performed only. If a server port
is set to 0 and the transport type is set to DNS-NAPTR, NAPTR and SRV queries will be
tried before falling to A query. If no port is found through the DNS query, 5060 will be
used.
The following details the procedures of DNS query for the IP phone to resolve the
domain name (e.g., yealink.pbx.com) of working server into the IP address, port and
transport protocol.
NAPTR (Naming Authority Pointer)
First, the IP phone sends NAPTR query to get the NAPTR pointer and transport protocol.
Example of NAPTR records:
order pref flags service regexp replacement
IN NAPTR 90 50 "s" "SIP+D2T" "" _sip._tcp.yealink.pbx.com
IN NAPTR 100 50 "s" "SIP+D2U" "" _sip._udp.yealink.pbx.com
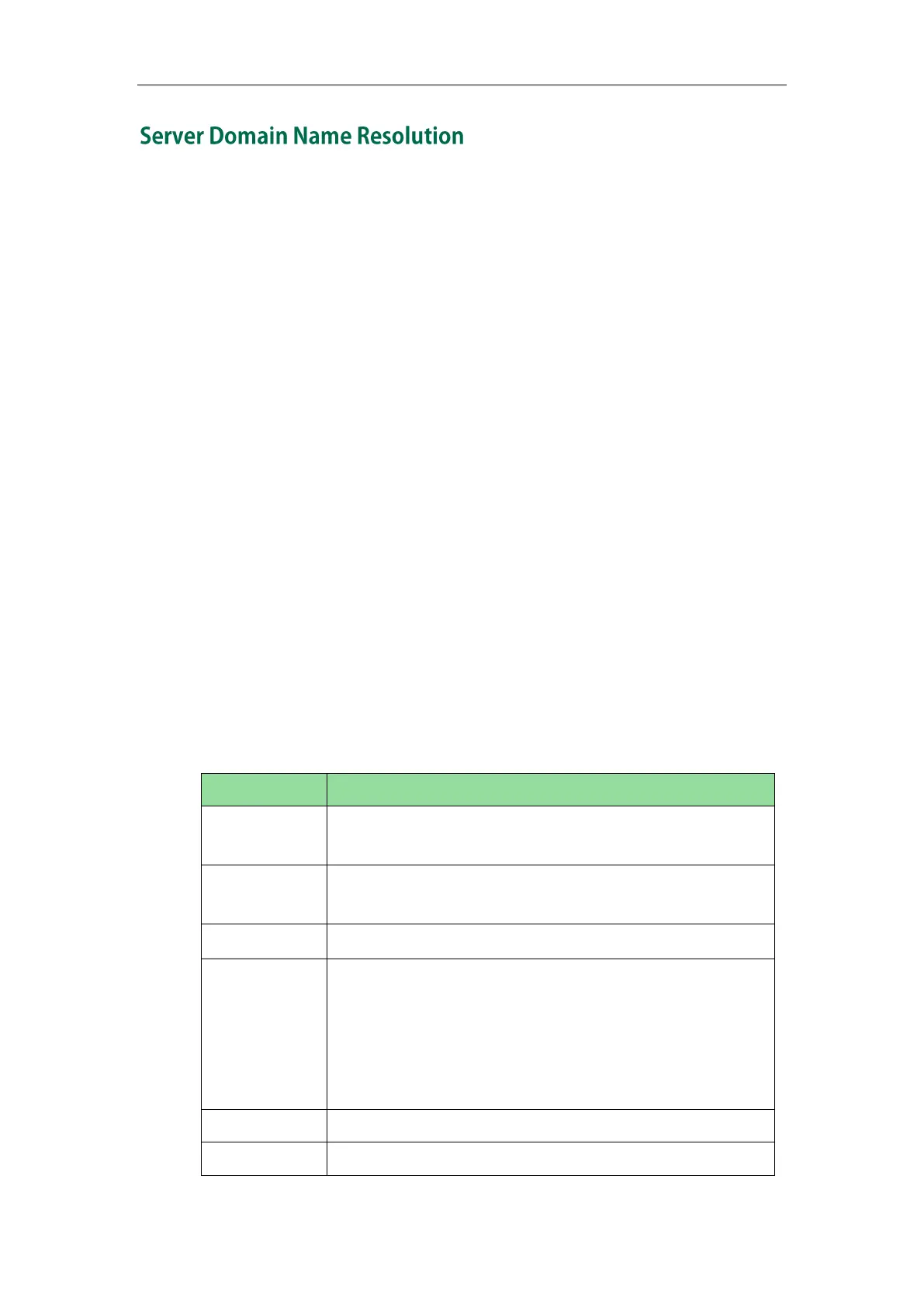
Parameters are explained in the following table:
Specify preferential treatment for the specific record. The order
is from lowest to highest, lower order is more preferred.
Specify the preference for processing multiple NAPTR records
with the same order value. Lower value is more preferred.
The flag “s” means to perform an SRV lookup.
Specify the transport protocols:
SIP+D2U: SIP over UDP
SIP+D2T: SIP over TCP
SIP+D2S: SIP over SCTP
SIPS+D2T: SIPS over TCP
Always empty for SIP services.
Specify a domain name for the next query.

 Loading...
Loading...






