Recommended separation distances
The system is intended for use in the electromagnetic environment in
which radiated RF disturbances are controlled. The customer and/or
user of the system can help prevent electromagnetic interference by
maintaining a minimum distance between portable and mobile RF
communications equipment (transmitters) and the system as
recommended below, according to the maximum power of the
communications equipment.
.
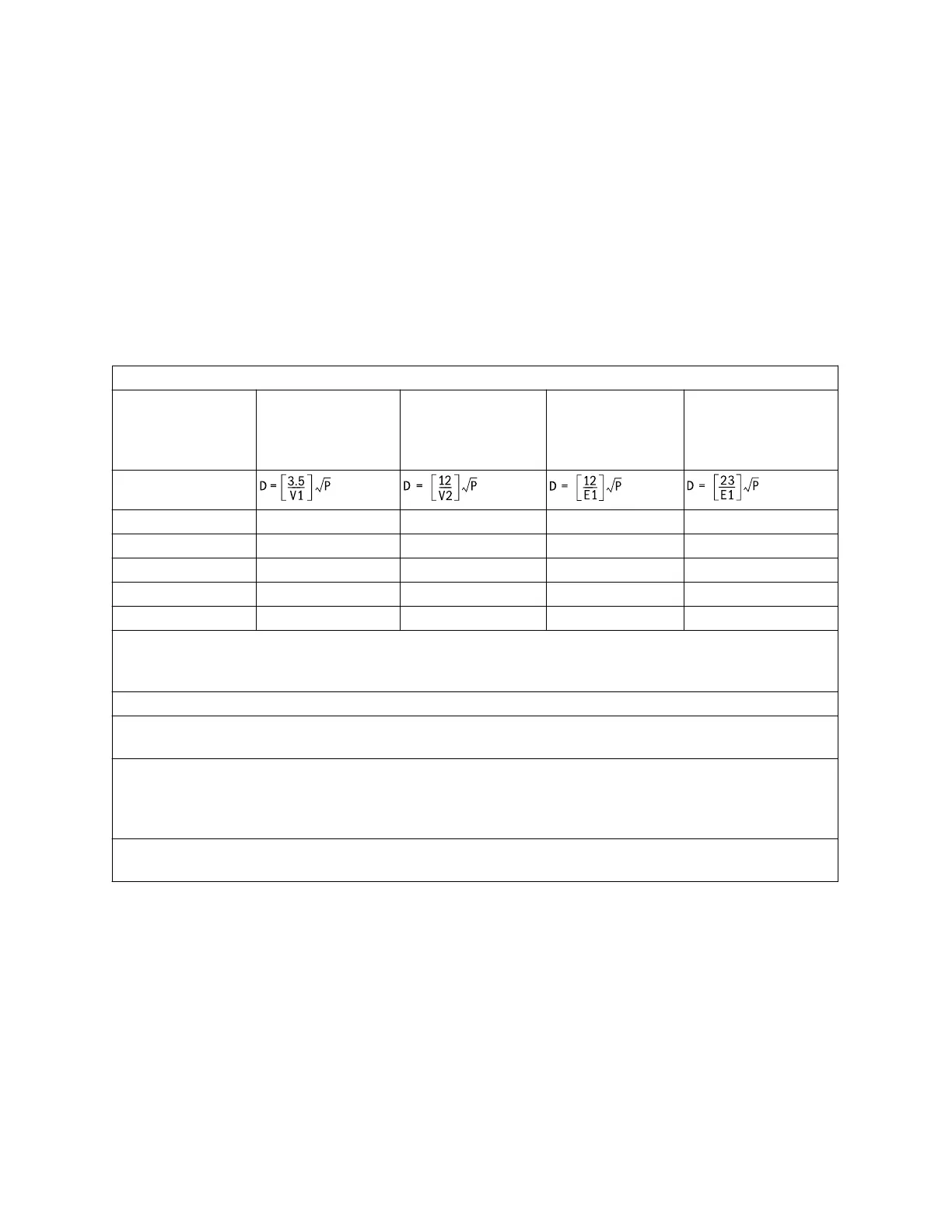
Separation distance in meters (m) according to frequency of the transmitter
Rated maximum
output power of
transmitter watts
(W)
150 kHz to 80 MHz
outside ISM bands
150 kHz to 80 MHz in
ISM bands
80 MHz to 800 MHz 800 MHz to 2.5 GHz
0.01 0.035 0.12 0.12 0.23
0.1 0.11 0.38 0.38 0.73
1 0.35 1.2 1.2 2.3
10 1.1 3.8 3.8 7.3
100 3.5 12 12 23
For transmitters rated at a maximum output power not listed above, the recommended separation distance D in
meters (m) can be determined using the equation applicable to the frequency of the transmitter, where P is the
maximum output power rating of the transmitter in watts (W) according to the transmitter manufacturer.
Note 1: At 80 MHz to 800 MHz the separation distance for the higher frequency range applies.
Note 2: The ISM (Industrial, Scientific, and Medical) bands between 150 kHz and 80 MHz are 6.765 MHz to 6.795
MHz, 13.553 MHz to 13.567 MHz, 26.957 MHz to 27.283 MHz, and 40.66 MHz to 40.70 MHz.
Note 3: An additional factor of 10/3 is used in calculating the recommended separation distance for transmitters in
the ISM frequency bands between 150 kHz and 80 MHz and in the frequency range of 80 MHz to 2.5 GHz to
decrease the likelihood that mobile/portable communications equipment could cause interference if it is inadvertently
brought into patient areas.
Note 4: These guidelines may not apply in all situations. Electromagnetic propagation is affected by absorption and
reflection from structures, objects, and people.
Aisys CS²
11-50 2067226-001
 Loading...
Loading...