226
3.21.2 High-speed I/O refresh function and high-speed buffer transfer
function
The high-speed I/O refresh function refreshes I/O signal data between I/O modules or intelligent function modules and
the CPU module at the specified interrupt intervals.
The high-speed buffer transfer function refreshes data between the buffer memory in intelligent function modules and
the devices in the CPU module at the specified interrupt intervals.
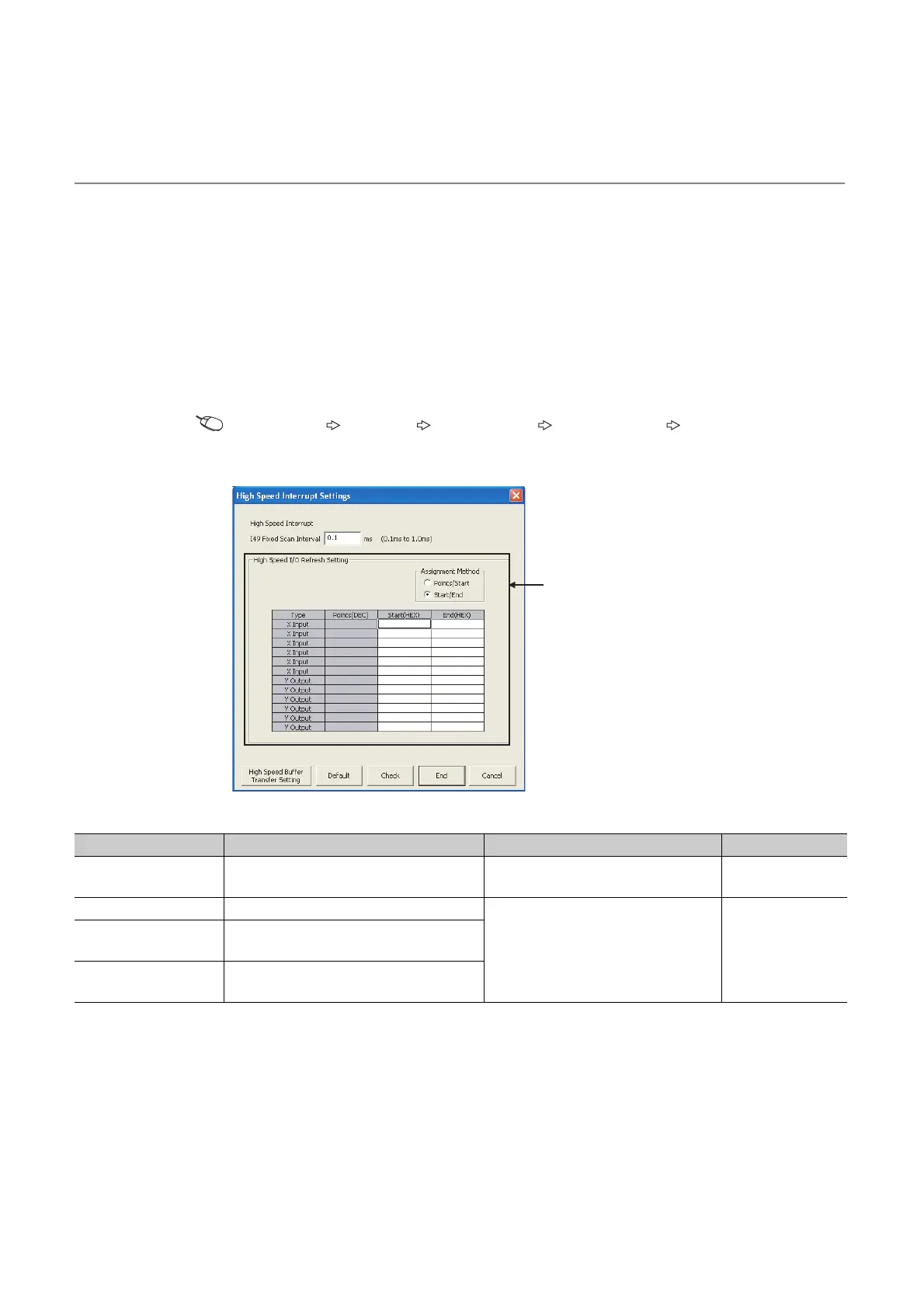
(1) Setting method
(a) High-speed I/O refresh function
Open the High Speed Interrupt Settings window and set the refresh ranges for X/Y.
Project window [Parameter] [PLC Parameter] "PLC System" tab "System Interrupt
Settings", "High Speed Interrupt Settings" button
*1 This applies to both the start device number and the number of bits transferred.
Item Description Restrictions Number of settings
Assignment Method
Select an assignment method (Points/Start or
Start/End).
--
Points(DEC) The number of bits transferred (16 to 4096)
• I/O modules and intelligent function
modules only
• Numbers in the multiples of 16 only
*1
Up to six settings for
X input and Y
output, respectively
Start(HEX)
Start device number (X0 to 0FF0 or Y0 to
0FF0)
End(HEX)
End device number (X000F to 0FFF or
Y000F to 0FFF)
Set the refresh ranges of X/Y.

 Loading...
Loading...











