Web-based Configuration Guide Wi-Fi Network Settings
120
Authentication: Determines whether a user can obtain access, and restricts
unauthorized users.
Authorization: Authorizes services available for authorized users, and controls the
permissions of unauthorized users.
Accounting: Records the usage of network resources by users, and provides a basis for
traffic billing.
The 802.1X feature can be deployed on networks to control user authentication,
authorization, and more.
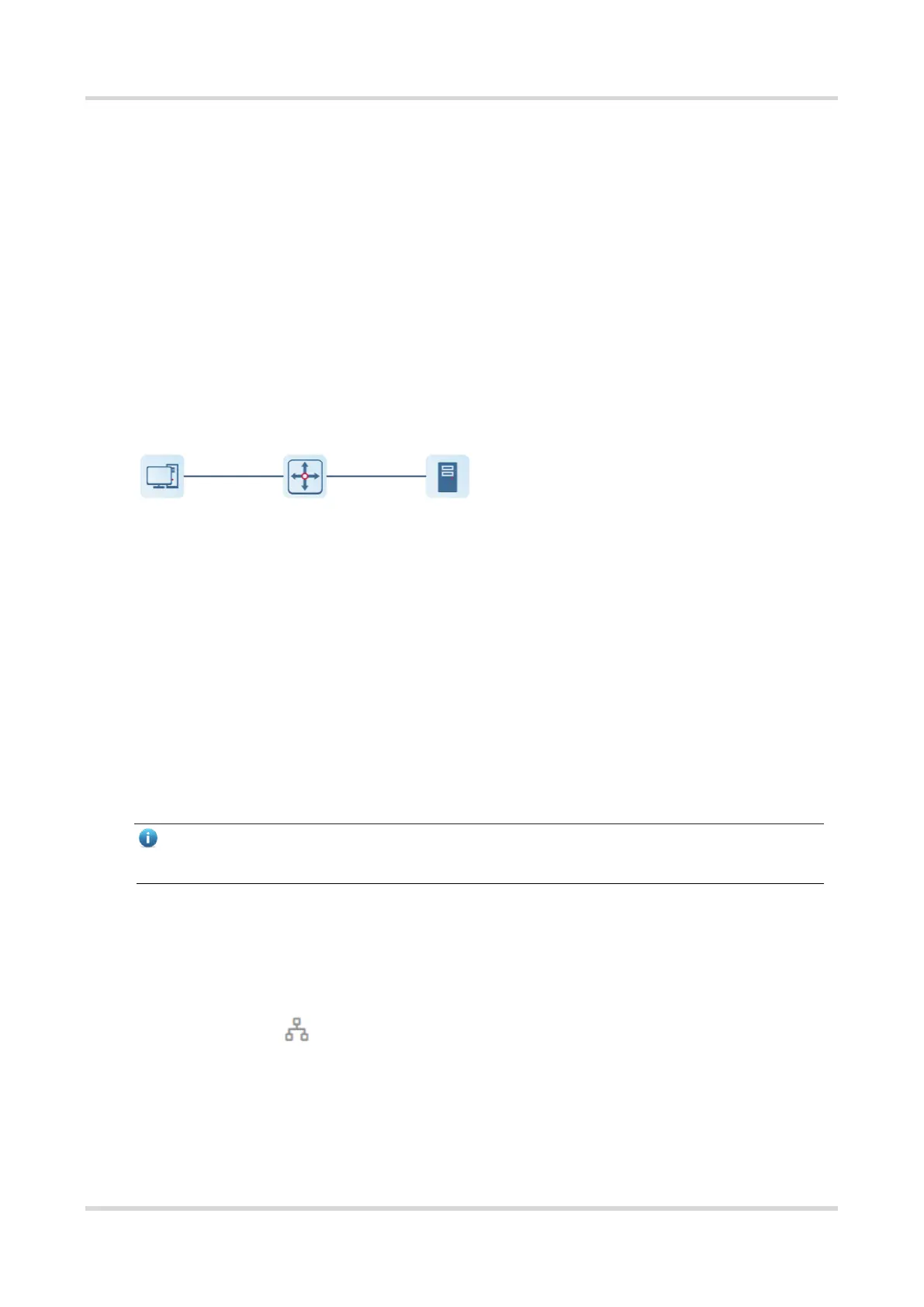
An 802.1X network uses a typical client/server architecture, consisting of three entities:
client, access device, and authentication server. A typical architecture is shown here.
Figure 3-1 Typical Architecture of 802.1X Network
The client is usually an endpoint device which can initiate 802.1X authentication
through the client software. The client must support the Extensible Authentication
Protocol over LANs (EAPoL) on the local area network.
The access device is usually a network device (AP or switching device) that supports
the IEEE 802.1X protocol. It provides an interface for clients to access the local area
network, which can be a physical or a logical interface.
The authentication server can realize user authentication, authorization, and
accounting. Usually a RADIUS server is used as the authentication server.
Note
The RG-RAP APs only support the authentication.
3.22.2 Configuring 802.1X Authentication
(1) To access the configuration page, perform the following operations: In Network
mode, choose Network > 802.1x Authentication.
(2) Click Global 802.1x. A pop-up window is displayed. Click OK.
Client Access Device Authentication Server

 Loading...
Loading...