1-7
Cisco ASA Series CLI Configuration Guide
Chapter 1 Starting Interface Configuration (ASA 5510 and Higher)
Information About Starting ASA 5510 and Higher Interface Configuration
You can configure each physical interface in an EtherChannel to be:
• Active—Sends and receives LACP updates. An active EtherChannel can establish connectivity with
either an active or a passive EtherChannel. You should use the active mode unless you need to
minimize the amount of LACP traffic.
• Passive—Receives LACP updates. A passive EtherChannel can only establish connectivity with an
active EtherChannel.
• On—The EtherChannel is always on, and LACP is not used. An “on” EtherChannel can only
establish a connection with another “on” EtherChannel.
LACP coordinates the automatic addition and deletion of links to the EtherChannel without user
intervention. It also handles misconfigurations and checks that both ends of member interfaces are
connected to the correct channel group. “On” mode cannot use standby interfaces in the channel group
when an interface goes down, and the connectivity and configurations are not checked.
Load Balancing
The ASA distributes packets to the interfaces in the EtherChannel by hashing the source and destination
IP address of the packet (this criteria is configurable; see the “Customizing the EtherChannel” section
on page 1-30). The hash result is a 3-bit value (0 to 7).
The eight hash result values are distributed in a round robin fashion between the channel group
interfaces, starting with the interface with the lowest ID (slot/port). For example, all packets with a hash
result of 0 go to GigabitEthernet 0/0, packets with a hash result of 1 go to GigabitEthernet 0/1, packets
with a hash result of 2 go to GigabitEthernet 0/2, and so on.
Because there are eight hash result values regardless of how many active interfaces are in the
EtherChannel, packets might not be distributed evenly depending on the number of active interfaces.
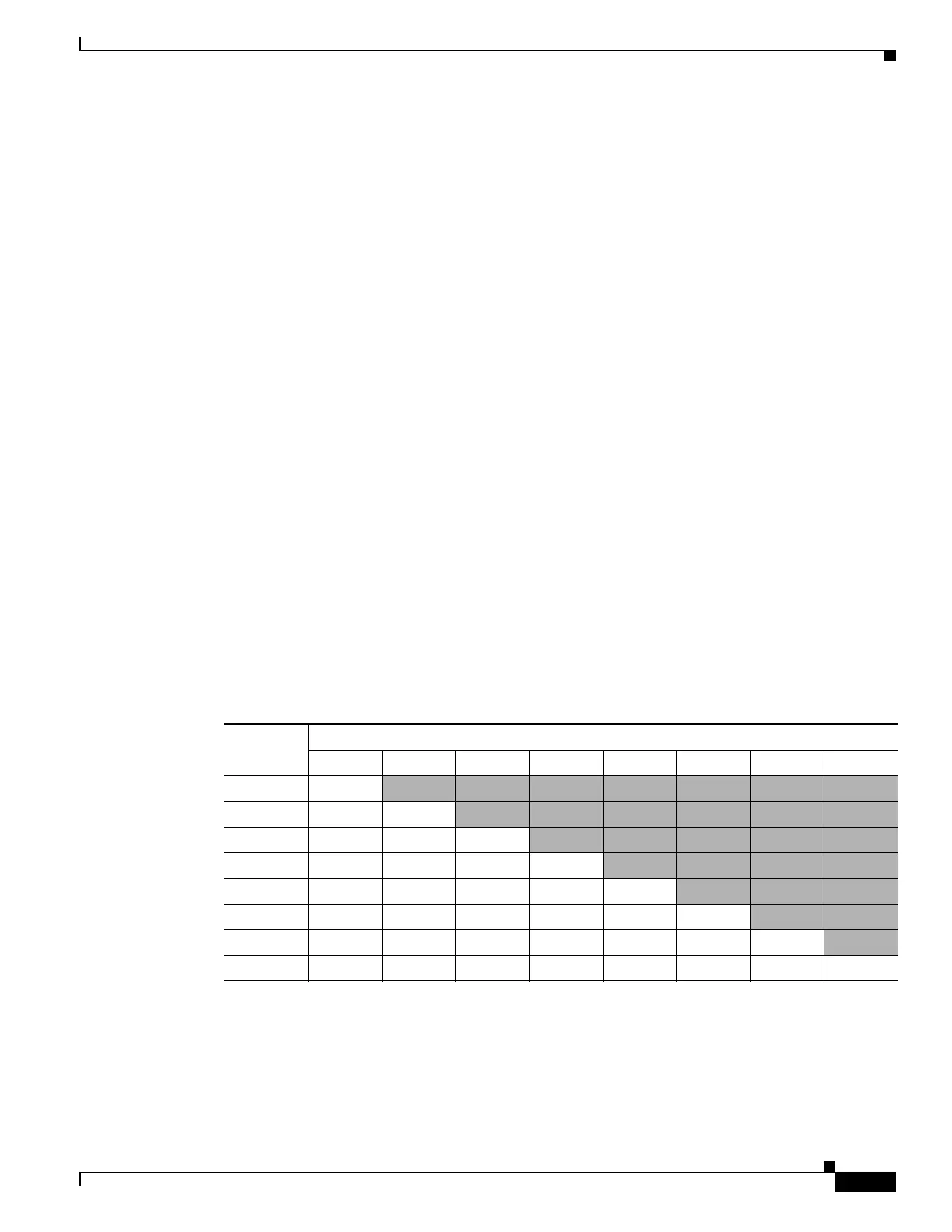
Table 1-2 shows the load balancing amounts per interface for each number of active interfaces. The
active interfaces in bold have even distribution.
If an active interface goes down and is not replaced by a standby interface, then traffic is rebalanced
between the remaining links. The failure is masked from both Spanning Tree at Layer 2 and the routing
table at Layer 3, so the switchover is transparent to other network devices.
Table 1-2 Load Distribution per Interface
# of Active
Interfaces
% Distribution Per Interface
12345678
1 100%
— — — — — — —
2 50% 50%
— — — — — —
3 37.5% 37.5% 25%
— — — — —
4 25% 25% 25% 25%
— — — —
5 25% 25% 25% 12.5% 12.5%
— — —
6 25% 25% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5%
— —
7 25% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5%
—
8 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5% 12.5%
 Loading...
Loading...