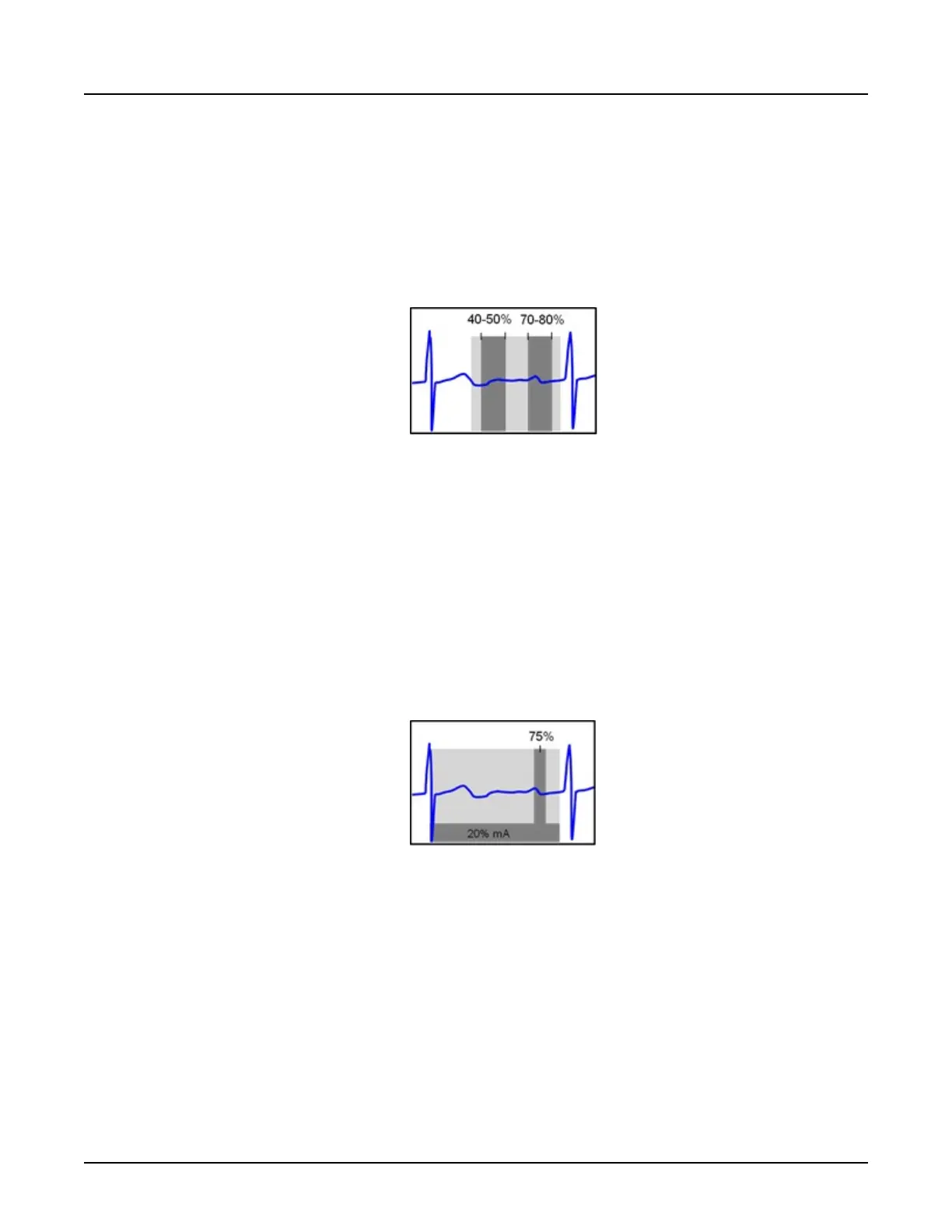
Example 1: Coronary Imaging for 75BPM Patient
Description: Acquire systolic and diastolic phases of the heart cycle
•
Acq. Window Part 1: 70-80% R-to-R, 100% of specified mA (based on Auto mA or
prescribed manual mA)
•
Acq. Window Part 2: 40-50% R-to-R, 100% of specified mA
Illustration 3: Example 1
Example 1, dark grey indicates the approximate range of phases available for image recon at
100% mA; light grey indicates full range of phases available for recon, with increasing image
noise as the recon phase moves further away from the 100% mA ranges at 40-50% and
70-80%
Example 2: Coronary + Functional Imaging for 60BPM Patient:
Description: Acquire low-noise coronary images at diastole and lower dose data for functional
assessment over the full cardiac cycle.
•
Acq. Window Part 1: 75% R-to-R, 100% of specified mA
•
Acq. Window Part 2: 0-95% R-to-R, 20% of specified mA
Illustration 4: Example 2
Example 2, dark grey indicates approximate range of phases available for image recon at 100%
mA and 20% mA
In the event that the patient should experience a premature ventricular contraction (PVC) or
other irregular heart rhythm, there is the possibility that low noise images could become shifted
from the prescribed phases.
5.8 SmartTrack
The purpose of SmartTrack (also known as z-axis tracking, or beam tracking) is to follow the
focal spot so that we can keep the most uniform part of the X-ray beam and the narrowest
possible beam on the detector to reduce dose and still avoid artifacts. The focal spot moves in
the z-axis due to thermal changes in the tube and mechanical forces during gantry rotation. In
order to maintain the narrowest possible beam, the system employs a closed loop control
Revolution CT User Manual
Direction 5480385-1EN, Revision 1
Chapter 21 General Information 651

 Loading...
Loading...