
 Loading...
Loading...
Do you have a question about the Qlogic 8100 Series and is the answer not in the manual?
| Maximum Bandwidth | 10 Gbps |
|---|---|
| Number of Ports | 1 or 2 |
| Data Transfer Rate | 10 Gbps |
| PCI Express Version | 2.0 |
| Series | 8100 |
| Interface Type | PCI Express |
| Supported Protocols | TCP/IP, iSCSI |
| Product Type | Network Adapter |
Overview of the guide's sections and appendices, including Quick Start and detailed sections.
Information regarding the QLogic Software End User License Agreement.
Contact details and resources for technical assistance and product support.
Includes warranty, laser safety, FDA notice, and agency certification compliance.
Details FCC, ICES, CE, VCCI, AS/NZS, and CNS compliance for Class A apparatus.
Lists UL, cUL, and TUV safety compliance certifications for the product.
Four simple steps to install and configure the QLogic Converged Network Adapter.
Information on obtaining drivers, documentation, and using the built-in help system.
Explanation of the adapter's multifunction capabilities combining Fibre Channel and Ethernet.
Description of standard Ethernet enhancements for lossless data transport.
Details on transporting Fibre Channel frames over an Ethernet infrastructure.
Overview of the second-generation adapter's features, performance, and compatibility.
Description of the major hardware components of the QLogic 8100 Series Adapter.
Overview of the adapter's software components, including boot code, drivers, and utilities.
Lists the physical and electrical specifications for the QLogic 8100 Series Adapters.
Introduction to the tools available for managing the QLogic 8100 Series Converged Network Adapter.
Web-based client/server application for centralized management and configuration of adapters.
Agents (qlremote/netqlremote) providing remote management via QConvergeConsole.
Unified CLI for managing Ethernet and Fibre Channel functions on QLogic adapters.
Utilities for adapter maintenance functions, including Fast!UTIL and FlasUTIL.
Details operating system, server, and switch requirements for adapter installation.
Instructions on how to download the necessary adapter drivers from the QLogic website.
Step-by-step guide for physically installing the adapter into the server hardware.
Procedures for installing FCoE and NIC drivers, and management software.
Steps to confirm that the adapter drivers have been installed successfully and are operational.
Procedures for obtaining and updating the adapter firmware/boot code.
Instructions for installing QLogic management utilities like QConvergeConsole.
Details operating system, server, and switch requirements for adapter installation.
Step-by-step guide for physically installing the adapter into the server hardware.
Procedures to verify correct hardware installation and server recognition.
Instructions for installing FCoE and Networking drivers and utilities.
Methods to confirm successful installation and operation of FCoE and networking drivers.
Procedures for downloading and updating the adapter's multi-boot image and firmware.
Steps to install QLogic management tools and Linux utilities for adapter management.
Guide for physically installing the QLogic adapter in VMware ESX/ESXi environments.
Instructions for downloading and installing adapter drivers for VMware ESX/ESXi.
Methods to verify the correct installation and operation of adapter drivers in VMware.
Using console commands to identify adapter driver and firmware versions.
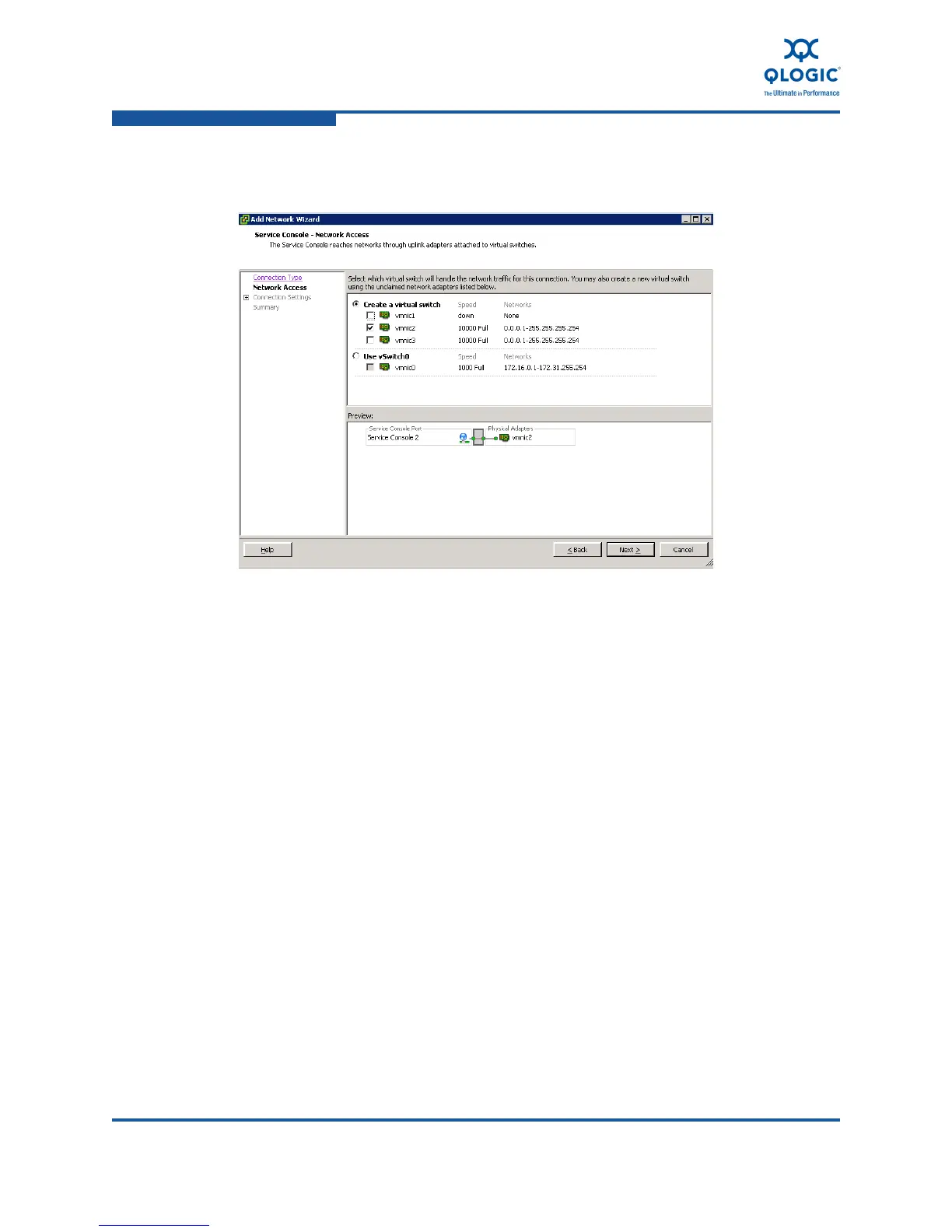
Using the vSphere client to identify adapter configurations on ESX/ESXi host servers.
Steps to configure the adapter's NIC function using the vSphere client interface.
Using esxcfg-module to configure QLogic Fibre Channel and Converged Network Adapter parameters.
Procedure for adding and configuring a hard drive for a virtual machine.
Procedure for adding and configuring a network adapter for a virtual machine.
Enabling N_Port ID Virtualization (NPIV) for Fibre Channel and FCoE SANs.
Process for assigning WWNs to virtual machines for NPIV-ready configurations.
Configuration steps and requirements for booting the operating system from a SAN.
Description of the simplest boot-from-SAN topology with a single adapter port connection.
Configuration for fault tolerance using redundant SAN components and multiple paths.
Steps to configure the adapter for booting the Windows OS from the SAN.
Additional configuration for nonzero LUN installation during RHEL 5 setup.
Methods to configure adapter NIC function using Windows property pages or CLI.
Configuring adapter NIC driver properties via Device Manager.
Using QConvergeConsole CLI for teaming, VLANs, and NIC parameter configuration.
Details on configurable NIC driver parameters, default values, and methods.
Description of hardware offload features for improved performance and reduced CPU usage.
Explanation of Receive Side Scaling (RSS) for efficient packet processing across CPUs.
Details on Header Data Split (HDS) feature for increased system performance.
Combining multiple interfaces for increased bandwidth, load balancing, and high availability.
Configuration of VLAN tagging for network segmentation and traffic management.
Information on PXE boot functionality for network booting from remote servers.
Lists FCoE driver parameters, default values, and configuration methods.
Parameter specifying reduced interrupt operation (ZIO) modes for multiple command completions.
Specifies time interval between response queue update and interrupt generation.
Enables multiple logical ports with unique WWPNs from a single physical adapter port.
QLogic's virtualization capabilities through NPIV for server environments.
Steps to create virtual adapter ports using the QConvergeConsole GUI.
Procedures for deleting virtual adapter ports using QConvergeConsole GUI.
Details available features and limitations when using virtual ports in QConvergeConsole.
Configuring Quality of Service (QoS) using priority or bandwidth methods for virtual ports.
Configuration steps and requirements for booting the operating system from a SAN.
Description of the simplest boot-from-SAN topology with a single adapter port connection.
Configuration for fault tolerance using redundant SAN components and multiple paths.
Steps to configure the adapter for booting the Windows OS from the SAN.
Additional configuration for nonzero LUN installation during RHEL 5 setup.
Lists FCoE driver parameters for Linux, default values, and configuration methods.
Modifying driver parameters using modprobe for nonpersistent and persistent changes.
Using sysfs to display and modify adapter driver parameters.
Using QConvergeConsole and Fast!UTIL to configure FCoE driver parameters.
Listing FCoE driver parameters and their sysfs locations for display.
Steps to identify the SCSI host ID for QLogic adapter PCI devices.
Information on configuring and reconfiguring storage devices in RHEL 5.
Tuning FCoE driver parameters like Operation Mode, Interrupt Delay Timer, and Queue Depth.
Enabling NPIV to allow multiple logical ports from a single physical Fibre Channel adapter port.
QLogic's virtualization capabilities through NPIV for server environments.
Steps to create virtual adapter ports using the sysfs interface.
Procedures for deleting virtual adapter ports using sysfs.
Comparing sysfs parameters to distinguish between virtual and physical ports.
Configuration process and requirements for booting the RHEL 5 OS from SAN.
Description of the simplest boot-from-SAN topology with a single adapter port connection.
Configuration for fault tolerance using redundant SAN components and multiple paths.
Steps to configure the adapter for booting the RHEL 5 OS from the SAN.
Additional configuration for nonzero LUN installation during RHEL 5 setup.
Describes obtaining, installing, and launching QLogic Linux utilities for FCoE configuration.
DOS utility for adapter configuration and Flash programming on BIOS servers.
Utility for updating multi-boot image and NVRAM on BIOS servers.
Utility for accessing and modifying Flash memory on EFI/UEFI systems.
EFI/UEFI configuration utility for displaying and modifying adapter NVRAM.
Description of port LEDs indicating storage and link/Ethernet traffic status.
Steps to enable the FCoE function on the Cisco Nexus switch.
Procedure to create and configure the FCoE VLAN interface.
Configuring the physical Ethernet port for connecting the QLogic adapter.
Steps to create and configure a virtual Fibre Channel interface.
Verifying switch configuration and adapter login status using CLI commands.
Enabling the Ethernet switch service on Brocade DCX/DCX-4S backbone switches.
Creating and configuring the FCoE VLAN interface, using VLAN 1002.
Configuring CEE-MAP for enhanced transmission selection and priority flow control.
Configuring LLDP and DCBX for FCoE traffic on the switch.
Configuring the CEE switch port connected to the QLogic adapter.
Verifying adapter login status and switch configuration via CLI commands.