393
Configuring DHCP
Information About Configuring DHCP
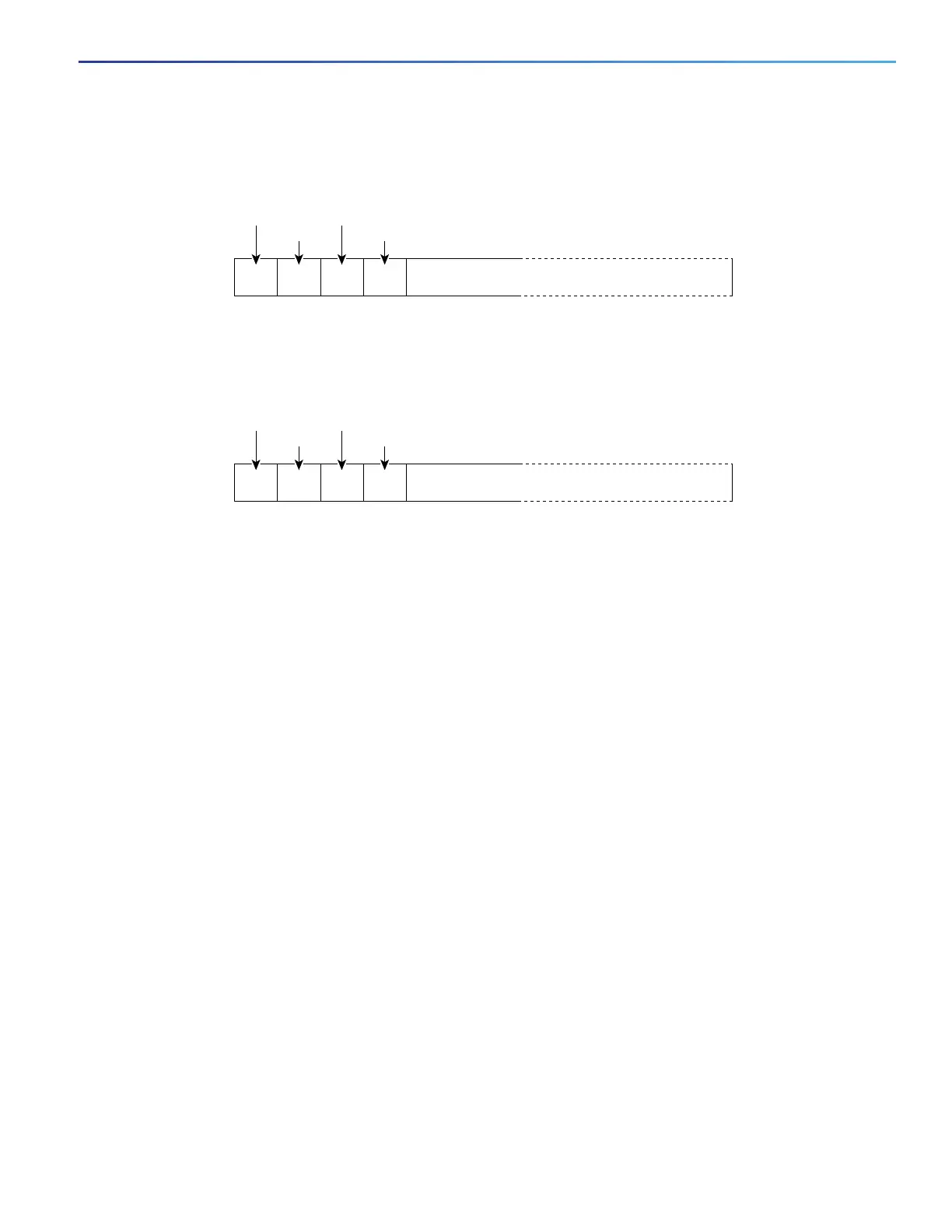
Figure 62 User-Configured Suboption Packet Formats
Cisco IOS DHCP Server Database
During the DHCP-based autoconfiguration process, the designated DHCP server uses the Cisco IOS DHCP server
database. It has IP addresses, address bindings, and configuration parameters, such as the boot file.
An address binding is a mapping between an IP address and a MAC address of a host in the Cisco IOS DHCP server
database. You can manually assign the client IP address, or the DHCP server can allocate an IP address from a DHCP
address pool.
DHCP Snooping Binding Database
When DHCP snooping is enabled, the switch uses the DHCP snooping binding database to store information about
untrusted interfaces. The database can have up to 8192 bindings.
Each database entry (binding) has an IP address, an associated MAC address, the lease time (in hexadecimal format),
the interface to which the binding applies, and the VLAN to which the interface belongs. The database agent stores the
bindings in a file at a configured location. At the end of each entry is a checksum that accounts for all the bytes from the
start of the file through all the bytes associated with the entry. Each entry is 72 bytes, followed by a space and then the
checksum value.
To keep the bindings when the switch reloads, you must use the DHCP snooping database agent. If the agent is disabled,
dynamic ARP inspection or IP source guard is enabled, and the DHCP snooping binding database has dynamic bindings,
the switch loses its connectivity. If the agent is disabled and only DHCP snooping is enabled, the switch does not lose
its connectivity, but DHCP snooping might not prevent DHCP spoofing attacks.
When reloading, the switch reads the binding file to build the DHCP snooping binding database. The switch updates the
file when the database changes.
When a switch learns of new bindings or when it loses bindings, the switch immediately updates the entries in the
database. The switch also updates the entries in the binding file. The frequency at which the file is updated is based on
a configurable delay, and the updates are batched. If the file is not updated in a specified time (set by the write-delay
and abort-timeout values), the update stops.
Length Length
Circuit
ID type
Suboption
type
Circuit ID Suboption Frame Format (for user-configured string):
Remote ID Suboption Frame Format (for user-configured string):
Suboption
type
Length Length
Remote
ID type
145774
N1N+2 1
N1N+2 2
ASCII Circuit ID string
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte N bytes (N = 3-63)
ASCII Remote ID string or hostname
N bytes (N = 1-63)
1 byte
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte1 byte
 Loading...
Loading...











