549
Configuring Network Security with ACLs
Information About Network Security with ACLs
Note: In addition to numbered standard and extended ACLs, you can also create standard and extended named IP ACLs
by using the supported numbers. That is, the name of a standard IP ACL can be 1 to 99; the name of an extended IP ACL
can be 100 to 199. The advantage of using named ACLs instead of numbered lists is that you can delete individual entries
from a named list.
ACL Logging
The switch software can provide logging messages about packets permitted or denied by a standard IP access list. That
is, any packet that matches the ACL causes an informational logging message about the packet to be sent to the console.
The level of messages logged to the console is controlled by the logging console commands controlling the syslog
messages.
Note: Because routing is done in hardware and logging is done in software, if a large number of packets match a permit
or deny ACE containing a log keyword, the software might not be able to match the hardware processing rate, and not
all packets will be logged.
The first packet that triggers the ACL causes a logging message right away, and subsequent packets are collected over
5-minute intervals before they appear or logged. The logging message includes the access list number, whether the
packet was permitted or denied, the source IP address of the packet, and the number of packets from that source
permitted or denied in the prior 5-minute interval.
Numbered Extended ACL
Although standard ACLs use only source addresses for matching, you can use extended ACL source and destination
addresses for matching operations and optional protocol type information for finer granularity of control. When you are
creating ACEs in numbered extended access lists, remember that after you create the ACL, any additions are placed at
the end of the list. You cannot reorder the list or selectively add or remove ACEs from a numbered list.
Some protocols also have specific parameters and keywords that apply to that protocol.
These IP protocols are supported (protocol keywords are in parentheses in bold):
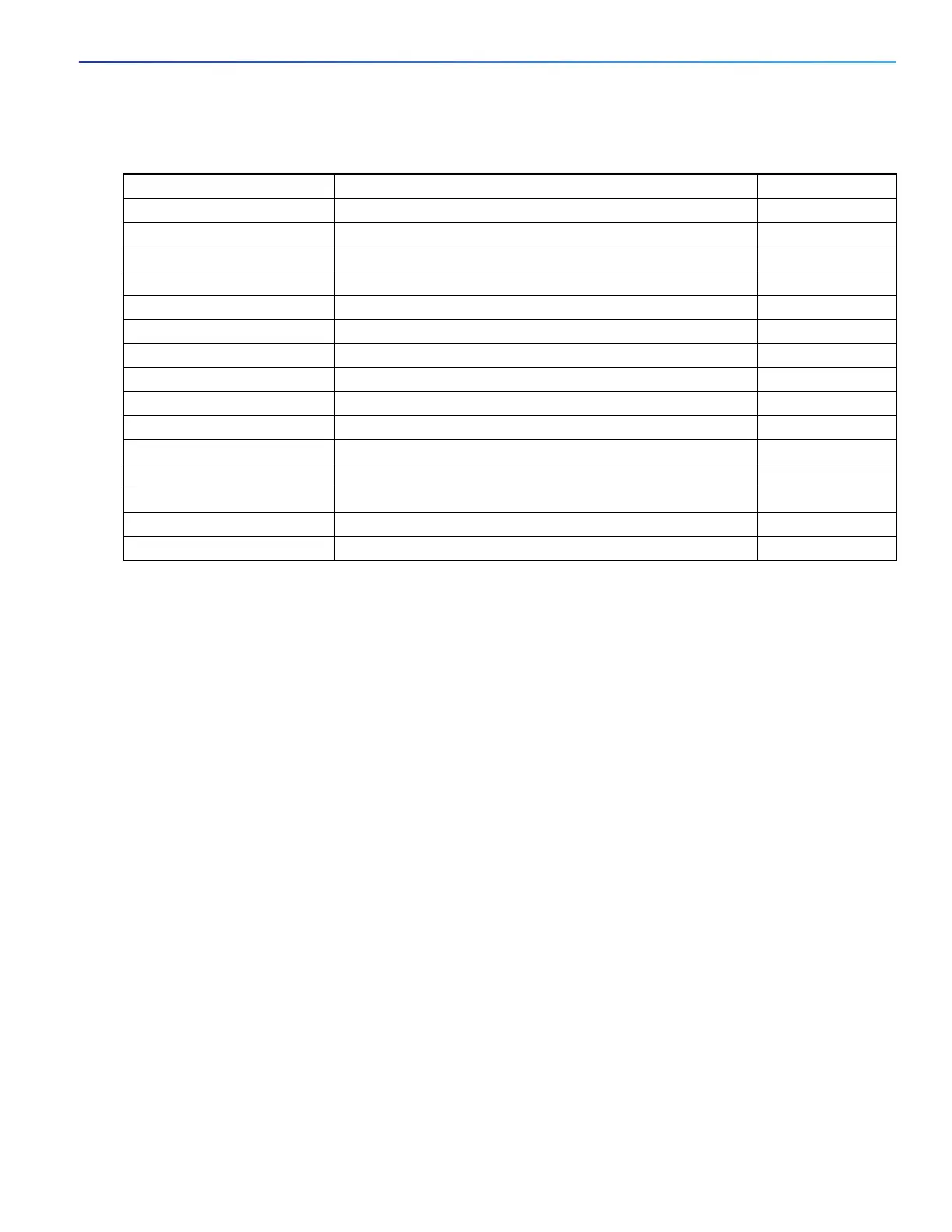
Table 55 Access List Number Support
Access List Number Type Supported
1–99 IP standard access list Yes
100–199 IP extended access list Yes
200–299 Protocol type-code access list No
300–399 DECnet access list No
400–499 XNS standard access list No
500–599 XNS extended access list No
600–699 AppleTalk access list No
700–799 48-bit MAC address access list No
800–899 IPX standard access list No
900–999 IPX extended access list No
1000–1099 IPX SAP access list No
1100–1199 Extended 48-bit MAC address access list No
1200–1299 IPX summary address access list No
1300–1999 IP standard access list (expanded range) Yes
2000–2699 IP extended access list (expanded range) Yes
 Loading...
Loading...











