490
Configuring LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
Information About LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service
Default LLDP Configuration
LLDP, LLDP-MED, and Wired Location Service Configuration Guidelines
If the interface is configured as a tunnel port, LLDP is automatically disabled.
If you first configure a network-policy profile on an interface, you cannot apply the switchport voice vlan command
on the interface. If the switchport voice vlan vlan-id is already configured on an interface, you can apply a
network-policy profile on the interface. This way the interface has the voice or voice-signaling VLAN network-policy
profile applied on the interface.
You cannot configure static secure MAC addresses on an interface that has a network-policy profile.
You cannot configure a network-policy profile on a private-VLAN port.
For wired location to function, you must first enter the ip device tracking global configuration command.
LLDP-MED TLVs
By default, the switch only sends LLDP packets until it receives LLDP-MED packets from the end device. It then sends
LLDP packets with MED TLVs. When the LLDP-MED entry has been aged out, it only sends LLDP packets.
By using the lldp interface configuration command, you can configure the interface not to send the TLVs listed in this
table.
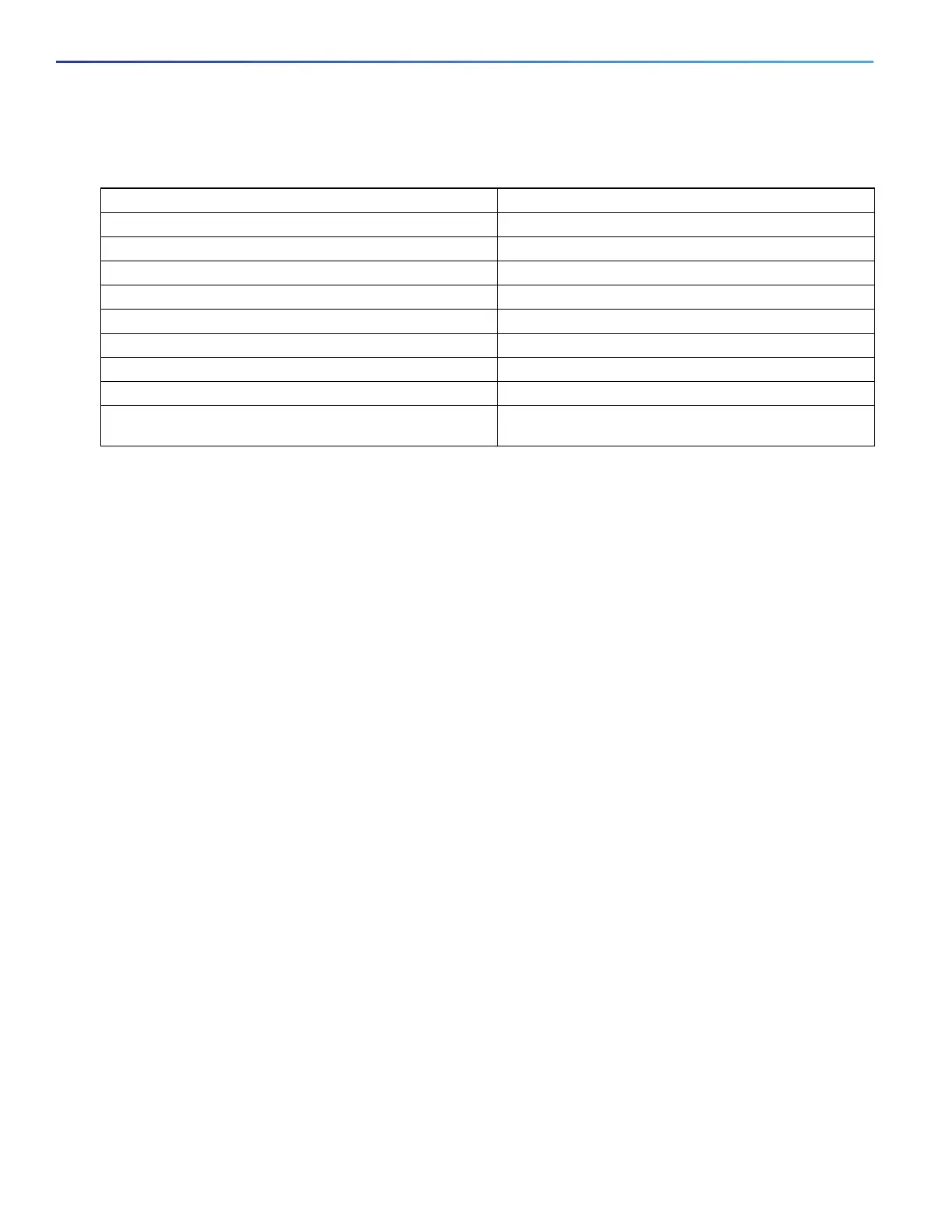
Feature Default Setting
LLDP global state Disabled.
LLDP holdtime (before discarding) 120 seconds.
LLDP timer (packet update frequency) 30 seconds.
LLDP reinitialization delay 2 seconds.
LLDP tlv-select Disabled to send and receive all TLVs.
LLDP interface state Disabled.
LLDP receive Disabled.
LLDP transmit Disabled.
LLDP med-tlv-select Disabled to send all LLDP-MED TLVs. When LLDP is
globally enabled, LLDP-MED-TLV is also enabled.
 Loading...
Loading...











