HUAWEI NetEngine40E Universal ServiceRouter
Hardware Description
2 NE40E-X16 Chassis Overview
Huawei Proprietary and Confidential
Copyright © Huawei Technologies Co., Ltd.
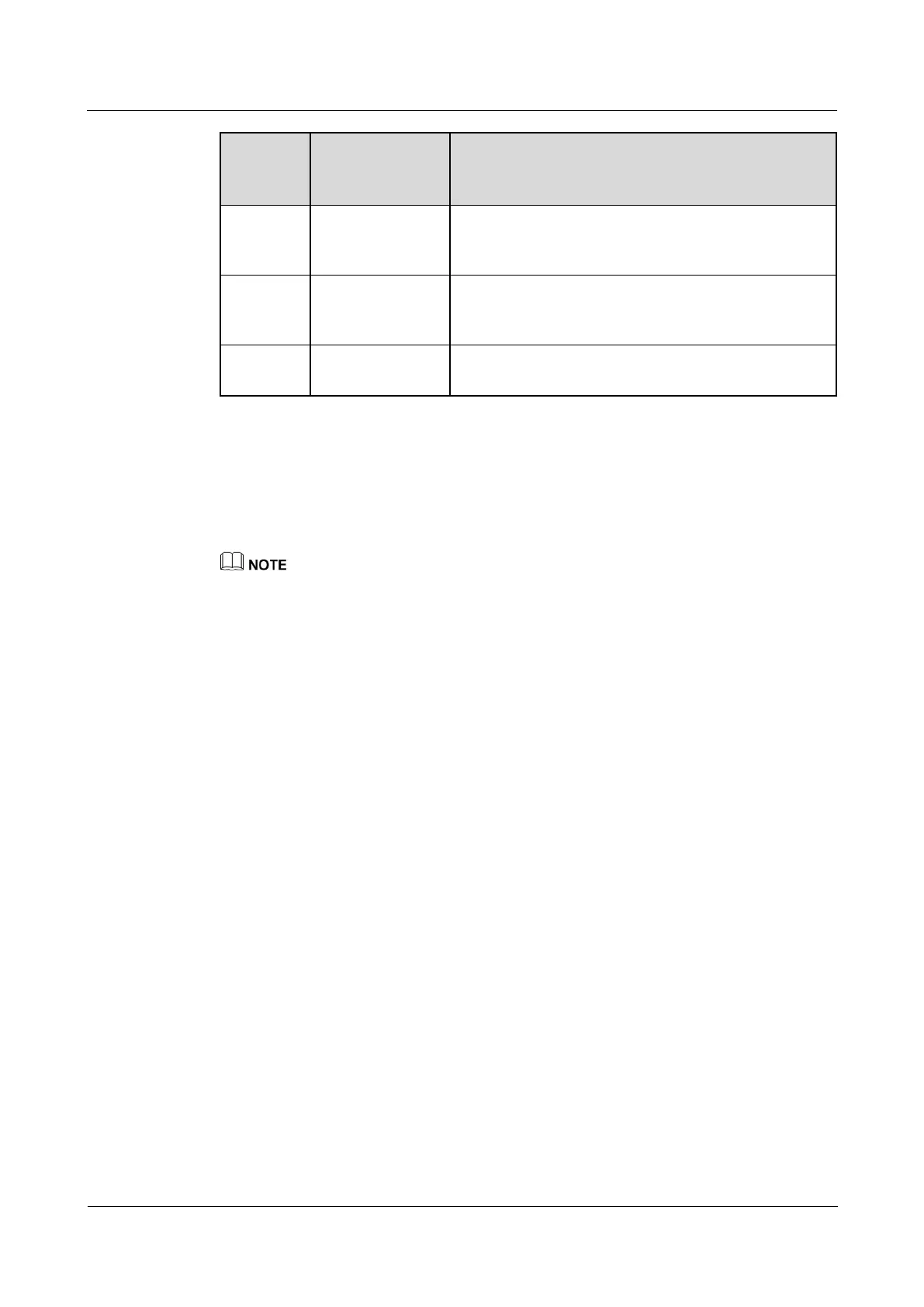
Noise and Dissipation Standards
-5°C-+27°
C ( 23°F -
80.6°F )
When fans rotate at a constantly low speed, the noises
meet the ETSI standard and the fans meet heat
dissipation requirements of a fully configured system.
27°C-50°C
(80.6°F -
122°F)
The fan speed is adjusted smoothly in linear mode,
without a sharp increase in noises.
Fans rotate at high speed to meet heat dissipation
requirements.
2.4 Switching Network
This section describes the functions of the switch fabric unit.
The 200G switch fabric unit cannot be used together with 40G switch fabric unit for long-term
working, and can be used together only for short-term operation during upgrade.
2.4.1 Introduction to the Switching Network
This section describes the principle of the SFU.
The switching network responsible for switching data between LPUs is a key component of
the NE40E. The NE40E uses switching chips developed by Huawei and
Memory-Crossbar-Memory (M-C-M) to provide a three-level switching mode. Level-1 and
level-3 switching use a shared-memory model and are performed on LPUs; level-2 switching
uses a Crossbar model and is performed on SFUs. Figure 2-15 shows the switching network
of the NE40E.
The level-1 switching chip on one LPU is fully connected to the level-2 switching chips on
SFUs. The level-2 switching chips on the SFUs are also fully connected to the level-3
switching chip on another LPU. In addition, the level-2 crossbar switching chips work in load
balancing mode on multiple switching planes. The entire switching network is unblocked. The
following describes how data packets are transmitted across the switching network.
1. Data packets enter an LPU through physical interfaces and are fragmented into cells of a
fixed length. These cells are then sent to the level-1 switching chips. After being
buffered and scheduled, the cells enter the crossbar switching chips on the SFU. The
level-1 switching chip on an LPU is fully connected with all of the level-2 switching
chips. As a result, the same number of cells can be distributed to each level-2 switching
plane. This implements load balancing on switching planes and facilitates fault tolerance.
2. After the cells reach the crossbar switching chips, the crossbar switching chips schedule
the cells to the corresponding outbound interfaces according to the destination interfaces
of the data packets. The cells are then sent to the level-3 switching chips on another LPU.
At this point, the switching of the cells by the level-2 switching chips is completed.

 Loading...
Loading...











