Chapter 5 Understanding Common Devices
5-5
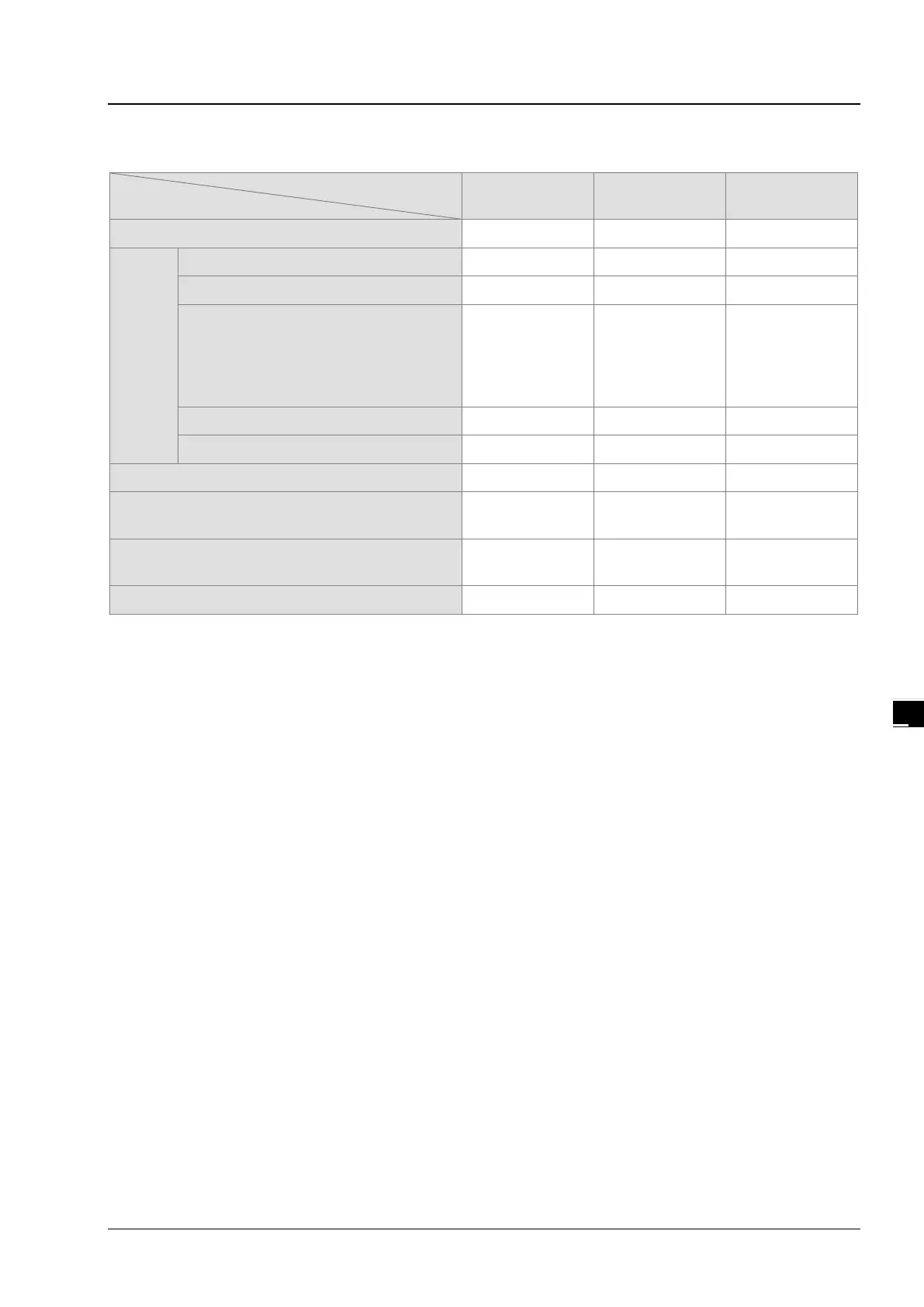
Behavior of non-latched and latched devices
Device type
Non-latched Latched Output relay
→
STOP
↓
RUN
The output relay is cleared.
The state of the output relay is retained.
The state of the output relay returns to
that before the PLC’s stopping.
Retained Retained
The state of the
output relay
returns to that
before the PLC’s
stopping.
The non-latched devices are cleared.
Cleared Retained Cleared
The state of latched devices is retained.
→
SM204 is ON.
(All non-latched devices are cleared.)
Cleared Retained Cleared
SM205 is ON.
(All latched devices are cleared.)
Retained Cleared Retained
0 0 0
5.2.4. Input Relays (X)
The function of the input
The input is connected to the input device (e.g. external devices such as button switches, rotary switches, number
switches, and etc.), and the input signal is read into the PLC. Besides, contact A or contact B of the input can be used
several times in the program, and the ON/OFF state of the input varies with the ON/OFF state of the input device.
The input number (the decimal number)
For the PLC, the input numbers start from X0.0. The number of inputs varies with the number of inputs on the digital
input/output modules, and the inputs are numbered according to the order in which the digital input/output modules are
connected to the CPU module. The maximum number of inputs on the PLC can reach up to 8192, and the range is
between X0.0 and X511.15.
The input type
The inputs are classified into two types.
1. Regenerated input: Before the program is executed, the data is fed into the PLC according to the states of the
inputs which are regenerated. For example, LD X0.0.
2. Direct input: During the execution of the instructions, the data is fed into the PLC according to the states of the
inputs. For example, LD DX0.0.
5.2.5. Output Relays (Y)
The function of the output
The task of the output is sending the ON/OFF signal to drive the load connected to the output. The load can be an
external signal lamp, a digital display, or an electromagnetic valve. There are three types of outputs. They are relays,
 Loading...
Loading...











