AH Motion Controller – Operation Manual
5-12
The hexadecimal number in the PLC is used as;
the constant 16#: It is used as the operand in the applied instruction. For example, MOV 16#1A2B D0
(hexadecimal constant).
5.2.17. Floating-point Numbers (F, DF)
The floating-point numbers are represented by decimal points in ISPSoft. For example, the floating-point number of 500 is
500.0.
Single-precision Floating-point Numbers
The floating-point number is represented by the 32-bit register. The representation adopts the IEEE754 standard, and
the format is as follows.
S
Exponent
Mantissa
8-bit 23-bit
b
31
b
0
Sign bit
0: Positive
1: Negative
Equation:
The single-precision floating-point numbers range from ±2
-126
to ±2
+128
, and correspond to the range from
±1.1755×10
-38
to ±3.4028×10
+38
.
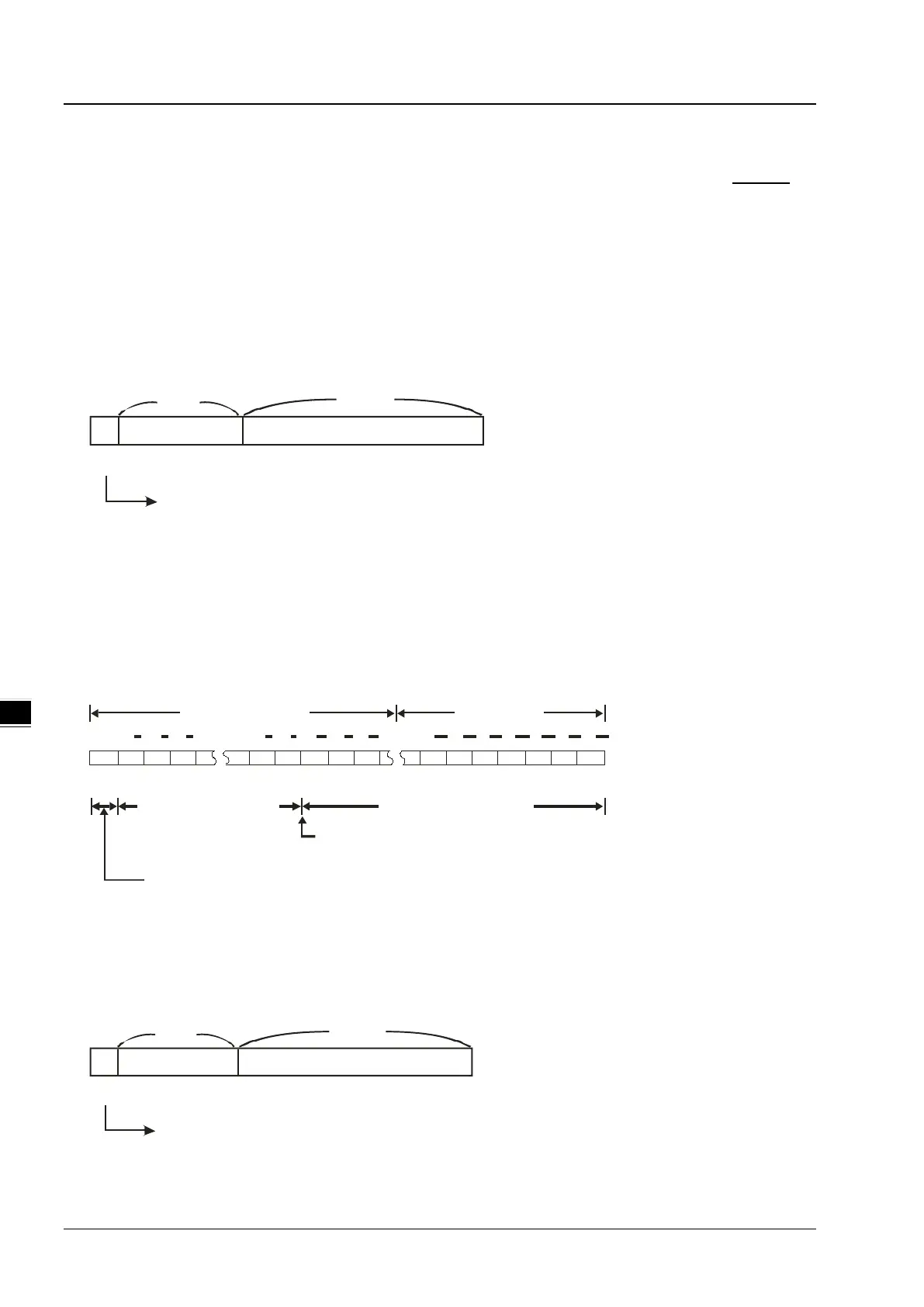
The AH500 series PLC uses two consecutive registers to form a 32-bit floating-point number. Take (D1, D0) for
example.
S E7 E6 E5 E1 E0 A22 A21 A20 A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
b0b1b2b3b4b5b6b20b21b22b23b24b28b29b30b31
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 22 2
D1(b15~b0) D0(b15~b0)
Exponent (8 bits)
Mantissa (23bits)
Mantissa sign bit (0: Positive; 1: Negative)
When b0~b31 are zeros, the content is zero.
The position where the decimal point is hidden
Double-precision Floating-point Numbers
The floating-point number is represented by the 64-bit register. The representation adopts the IEEE754 standard, and
the format is as follows.
S
Exponent
Mantissa
11-bit
52-bit
b
63
b
0
Sign bit
0: Positive
1: Negative
 Loading...
Loading...











