9 TIME SYNCHRONISATION
In modern protection schemes it is necessary to synchronise the IED's real time clock so that events from different
devices can be time stamped and placed in chronological or
der. This is achieved in various ways depending on the
chosen options and communication protocols.
● Using the IRIG-B input (if fitted)
● Using the SNTP time protocol (for Ethernet IEC 61850 versions + DNP3 OE)
● By using the time synchronisation functionality inherent in the data protocols
9.1 DEMODULATED IRIG-B
IRIG stands for Inter Range Instrumentation Group, which is a standards body responsible for standardising
different time code formats. Ther
e are several different formats starting with IRIG-A, followed by IRIG-B and so on.
The letter after the "IRIG" specifies the resolution of the time signal in pulses per second (PPS). IRIG-B, the one which
we use has a resolution of 100 PPS. IRIG-B is used when accurate time-stamping is required.
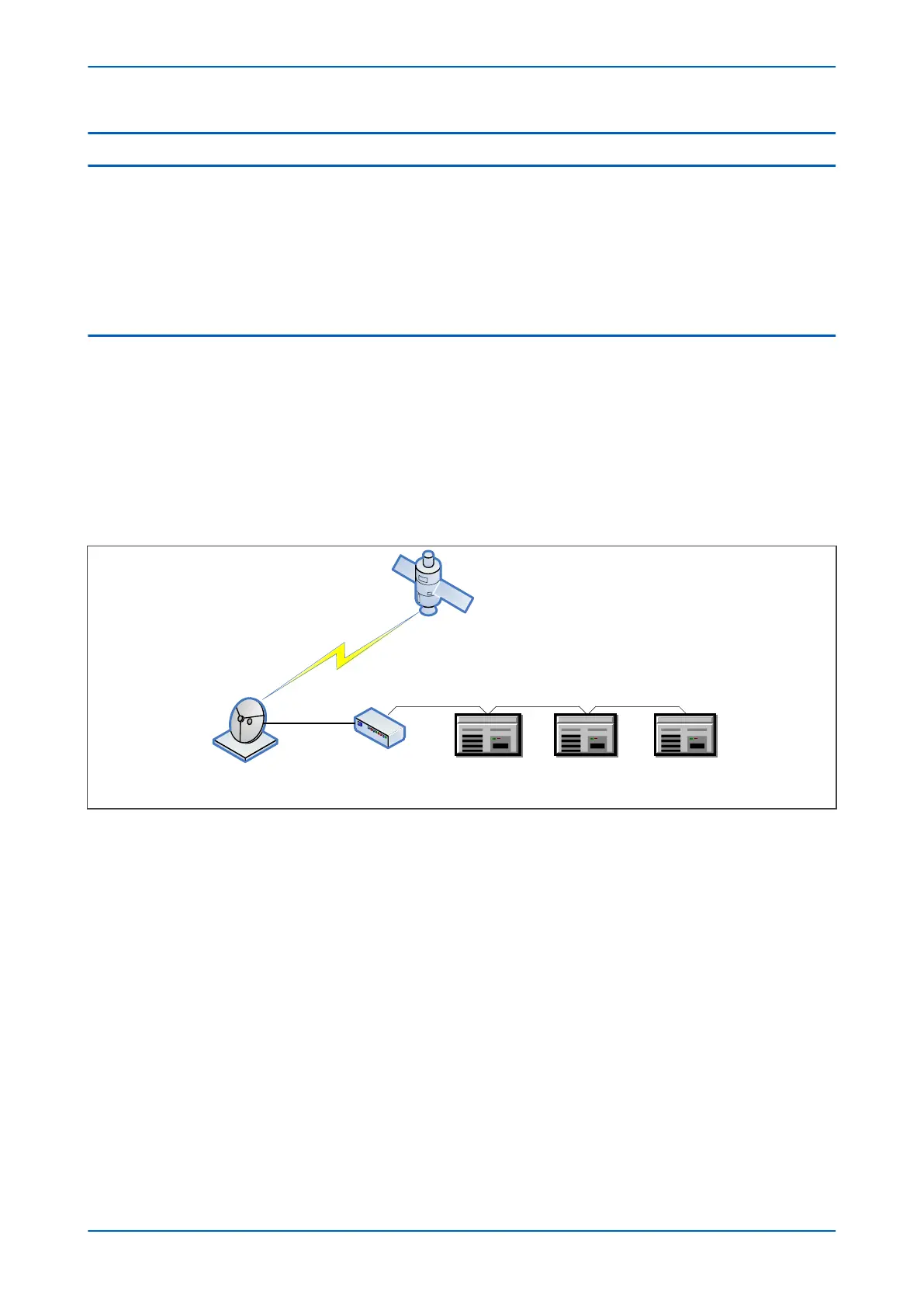
The following diagram shows a typical GPS time-synchronised substation application. The satellite RF signal is
picked up by a satellite dish and passed on to receiver. The receiver receives the signal and converts it into time
signal suitable for the substation network. IEDs in the substation use this signal to govern their internal clocks and
event recorders.
IED IED IED
ReceiverSatellite dish
GPS time signal GPS satellite
V0
1040
IRIG-B
Figure 209: GPS Satellite timing signal
The IRIG-B time code signal is a sequence of one second time frames. Each frame is split up into ten 100 mS slots
as follows:
● Time-slot 1: Seconds
● Time-slot 2: Minutes
● Time-slot 3: Hour
s
● Time-slot 4: Days
● Time-slot 5 and 6: Contr
ol functions
● Time-slots 7 to 10: Straight binary time of day
The first four time-slots define the time in BCD (Binary Coded Decimal). Time-slots 5 and 6 are used for control
functions, which control deletion commands and allow different data groupings within the synchronisation strings.
Time-slots 7-10 define the time in SBS (Straight Binary Second of day).
Chapter 18 - Communications P14x
452 P14xEd1-TM-EN-1

 Loading...
Loading...