Goodrive350 series high-performance multi-function inverter Chapter 9
-261-
of function code address data, the code is generated as follows:
0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 (03H in the hexadecimal form)
For a normal response, the same code is returned.
For an exception response, the following code is returned:
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 (83H in the hexadecimal form)
In addition to the modification of the code, the slave returns a byte of exception code that describes
the cause of the exception. After receiving the exception response, the typical processing of the
master device is to transmit the request message again or modify the command based on the fault
information.
For example, to set the "Running command channel" (P00.01, the parameter address is 0001H) of
the inverter whose address is 01H to 03, the command is as follows:
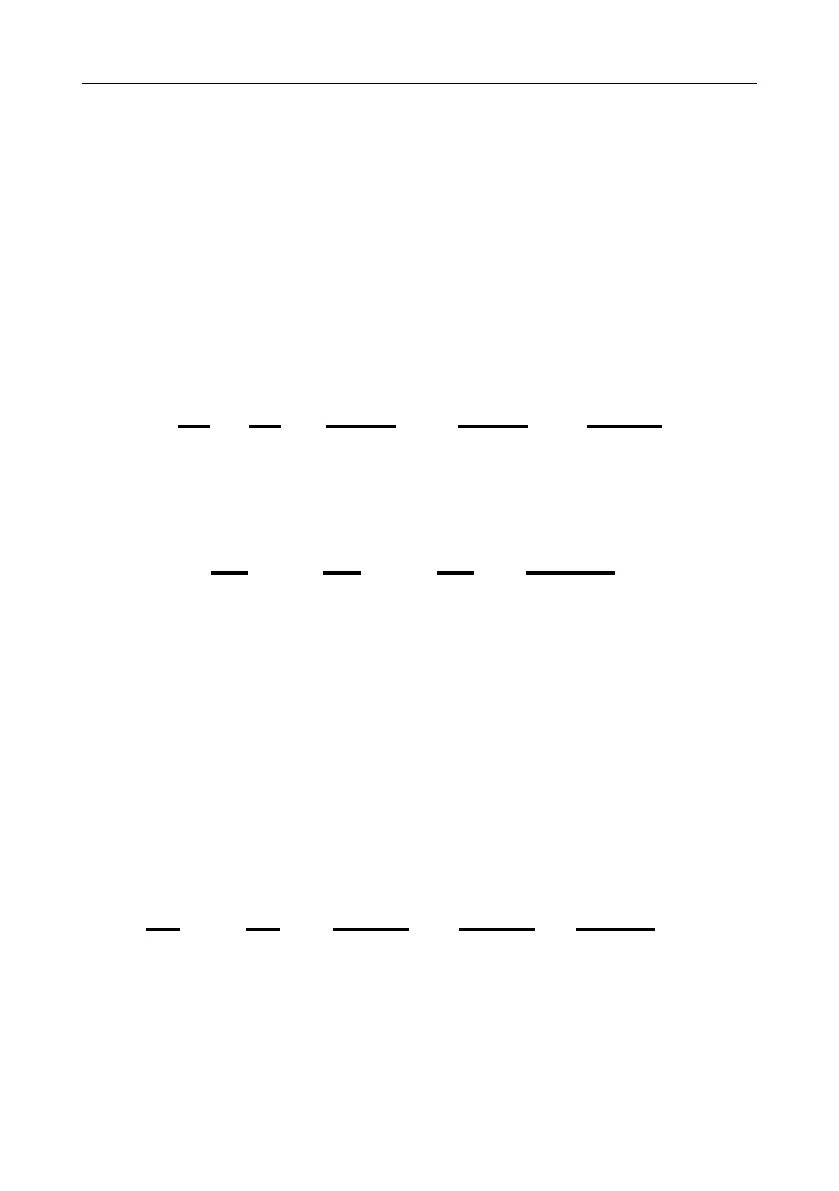
Inverter
address
Write
command
Parameter
address
Parameter
data
CRC
01 06 00 01 00 03 98 0B
But the setting range of the "Running command channel" is 0 to 2. The value 3 exceeds the setting
range. In this case, the inverter returns an error message response as shown in the following:
Inverter
address
CRC Error code
Exception
response code
01 86 04 43 A3
The exception response code 86H (generated based on the MSB "1" of the write command 06H)
indicates that it is an exception response to the write command (06H). The error code is 04H. From
the preceding table, we can see that it indicates the error "Operation failure", which means "The
parameter is set to an invalid value in the write operation".
9.4.8 Read/Write operation example
For the formats of the read and write commands, see sections 9.4.1 and 9.4.2.
9.4.8.1 Read command 03H examples
Example 1: Read state word 1 of the inverter whose address is 01H. From the table of other function
parameters, we can see that the parameter address of state word 1 of the inverter is 2100H.
The read command transmitted to the inverter is as follows:
Read
command
Inverter
address
CRC
Parameter
address
Data quantity
01 03 21 00 00 01 8E 36
Assume that the following response is returned:

 Loading...
Loading...











