Voltage burden is frequently a consideration when making
current measurements. Ideally, the input voltage burden
should be zero in order for the instrument to have absolutely
no effect on the circuit it is measuring. If the voltage burden is
too high, its effects can degrade measurement accuracy con-
siderably.
To see how voltage burden can upset measurement accuracy,
refer to Figure Z-10. A source, represented by ES with an out-
put resistance RS is shown connected to the input of a
picoammeter. The voltage burden is represented by a con-
stant voltage source at the input as Em. If En\l were zero, the
current as seen by the meter would simply be:
Es
,=-
Rs
However, if EIN has a non-zero value, the current now
becomes:
Es -6~
IA
RS
Additional considerations include source resistance and
capacitance, as discussed in paragraph 2.14.
00
cl
---_
SAFETY SHIELD
\
/
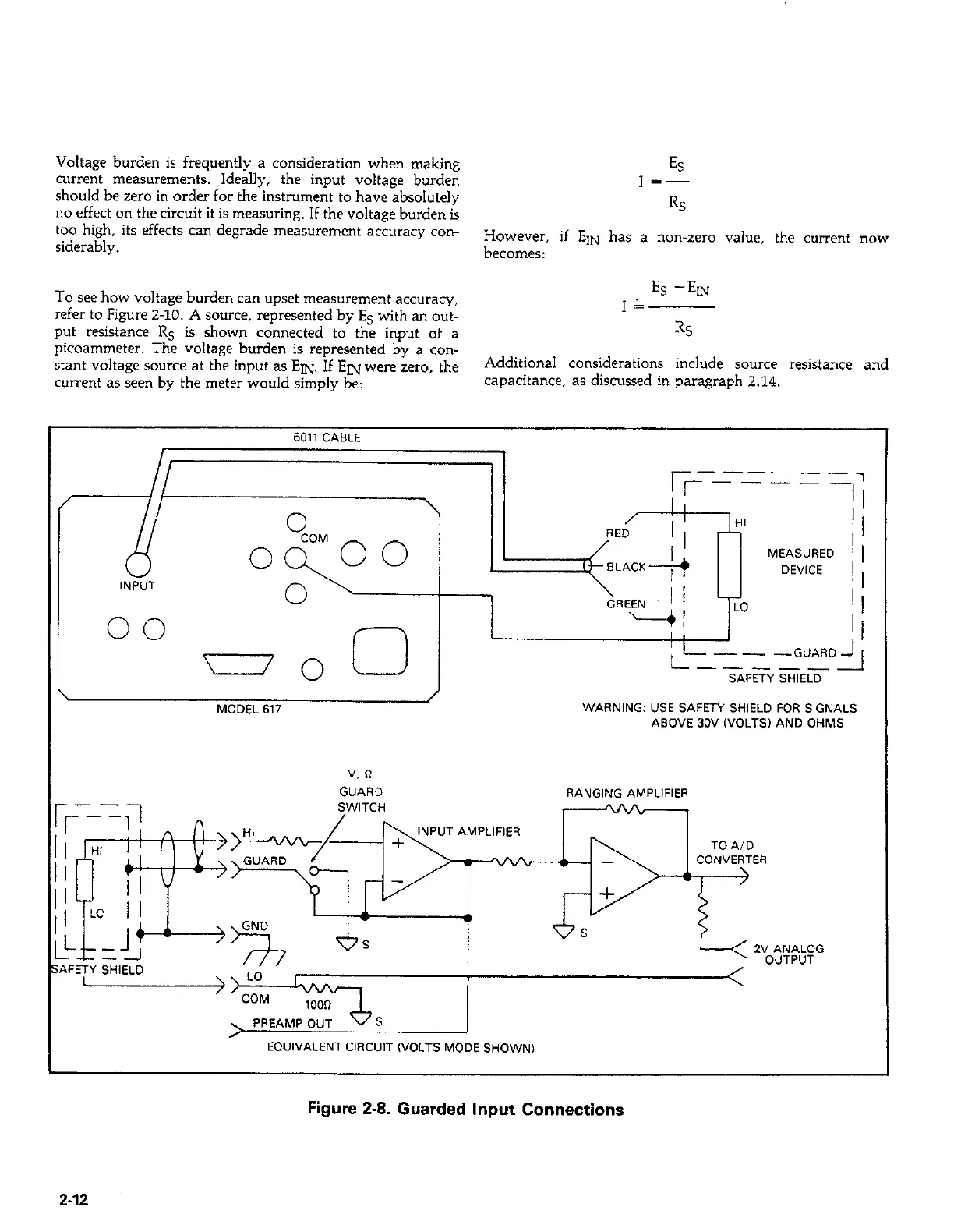
MODEL 617
WARNING: USE SAFETY SHIELD FOR SIGNALS
ABOVE 30V h!OLTSl AND OHMS
v. R
GUARD
RANGING AMPLIFIER
SWITCH
INPUT AMPLIFIER
TO AiD
CONVERTER
PREAMP OUT
EQUIVALENT CIRCUIT (VOLTS MODE SHOWN)
Figure 2-8. Guarded Input Connections
2-12

 Loading...
Loading...