UM353-1B Function Blocks
April 2012
3-25
3.2.17 AWE_ - Analog Write Ethernet
AWE_ function blocks use Modbus command 16
“Preset Multiple Registers” to enable the controller to
write analog data to other Modbus devices over the
Ethernet network.
Up to 32 AWE_ blocks are available. Blocks are
assigned in sequence (e.g. AWE01, AWE02, …),
controller wide, with each use.
Data can be written as a real floating-point number or
as a 16-bit integer as configured by the DATA TYP
parameter. A Floating point number can be selected to
have one of four byte orders (BYTE ORD) with 1
being the most common (see Table 3-4 under AIE
block description). An integer is converted from the
block input S, which is a floating point number, by the
MIN INT and MAX INT parameters using the range
scaling information obtained from the source function
block in the controller with the range pointer input R.
Both Unsigned Integer (Uint) and Signed Integer (Sint)
options are available. See the table listing parameters
and default values below right.
The IP ADRES parameter is used to configure the IP address of
the destination Modbus device. The MB ADRES parameter
allows a Modbus address to be configured. When connecting to
other Siemens 353 controllers the Modbus address is set to 1. In
some cases, other devices may use a different address or when
going through a Modbus/TCP gateway a Modbus network may
have multiple devices, each having a unique Modbus address.
There are three write update options that can be configured by the UD TYPE parameter.
1. oncE will write once to the MB REG (Modbus Register). The controller will write when the input value
changes by more than the value set with the TRIG DB parameter. This parameter is set based on a percentage
of the range determined by the range pointer input R.
2. P2P will update at the controller peer to peer rate set in the ETHERNET block.
3. Ct will update at the cycle time of the controller.
The Ct option is normally only used when writing to I/O outputs in a PID control loop. Input T can be used to
trigger a write. This would be used in cases where the oncE option has been selected, Input S does not change so as
to trigger a write based on the trigger dead band, and there may be a concern that the receiving device has lost the
value.
Output QS indicates the quality of the write operation and will go high (1) when the write is not completed
successfully. This is normally associated with failure of the destination device to receive data due to a
communication failure or a misconfiguration of the device.
Selection Parameter Default Value
Uint
MIN INT 0
Uint
MAX INT 65535
Sint
MIN INT -32768
Sint
MAX INT +32767
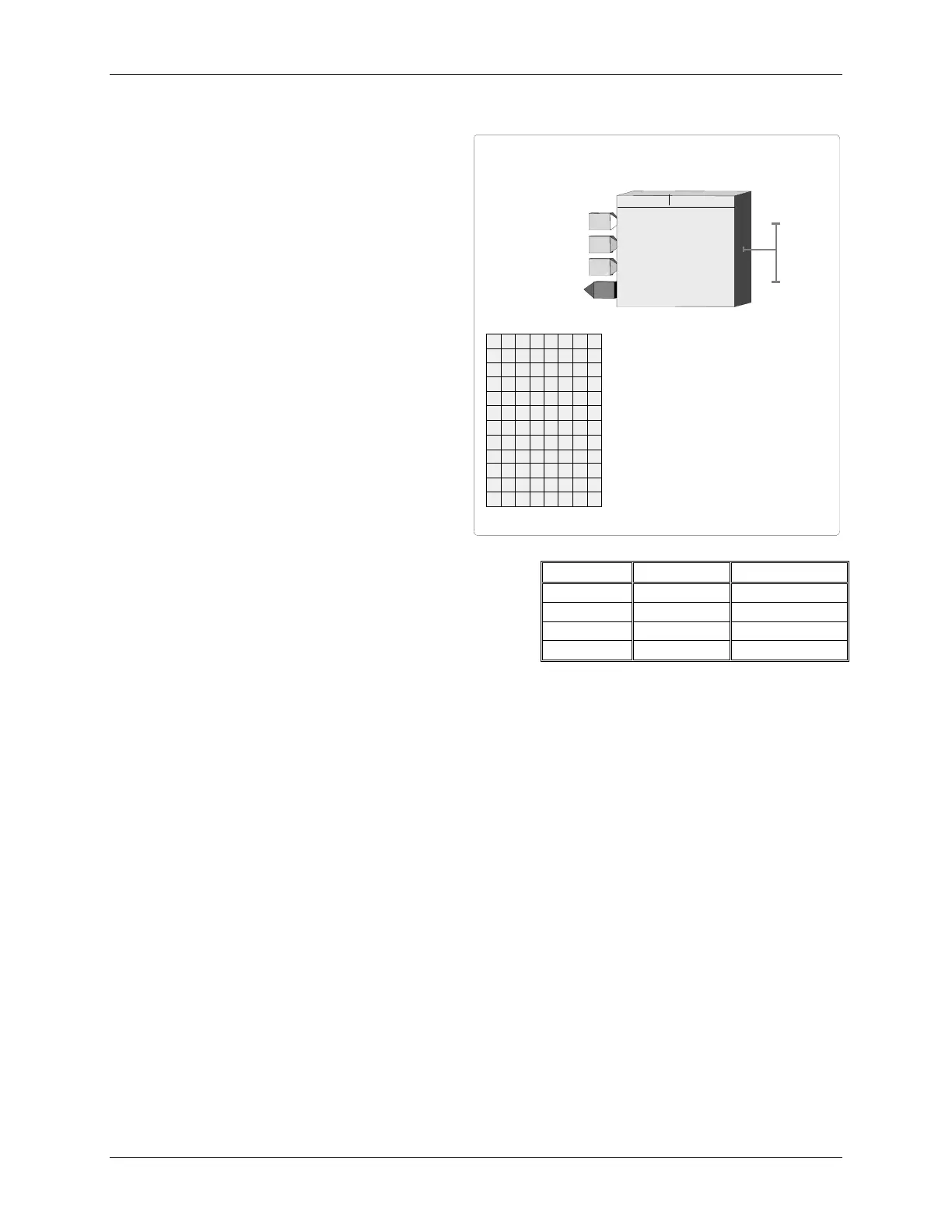
ANALOG WRITE - ETHERNET
ANALOG WRITE
AWE_
Input T
T
INPUT
S
(H)
........... loop tag.block tag.output
(null)
GPTR
R
an
G
e
P
oin
T
e
R
(H) .......... loop tag.block tag
(null)
R
ange
R
ETHERNET
Ethernet Network
R
NIPUTS
MB ADRES
MB AD
d
RES
s
(H)
.............................. 0 - 255
(0)
R
EGBM
M
od
B
us
REG
ister
(H)
.................... 1 - 65535
(1)
D
AT A TYP
Modbus
DATA
TYP
e
(H)
..........
FP
/
Uint
/
Sint
(FP)
B
YEOR
BYTE
ORD
er
(S)
................................ 1/2/3/4 (1)
MIN
imum
INT
eger
(S)
................. (see table)
(*)
MAX
imum
INT
eger
(S)
................ (see table)
(*)
INTMIN
MA X I N T
U
D
D
TYP
U
p
D
ate
TYPE
(H) .................... oncE/P2P/Ct
(oncE)
T
R
IG
TRIG
ger
D
ead
B
and
(S)
............ 0.1 - 10.0 %
(0.2)
QS
Q
uality
S
tatus
DB
IP ADRES
IP AD
d
RES
s
(H)
............ nnn.nnn.nnn.nnn
(192.168.0.0)
T
Input
S
S
E
NIPUTT
INPUT
T
(H)
........... loop tag.block tag.output
(null)
 Loading...
Loading...











