74 Rev 2.2 • 27 Mar 10
2. Installation
Making Diagnostic Connections
How to Make Expansion Connections Between Two Routers
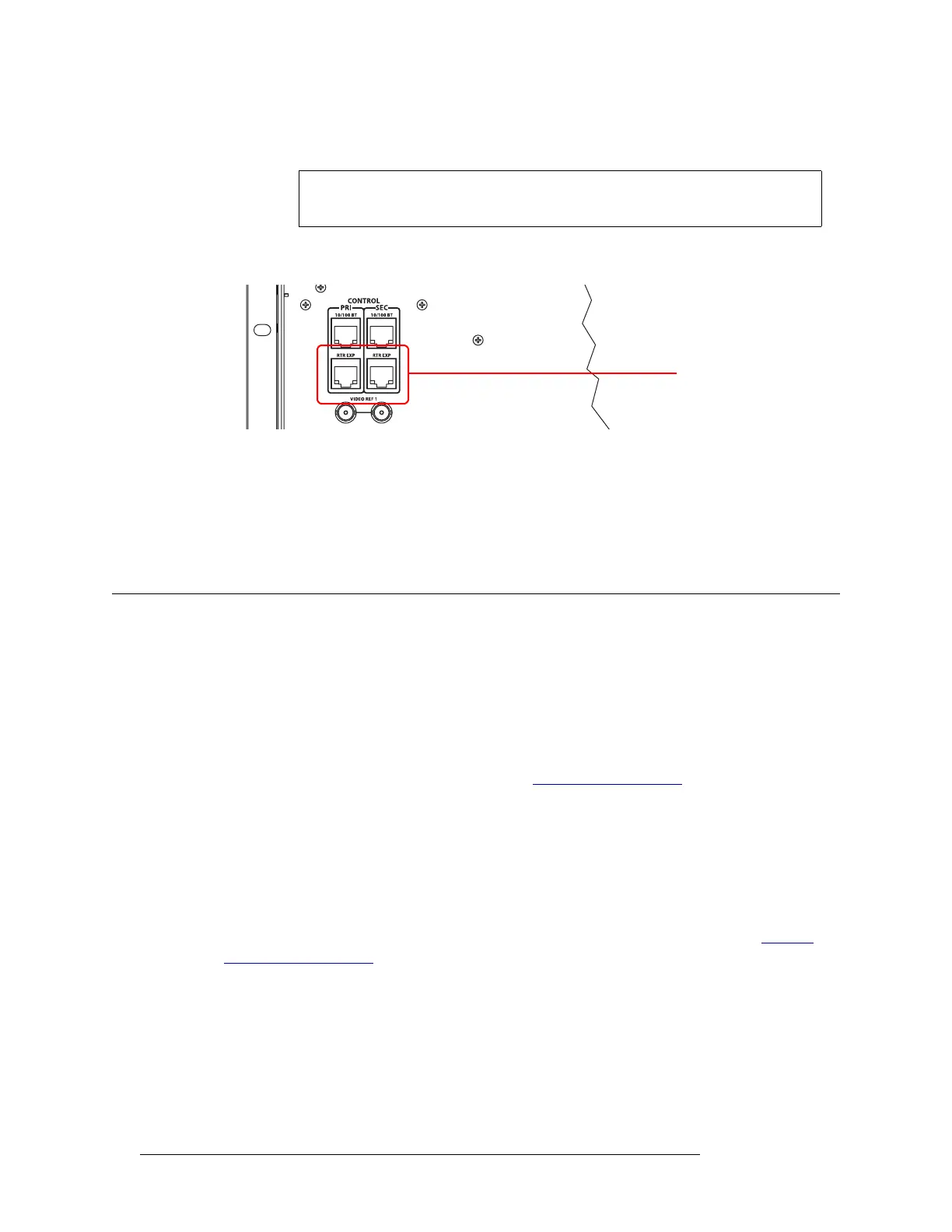
1 Locate the RJ-45 expansion control connections at the rear of the router. The connections are
labeled ‘PRI’ and ‘SEC’:
Figure 2-18. Ethernet Connections to Control System (Rear View)
2 Using a standard Ethernet cable, connect one of the ‘RTR EXP’ ports of the primary router (the
router directly connected to the control system) to one of the ‘RTR EXP’ ports of the secondary
router.
3 Insert a terminator (WC0084) in each of the unused RJ-45 ports.
Making Diagnostic Connections
The diagnostic connections enable routers in the NV8500 family to communicate with the UniCon-
fig application. UniConfig is installed on a unit, separate from the router (e.g., PC), and is used to
perform system setup tasks, and configure and monitor the router. For information about using Uni-
Config, see the UniConfig User’s Guide.
Diagnostic connections are made by connecting the router to the unit running the UniConfig appli-
cation. Diagnostic serial connections are located on the rear of the router, labeled ‘DIAG’. For a
detailed description of the serial connections, see Diagnostic Connections
on page 34.
Router IP Address
If you are using an Ethernet connection between the router and the router control system, an IP
address for the router must be set on the control card. Use UniConfig to set the IP address. How-
ever, the PC running UniConfig cannot communicate with the router until an IP address for the
router is entered. To solve this problem, create a diagnostic connection to UniConfig that lets you
enter the IP address before completing all router connections and configurations. (See Making
Diagnostic Connections on page 74.).
There are two diagnostic ports located on the rear of the router, labeled ‘DIAG’. The diagnostic
ports are fixed at 38400 baud, RS-232. For more information, see the UniConfig User’s Guide.
Note Miranda provides the terminators (WC0084). They are small. Be careful not to
overlook them.
Expansion Connectors
 Loading...
Loading...