225/617
Building Technologies Division User Manual LMS14... CC1U7471en
6 The settings in detail 07.05.2014
6.11.18 Dynamic switching differentials
To avoid unnecessary cycling during startup, the switch-off differential is dynamically
adapted, depending on the progression of temperature. As a matter of principle, the
switch-off differential is reduced depending on the extent of oscillation during the
settling out process. In the case of a periodic processes, the reduction is made via a
time criterion.
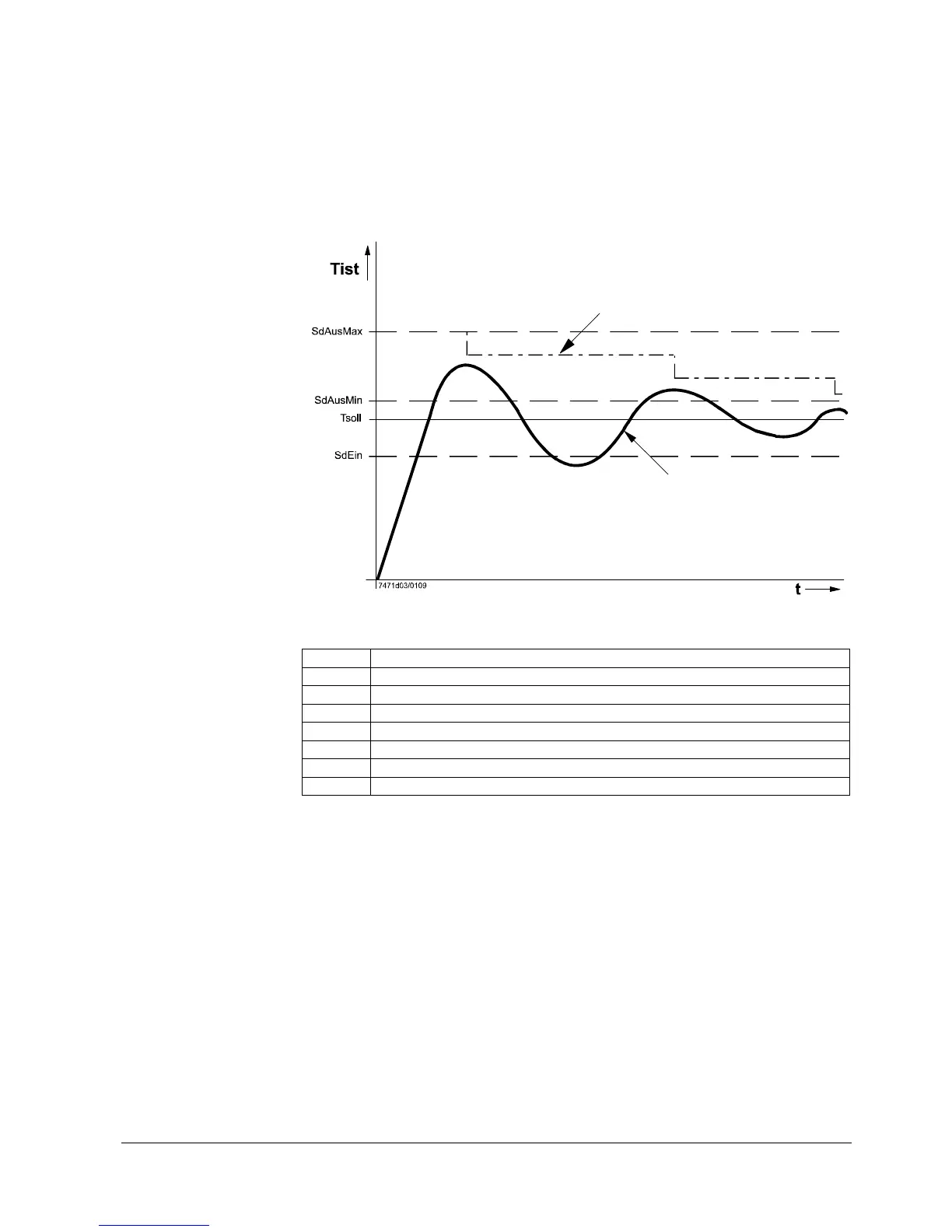
The following graph shows a typical settling out process:
SdAus = f (Tist, SdAusMin, SdAusMax)
Tist
Figure 43: Switching differentials
Key
Line no. Meaning
TIst Actual value of temperature
SdAus Dynamic switch-off threshold
SdEin Switch-on threshold (heating circuit/DHW)
Tsoll Temperature setpoint
SdAusMin Minimum switch-off threshold
SdAusMax Maximum switch-off threshold
TKAus Switch-off threshold boiler
During the time parameterized for the dynamic adaption of the switch-off differential, the
local maximum (highest point of overshoot) leads to the dynamic reduction of the
switch-off threshold: Switch-off threshold boiler = (temperature setpoint + maximum
switch-off threshold – actual value of temperature)/2.
But the switch-off threshold is always limited at the bottom:
Switch-off threshold boiler > = temperature setpoint + minimum switch-off threshold.
The switch-on differential is ready parameterized.

 Loading...
Loading...











