[scspsfas-140613-01.tif, 1, en_US]
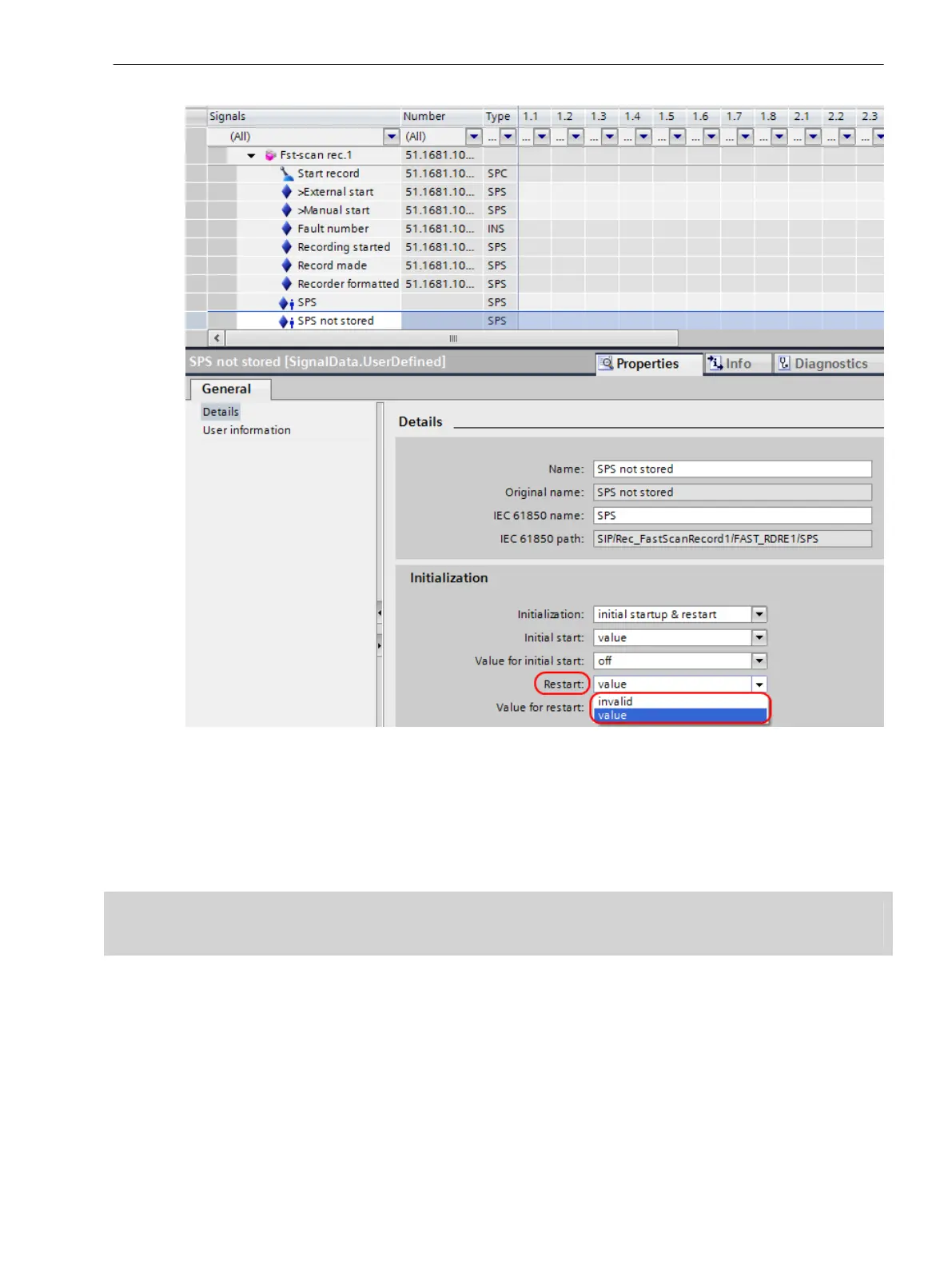
Figure 3-37
Single-Point Indication SPS Unsaved (Example: 7KE85 Fault Recorder)
Double-Point Indication (Type DPS: Double-Point Status)
When using a double-point indication, the status of 2 binary inputs can be captured simultaneously and
mapped in an indication with 4 possible conditions (ON, Intermediate position, OFF, Disturbed
position).
EXAMPLE
Acquisition of a disconnector or circuit-breaker switch position.
Marker Command (Type SPC, Single-Point Controllable)
This data type can be used as a command without feedback for simple signaling or as an internal variable
(marker).
Integer Status Value (Type INS)
The data type INS is used to create a whole number that represents a CFC result.
System Functions
3.5 User-Defined Objects
SIPROTEC 5, Fault Recorder, Manual 89
C53000-G5040-C018-5, Edition 11.2017