User's Manual 598 Document #: LTRT-27045
Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
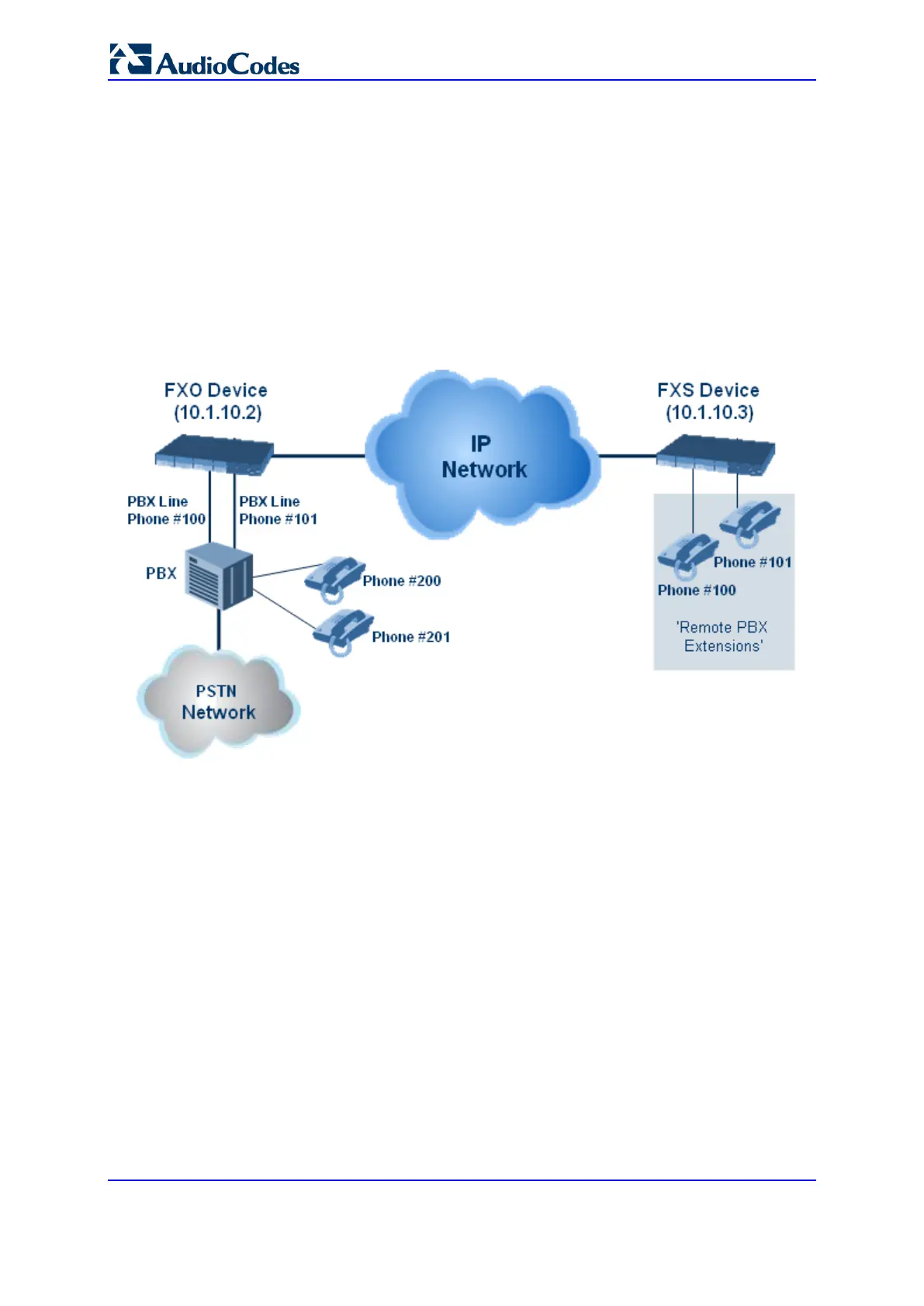
This section provides an example on how to implement a remote telephone extension
through the IP network, using FXO andFXS interfaces. In this configuration, the FXO
device routes calls received from the PBX to the ‘Remote PBX Extension’ connected to the
FXS device. The routing is transparent as if the telephone connected to the FXS device is
directly connected to the PBX.
The following is required:
FXO interfaces with ports connected directly to the PBX lines (shown in the figure
below)
FXS interfaces for the 'remote PBX extension'
Analog phones (POTS)
PBX (one or more PBX loop start lines)
LAN network
27.14.1 Dialing from Remote Extension (Phone at FXS)
The following procedure describes how to dial from the 'remote PBX extension' (i.e., phone
connected to the FXS interface).
To make a call from the FXS interface:
1. Off-hook the phone and wait for the dial tone from the PBX. This is as if the phone is
connected directly to the PBX. The FXS and FXO interfaces establish a voice path
connection from the phone to the PBX immediately after the phone is off-hooked.
2. Dial the destination number (e.g., phone number 201). The DTMF digits are sent over
IP directly to the PBX. All the audible tones are generated from the PBX (such as
ringback, busy, or fast busy tones). One-to-one mapping occurs between the FXS
ports and PBX lines.
3. The call disconnects when the phone connected to the FXS goes on-hook.

 Loading...
Loading...



















