User's Manual 80 Document #: LTRT-27045
Mediant 1000B Gateway & E-SBC
7.2 Enabling CLI
By default, access to the device's CLI through Telnet and SSH is disabled. This section
describes how to enable these protocols.
7.2.1 Enabling Telnet for CLI
The following procedure describes how to enable Telnet. You can enable a secured Telnet
that uses Secure Socket Layer (SSL) where information is not transmitted in clear text. If
SSL is used, a special Telnet client is required on your PC to connect to the Telnet
interface over a secured connection; examples include C-Kermit for UNIX and Kermit-95
for Windows.
For security, some organizations require the display of a proprietary notice upon starting a
Telnet session. To configure such a message, see ''Creating a Login Welcome Message''
on page 63.
To enable Telnet:
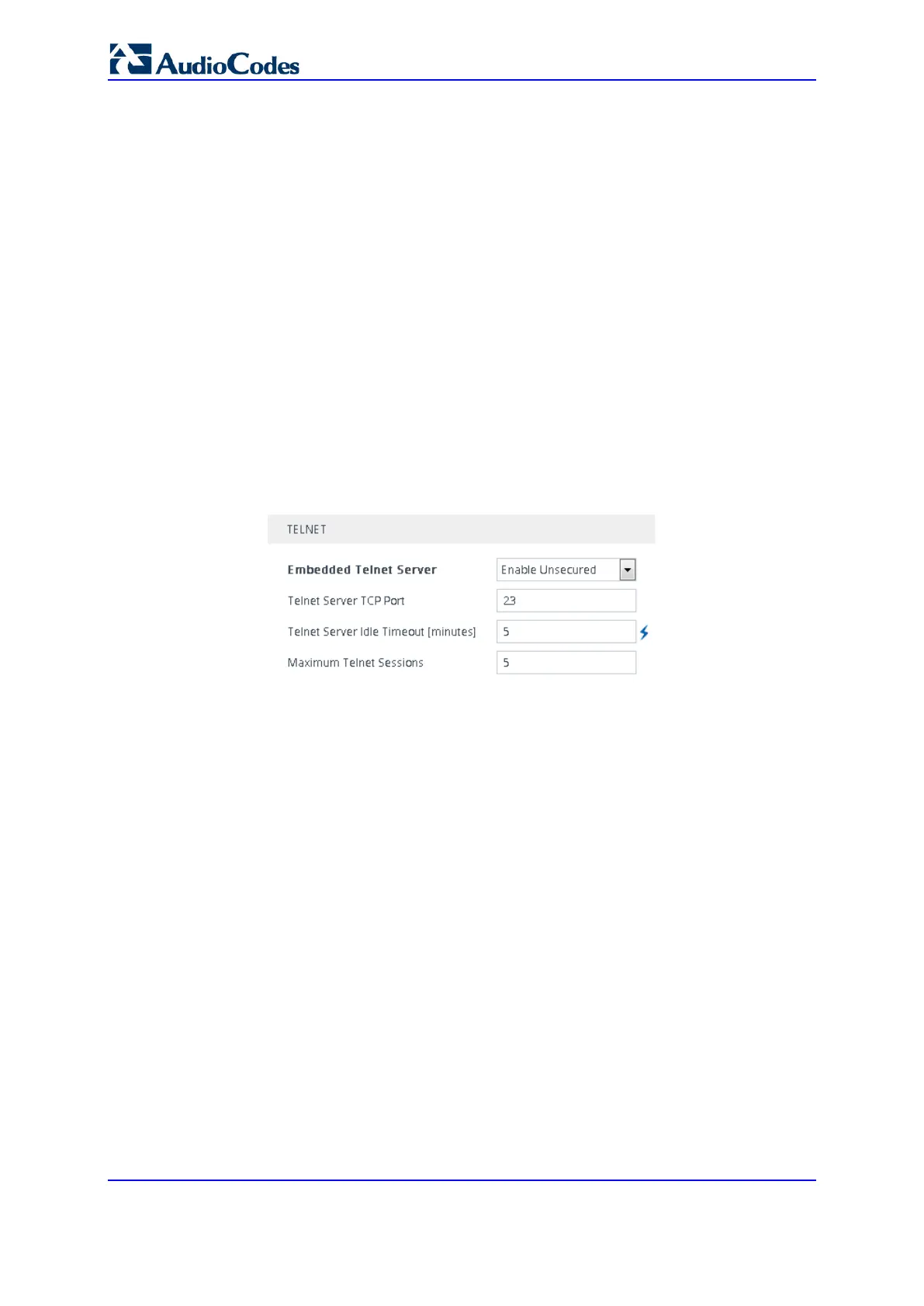
1. Open the CLI Settings page (Setup menu > Administration tab > Web & CLI folder >
CLI Settings).
2. Configure the following parameters:
• 'Embedded Telnet Server': Select Enable Unsecured or Enable Secured (i.e,
SSL) to enable Telnet.
• 'Telnet Server TCP Port': Enter the port number of the embedded Telnet server.
• 'Telnet Server Idle Timeout': Enter the duration of inactivity in the Telnet session
after which the session automatically ends.
3. Click Apply, and then reset the device with a save-to-flash for your settings to take
effect.
For a detailed description of the Telnet parameters, see ''Telnet Parameters'' on page 930.
7.2.2 Enabling SSH with RSA Public Key for CLI
Unless configured for TLS, Telnet is not secure as it requires passwords to be transmitted
in clear text. To overcome this, you can use Secure SHell (SSH) which is the de-facto
standard for secure CLI. SSH 2.0 is a protocol built above TCP providing methods for key
exchange, authentication, encryption, and authorization. SSH requires appropriate client
software for the management PC. Most Linux distributions have OpenSSH pre-installed;
Windows-based PCs require an SSH client software such as PuTTY, which can be
downloaded from http://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/putty/. By default, SSH
uses the same username and password as the device's Telnet and Web server. SSH
supports 1024/2048-bit RSA public keys, providing carrier-grade security.
Follow the instructions below to configure the device with an administrator RSA key as a
means of strong authentication.

 Loading...
Loading...



















